OpenPose 可以输出 Body,Hands,Facial 等关键点信息.
1. Demos
[1] - Video
# Ubuntu
./build/examples/openpose/openpose.bin --video examples/media/video.avi
# 多 GPUs,如采用两块 GPUs,GPUs 1 和 2,跳过 GPUs 0.
./build/examples/openpose/openpose.bin --video examples/media/video.avi
--num_gpu 2 --num_gpu_start 1[2] - Wecam
# Ubuntu
./build/examples/openpose/openpose.bin[3] - Images
# Ubuntu
./build/examples/openpose/openpose.bin --image_dir examples/media/[4] - Rendering Face and Hands Without Pose:
# CPU rendering (faster)
./build/examples/openpose/openpose.bin --render_pose 0 --face --face_render 1 --hand --hand_render 1
# GPU rendering
./build/examples/openpose/openpose.bin --render_pose 0 --face --face_render 2 --hand --hand_render 2[5] - Hands:
# Fast method for speed
./build/examples/openpose/openpose.bin --hand
# Best results found with 6 scales
./build/examples/openpose/openpose.bin --hand
--hand_scale_number 6 --hand_scale_range 0.4
# Adding tracking to Webcam (if FPS per GPU > 10 FPS) and Video
./build/examples/openpose/openpose.bin
--video examples/media/video.avi
--hand --hand_tracking
# Multi-scale + tracking is also possible
./build/examples/openpose/openpose.bin
--video examples/media/video.avi
--hand
--hand_scale_number 6
--hand_scale_range 0.4
--hand_tracking2. Pose 输出格式
OpenPose 提供了 BODY_25,COCO,Face,Hand 等模型输出对应的关键点信息.
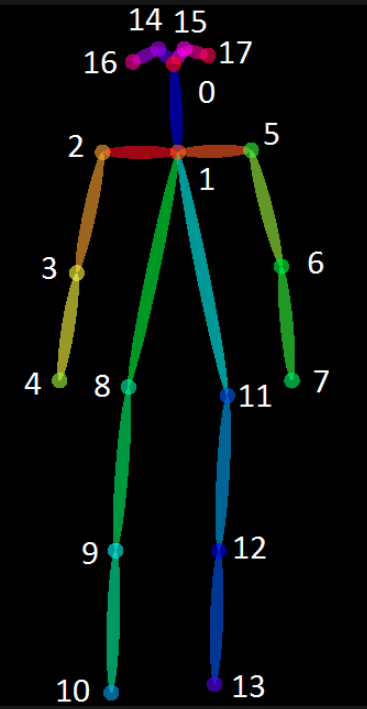
2.1 BODY_25

2.2 COCO
2.3 Face
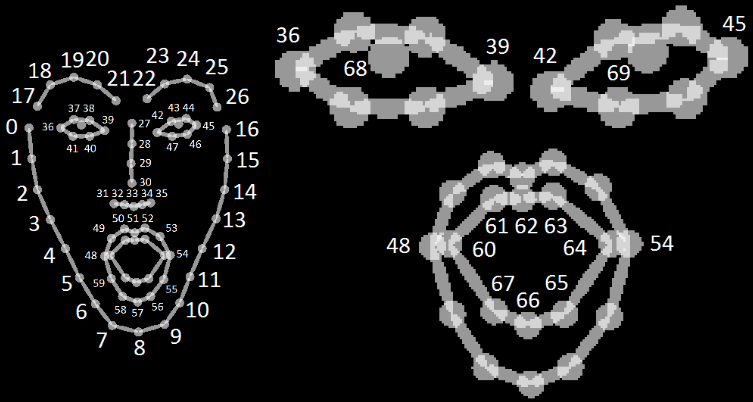
2.4 Hand

3. OpenPose Demo 输出格式
OpenPose Demo - Output
3.1 Output 保存格式
OpenPose 有两种可选的输出保存方式:
[1] - 采用 write_json flag 将人体姿态数据结果保存为 JSON writer 格式.
