InnerProductLayer, 全连接层,参数比较多
全连接层将卷积的 2D 特征图结果转化为 1D 向量.
图像分类中,网络结构的最后一般有一个或多个全连接层.
全连接层的每个节点都与其上层的所有节点相连,以综合前面网络层提取的特征. 其全连接性,导致参数较多.
全连接层将卷积的 2D 特征图结果转化为 1D 向量.
如 MNIST:
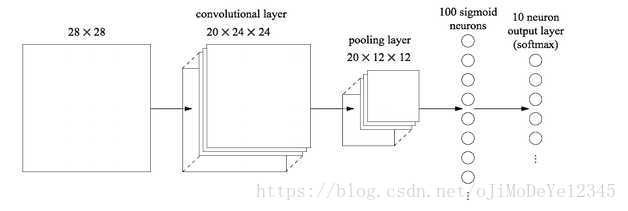
最后两层为全连接层,在pooling 层后,转化为 1D 的 1*100 长度的向量.
全连接层的前向计算中,是线性加权求和,其每一个输出是上一层的每个节点乘以一个权重 W,并加上一个偏置 b.
如,输入有 20 x 12 x 12 个神经元节点,输出是 100 个节点,则共有 20 x 12 x12 x 100=288000 个权重参数 W 和 100 个偏置参数 b.
- 输入: N x CI x HI x WI
- 输出:N x CO x 1 x 1
全连接层会破坏图像的空间结构.
1. prototxt 中的定义
layer {
bottom: "fc7"
top: "fc8"
name: "fc8"
type: "InnerProduct"
param { # 权重学习参数
lr_mult: 10 # 学习率
decay_mult: 1
}
param { # bias 学习参数
lr_mult: 20 # 一般情况,bias 学习率是权重学习率的两倍.
decay_mult: 0
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 1000 # 输出单元个数
weight_filler { # 权重初始化方法
type: "gaussian"
std: 0.005
}
bias_filler { # bias 初始化方法
type: "constant"
value: 0.1
}
}
}
2. caffe.proto 中的定义
message LayerParameter {
optional InnerProductParameter inner_product_param = 117;
}
message InnerProductParameter {
optional uint32 num_output = 1; // 网络层输出个数
optional bool bias_term = 2 [default = true]; // 是否有 bias 项
optional FillerParameter weight_filler = 3; // 权重weight filler
optional FillerParameter bias_filler = 4; // 偏置bias filler
// 在第一个 axis 进行单个内积计算.
// -1 表示最后一个 axis
optional int32 axis = 5 [default = 1];
//权重矩阵是否进行转置
optional bool transpose = 6 [default = false];
}
3. inner_product_layer.hpp
#ifndef CAFFE_INNER_PRODUCT_LAYER_HPP_
#define CAFFE_INNER_PRODUCT_LAYER_HPP_
#include <vector>
#include "caffe/blob.hpp"
#include "caffe/layer.hpp"
#include "caffe/proto/caffe.pb.h"
namespace caffe {
/**
* @brief Also known as a "fully-connected" layer, computes an inner product
* with a set of learned weights, and (optionally) adds biases.
*
* TODO(dox): thorough documentation for Forward, Backward, and proto params.
*/
template <typename Dtype>
class InnerProductLayer : public Layer<Dtype> {
public:
explicit InnerProductLayer(const LayerParameter& param)
: Layer<Dtype>(param) {}
virtual void LayerSetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
virtual void Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
virtual inline const char* type() const { return "InnerProduct"; }
virtual inline int ExactNumBottomBlobs() const { return 1; }
virtual inline int ExactNumTopBlobs() const { return 1; }
protected:
virtual void Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
virtual void Forward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
virtual void Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom);
virtual void Backward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down, const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom);
int M_; # 样本个数
int K_; # 特征维度
int N_; # 输出神经元个数
bool bias_term_;
Blob<Dtype> bias_multiplier_;
bool transpose_; ///< if true, assume transposed weights
};
} // namespace caffe
#endif // CAFFE_INNER_PRODUCT_LAYER_HPP_
4. inner_product_layer.cpp
#include <vector>
#include "caffe/filler.hpp"
#include "caffe/layers/inner_product_layer.hpp"
#include "caffe/util/math_functions.hpp"
namespace caffe {
template <typename Dtype>
void InnerProductLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
const int num_output = this->layer_param_.inner_product_param().num_output(); // 输出单元个数
bias_term_ = this->layer_param_.inner_product_param().bias_term();
transpose_ = this->layer_param_.inner_product_param().transpose();
N_ = num_output;
const int axis = bottom[0]->CanonicalAxisIndex(
this->layer_param_.inner_product_param().axis());
// axis 维数据被 flattened 为长度为 K_ 的向量
// 例如,bottom[0] - (N, C, H, W), axis=1, 则从 C 维开始,对维度CHW 进行 N 个内积.