如:
# Only body
./build/examples/openpose/openpose.bin
--video examples/media/video.avi
--write_json output/
--display 0
--render_pose 0
# Body + face + hands
./build/examples/openpose/openpose.bin
--video examples/media/video.avi
--write_video output/result.avi
--write_json output/
--display 0
--render_pose 0
--face
--hand每个 JSON 文件包含 objects 的people 数组(array),其中,每个 object:
- 数组
pose_keypoints_2d包含了人体 Body part 位置和检测的置信度(confidence),其格式为:x1,y1,c1,x2,y2,c2,.... 坐标x和y被归一化到 [0, 1], [-1, 1], [0, source size], [0, output size] 等范围,其取决于keypoint_scaleflag.c是范围在 [0, 1] 的置信度分数(confidence score). - 数组
face_keypoints_2d,hand_left_keypoints_2d和hand_right_keypoints_2d, 类似于pose_keypoints_2d. - 如果
--3d开启(enabled),数组body_keypoints_3d,face_keypoints_3d,hand_left_keypoints_2d, 和hand_right_keypoints_2d是类似形式;否则是空. 其格式为x1,y1,z1,c1,x2,y2,z2,c2,.... 其中,c值为 0 或 1,取决于 3D reconstruction 是否成功. - 如果
--part_candidates开启(enabled),则 The body part candidates before being assembled into people.
{
"version":1.1,
"people":[
{
"pose_keypoints_2d":[582.349,507.866,0.845918,746.975,631.307,0.587007,...],
"face_keypoints_2d":[468.725,715.636,0.189116,554.963,652.863,0.665039,...],
"hand_left_keypoints_2d":[746.975,631.307,0.587007,615.659,617.567,0.377899,...],
"hand_right_keypoints_2d":[617.581,472.65,0.797508,0,0,0,723.431,462.783,0.88765,...]
"pose_keypoints_3d":[582.349,507.866,507.866,0.845918,507.866,746.975,631.307,0.587007,...],
"face_keypoints_3d":[468.725,715.636,715.636,0.189116,715.636,554.963,652.863,0.665039,...],
"hand_left_keypoints_3d":[746.975,631.307,631.307,0.587007,631.307,615.659,617.567,0.377899,...],
"hand_right_keypoints_3d":[617.581,472.65,472.65,0.797508,472.65,0,0,0,723.431,462.783,0.88765,...]
}
],
// If `--part_candidates` enabled
"part_candidates":[
{
"0":[296.994,258.976,0.845918,238.996,365.027,0.189116],
"1":[381.024,321.984,0.587007],
"2":[313.996,314.97,0.377899],
"3":[238.996,365.027,0.189116],
"4":[283.015,332.986,0.665039],
"5":[457.987,324.003,0.430488,283.015,332.986,0.665039],
"6":[],
"7":[],
"8":[],
"9":[],
"10":[],
"11":[],
"12":[],
"13":[],
"14":[293.001,242.991,0.674305],
"15":[314.978,241,0.797508],
"16":[],
"17":[369.007,235.964,0.88765]
}
]
}[2] - (已废弃) 采用 write_keypoint flag将人体姿态数据结果保存为 OpenCV cv::FileStorage 默认格式,如 JSON(OpenCV3.0 后可用),XML,YML. 其只能保存关键点,不包含其它信息.
3.2 Keypoints 次序
采用poseParameters.hpp 中的 getPoseBodyPartMapping(const PoseModel poseModel)函数,基于 C++ API 可以提取任何 Body 模型(如 COCO, MPI) 的 Body Part 映射次序.
// C++ API call
#include <openpose/pose/poseParameters.hpp>
const auto& poseBodyPartMappingBody25 = getPoseBodyPartMapping(PoseModel::BODY_25);
const auto& poseBodyPartMappingCoco = getPoseBodyPartMapping(PoseModel::COCO_18);
const auto& poseBodyPartMappingMpi = getPoseBodyPartMapping(PoseModel::MPI_15);
// Result for BODY_25 (25 body parts consisting of COCO + foot)
// const std::map<unsigned int, std::string> POSE_BODY_25_BODY_PARTS {
// {0, "Nose"},
// {1, "Neck"},
// {2, "RShoulder"},
// {3, "RElbow"},
// {4, "RWrist"},
// {5, "LShoulder"},
// {6, "LElbow"},
// {7, "LWrist"},
// {8, "MidHip"},
// {9, "RHip"},
// {10, "RKnee"},
// {11, "RAnkle"},
// {12, "LHip"},
// {13, "LKnee"},
// {14, "LAnkle"},
// {15, "REye"},
// {16, "LEye"},
// {17, "REar"},
// {18, "LEar"},
// {19, "LBigToe"},
// {20, "LSmallToe"},
// {21, "LHeel"},
// {22, "RBigToe"},
// {23, "RSmallToe"},
// {24, "RHeel"},
// {25, "Background"}
// };3.3 Heatmap 次序
对于 heatmaps 的保存格式,OpenPose 库将所有的 heatmaps 连接为一个较大的矩阵:width x num_heatmaps x height(i.e., concatenated by columns),而不是将 67 个 heatmaps(18 body parts + background + 2 x 19 PAFs) 分别独立保存.
如,columns[0, individual heat map width] 是第一个 heatmap;
columns [individual heat map width + 1, 2 * individual heat map width] 是第二个 heatmap;依次.
保存次序为:body parts + background + PAFs. 可以根据相应的 flags 开启或关闭. 如果 background disabled,则最终图像是 body parts + PAF.
Body Parts 和 Background 的次序根据:getPoseBodyPartMapping(const PoseModel poseModel).
PAFs 的次序根据:getPosePartPairs(const PoseModel poseModel) 和 getPoseMapIndex(const PoseModel poseModel).
以 COCO 为例,
COCO 的 PAFs channels 从 19 开始(getPoseMapIndex 的最小值,等于#body parts + 1 ),结束于 56(最大值.)
然后,可以从 getPosePartPairs 匹配其值. 例如,getPoseMapIndex中的 19 (x-channel) 和 20 (y-channel) 对应于 Body Part 1 到 8 的 PAF;21 和 22 对应于 Body Part 8 到 9 的 x, y channels. 等等.
注:如果最小的 channel 是奇数(如 19),则,所有的 x-channels 都是奇数,所有的 y-channels 都是偶数. 也可反之.
// C++ API call
#include <openpose/pose/poseParameters.hpp>
const auto& posePartPairsBody25 = getPosePartPairs(PoseModel::BODY_25);
const auto& posePartPairsCoco = getPosePartPairs(PoseModel::COCO_18);
const auto& posePartPairsMpi = getPosePartPairs(PoseModel::MPI_15);
// getPosePartPairs(PoseModel::BODY_25) result
// Each index is the key value corresponding to each body part in `getPoseBodyPartMapping`. E.g., 1 for "Neck", 2 for "RShoulder", etc.
// 1,8, 1,2, 1,5, 2,3, 3,4, 5,6, 6,7, 8,9, 9,10,
// 10,11, 8,12, 12,13, 13,14, 1,0, 0,15, 15,17, 0,16, 16,18,
// 2,17, 5,18, 14,19,19,20,14,21, 11,22,22,23,11,24
// getPoseMapIndex(PoseModel::BODY_25) result
// 0,1, 14,15, 22,23, 16,17, 18,19, 24,25, 26,27, 6,7, 2,3, 4,5, 8,9,
// 10,11, 12,13, 30,31, 32,33, 36,37, 34,35, 38,39, 20,21, 28,29,
// 40,41,42,43,44,45, 46,47,48,49,50,51
在 OpenPose 中,可以直接保存所有的 Body Part 的 heatmaps, Background heatmap 和 PAFs(Part Affinity Fields) 到指定路径 output_heatmaps_folder,保存为 PNG 格式.