// 输出: N x (C1 + C2 + ... + CK) x H x W
// 样本个数 x 输出单元个数 x 1 x 1 (M x N x 1 x 1)
K_ = bottom[0]->count(axis);
// Check if we need to set up the weights
if (this->blobs_.size() > 0) {
LOG(INFO) << "Skipping parameter initialization";
} else {
if (bias_term_) {
this->blobs_.resize(2);
} else {
this->blobs_.resize(1);
}
// 权重初始化
vector<int> weight_shape(2);
if (transpose_) { // 权重矩阵是否进行转置
weight_shape[0] = K_;
weight_shape[1] = N_;
} else {
weight_shape[0] = N_;
weight_shape[1] = K_;
}
this->blobs_[0].reset(new Blob<Dtype>(weight_shape));
// 初始化权重
// blobs_[0],N_ x K_ x 1 x 1
shared_ptr<Filler<Dtype> > weight_filler(GetFiller<Dtype>(
this->layer_param_.inner_product_param().weight_filler()));
weight_filler->Fill(this->blobs_[0].get());
// 如果有 bias 项,则初始化
// blobs_[1],每个输出对应一个 bias,共 N_ 个.
if (bias_term_) {
vector<int> bias_shape(1, N_);
this->blobs_[1].reset(new Blob<Dtype>(bias_shape));
shared_ptr<Filler<Dtype> > bias_filler(GetFiller<Dtype>(
this->layer_param_.inner_product_param().bias_filler()));
bias_filler->Fill(this->blobs_[1].get());
}
} // 参数初始化
this->param_propagate_down_.resize(this->blobs_.size(), true);
}
template <typename Dtype>
void InnerProductLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
// Figure out the dimensions
const int axis = bottom[0]->CanonicalAxisIndex(
this->layer_param_.inner_product_param().axis());
const int new_K = bottom[0]->count(axis);
CHECK_EQ(K_, new_K)
<< "Input size incompatible with inner product parameters.";
// The first "axis" dimensions are independent inner products; the total
// number of these is M_, the product over these dimensions.
M_ = bottom[0]->count(0, axis); // 样本数,batchsize
// The top shape will be the bottom shape with the flattened axes dropped,
// and replaced by a single axis with dimension num_output (N_).
vector<int> top_shape = bottom[0]->shape();
top_shape.resize(axis + 1);
top_shape[axis] = N_;
top[0]->Reshape(top_shape);
// Set up the bias multiplier
if (bias_term_) {
vector<int> bias_shape(1, M_);
bias_multiplier_.Reshape(bias_shape);
caffe_set(M_, Dtype(1), bias_multiplier_.mutable_cpu_data()); // 均设为 1
}
}
// 前向计算
// Y = W * x + b
template <typename Dtype>
void InnerProductLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
Dtype* top_data = top[0]->mutable_cpu_data();
const Dtype* weight = this->blobs_[0]->cpu_data();
caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, transpose_ ? CblasNoTrans : CblasTrans,
M_, N_, K_, (Dtype)1.,
bottom_data, weight, (Dtype)0., top_data);
if (bias_term_) {
caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, M_, N_, 1, (Dtype)1.,
bias_multiplier_.cpu_data(),
this->blobs_[1]->cpu_data(), (Dtype)1., top_data);
}
}
// 反向计算
template <typename Dtype>
void InnerProductLayer<Dtype>::Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
if (this->param_propagate_down_[0]) {
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->cpu_diff(); // top_diff: N x M, 每一列为一个样本的 error.
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
// Gradient with respect to weight
// 关于 weight 的梯度
if (transpose_) {
caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasTrans, CblasNoTrans,
K_, N_, M_,
(Dtype)1., bottom_data, top_diff,
(Dtype)1., this->blobs_[0]->mutable_cpu_diff());
} else {
caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasTrans, CblasNoTrans,
N_, K_, M_,
(Dtype)1., top_diff, bottom_data,
(Dtype)1., this->blobs_[0]->mutable_cpu_diff());
}
}
if (bias_term_ && this->param_propagate_down_[1]) {
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->cpu_diff();
// Gradient with respect to bias
caffe_cpu_gemv<Dtype>(CblasTrans, M_, N_, (Dtype)1., top_diff,
bias_multiplier_.cpu_data(), (Dtype)1.,
this->blobs_[1]->mutable_cpu_diff());
}
if (propagate_down[0]) {
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->cpu_diff();
// Gradient with respect to bottom data
if (transpose_) {
caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasTrans,
M_, K_, N_,
(Dtype)1., top_diff, this->blobs_[0]->cpu_data(),
(Dtype)0., bottom[0]->mutable_cpu_diff());
} else {
caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans,
M_, K_, N_,
(Dtype)1., top_diff, this->blobs_[0]->cpu_data(),
(Dtype)0., bottom[0]->mutable_cpu_diff());
}
}
}
#ifdef CPU_ONLY
STUB_GPU(InnerProductLayer);
#endif
INSTANTIATE_CLASS(InnerProductLayer);
REGISTER_LAYER_CLASS(InnerProduct);
} // namespace caffe
5. Reference
[1] - 全连接层的作用是什么? - 知乎