共 67 个 heatmaps,18 body parts + background + 2 x 19 PAFs(保存次序:Body Parts + BKG + PAFs).
include/openpose/pose/poseParameters.hpp
./build/examples/openpose/openpose.bin
--video examples/media/video.avi
--heatmaps_add_parts
--heatmaps_add_bkg
--heatmaps_add_PAFs
--write_heatmaps output_heatmaps_folder/3.4 Face 和 Hands 关键点
Hand(hand_left_keypoints, hand_right_keypoints) 和 Face (face_keypoints) 的 JSON 文件格式类似于 Pose Keypoints 格式.
3.5 读取输出结果
采用标准格式,如 JSON,XML,PNG,JPG,保存 OpenPose 结果,因此可以在大部分编程语言中进行读取.
C++ 中,include/openpose/filestream/fileStream.hpp 里提供了相应的函数,如:函数 loadData( JSON, XML, YML 文件) 和函数 loadImage (PNG和 JPG 等图像格式,将数据加载为 cv::Mat格式.
3.6 C++ API 中 Keypoints 格式
在 Datum 类中有 3 种不同的关键点 Array<float> 元素:
[1] - 数组 poseKeypoints - 为了访问 Person person 和 Body Part part(其中,index 对应于 POSE_COCO_BODY_PARTS 或 POSE_MPI_BODY_PARTS),简单输出如下:
// Common patrameters needed
const auto numberPeopleDetected = poseKeypoints.getSize(0);
const auto numberBodyParts = poseKeypoints.getSize(1);
// Easy version
const auto x = poseKeypoints[{person, part, 0}];
const auto y = poseKeypoints[{person, part, 1}];
const auto score = poseKeypoints[{person, part, 2}];
// Slightly more efficient version
// If you want to access these elements on a huge loop, you can get the index
// by your own, but it is usually not faster enough to be worthy
const auto baseIndex = poseKeypoints.getSize(2)*(person*numberBodyParts + part);
const auto x = poseKeypoints[baseIndex];
const auto y = poseKeypoints[baseIndex + 1];
const auto score = poseKeypoints[baseIndex + 2];[2] - 数组 faceKeypoints - 完全类似于 poseKeypoints.
// Common parameters needed
const auto numberPeopleDetected = faceKeypoints.getSize(0);
const auto numberFaceParts = faceKeypoints.getSize(1);
// Easy version
const auto x = faceKeypoints[{person, part, 0}];
const auto y = faceKeypoints[{person, part, 1}];
const auto score = faceKeypoints[{person, part, 2}];
// Slightly more efficient version
const auto baseIndex = faceKeypoints.getSize(2)*(person*numberFaceParts + part);
const auto x = faceKeypoints[baseIndex];
const auto y = faceKeypoints[baseIndex + 1];
const auto score = faceKeypoints[baseIndex + 2];[3] - std::array<Array, 2> handKeypoints, 其中,handKeypoints[0] 对应于 left hand,handKeypoints[1] 对应于 right hand. 每个 handKeypoints[i] 类似于 poseKeypoints 和 faceKeypoints:
// Common parameters needed
const auto numberPeopleDetected = handKeypoints[0].getSize(0); // = handKeypoints[1].getSize(0)
const auto numberHandParts = handKeypoints[0].getSize(1); // = handKeypoints[1].getSize(1)
// Easy version
// Left Hand
const auto xL = handKeypoints[0][{person, part, 0}];
const auto yL = handKeypoints[0][{person, part, 1}];
const auto scoreL = handKeypoints[0][{person, part, 2}];
// Right Hand
const auto xR = handKeypoints[1][{person, part, 0}];
const auto yR = handKeypoints[1][{person, part, 1}];
const auto scoreR = handKeypoints[1][{person, part, 2}];
// Slightly more efficient version
const auto baseIndex = handKeypoints[0].getSize(2)*(person*numberHandParts + part);
// Left Hand
const auto xL = handKeypoints[0][baseIndex];
const auto yL = handKeypoints[0][baseIndex + 1];
const auto scoreL = handKeypoints[0][baseIndex + 2];
// Right Hand
const auto xR = handKeypoints[1][baseIndex];
const auto yR = handKeypoints[1][baseIndex + 1];
const auto scoreR = handKeypoints[1][baseIndex + 2];