OpenPose 可以对图片中单个人体目标的姿态估计,也可以处理图片中多人的姿态估计.
这里主要记录基于 OpenCV 4.x DNN 模块和 OpenPose 开源模型的多人人体姿态估计 的实现.
采用的模型的基于 COCO 数据集训练的人体关键点模型.
1. OpenPose 网络结构
OpenPose 的多人人体姿态估计的模型结构如图:
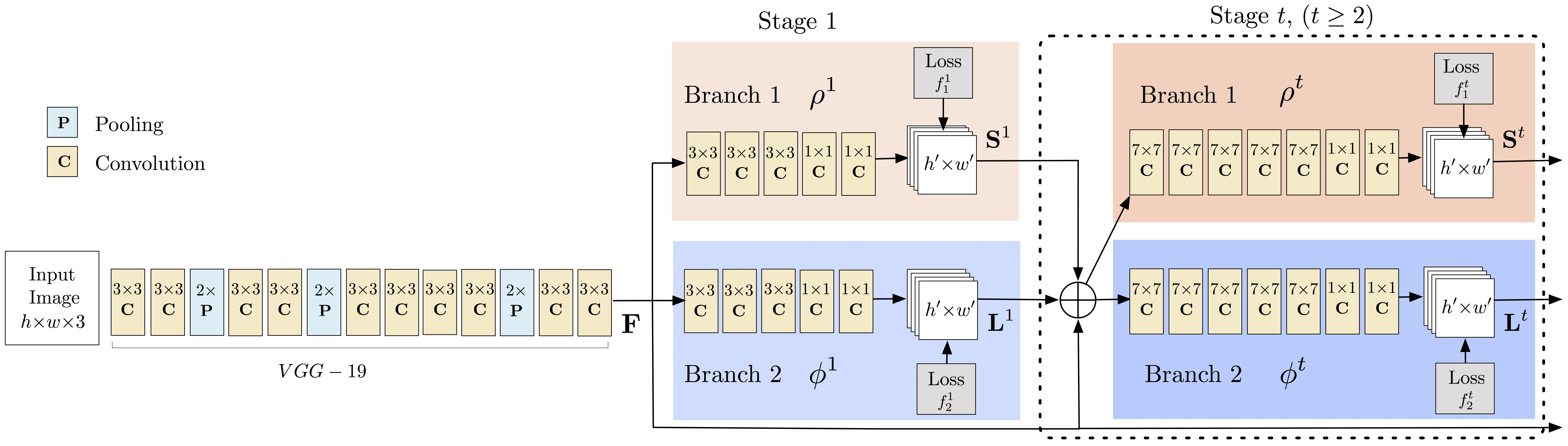
网络输入为 hxwx3 的图片,并输出包含关键点(Keypoints)的置信图(confidence maps) 和每个关键点对(keypoint pair) 的 Part Affinity Heatmaps 的两个输出数组.
[1] - Stage 0:
采用 VGGNet 的前 10 层,提取输入图片的特征图(feature maps).
[2] - Stage 1:
采用 2-分支的 multi-stage CNN 网络结构:
(1) - 分支一:
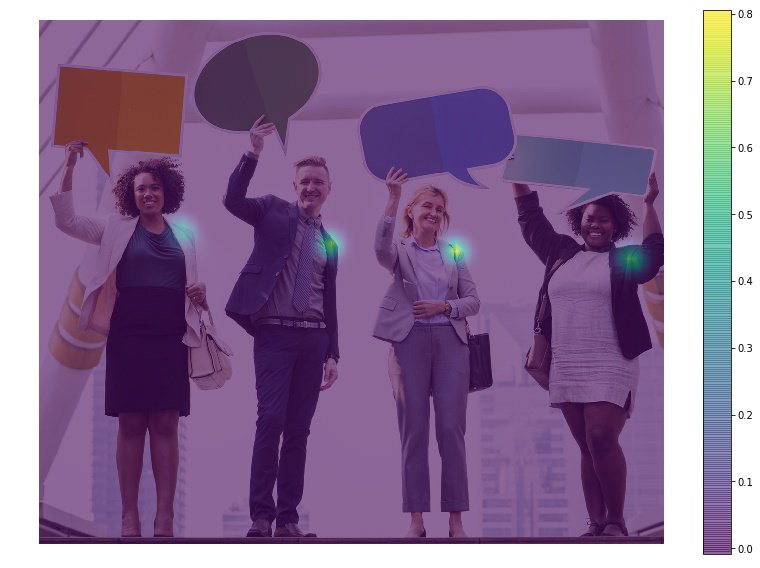
网络分支一预测人体关键点位置的 2D Confidence Maps ,如 elbow, knee, etc. 每个 Confidence Map 是一个灰度图(grayscale image),其最大值的位置坐标即为对应人体某个关键点的概率最高. 如图:

(2) - 分支二:
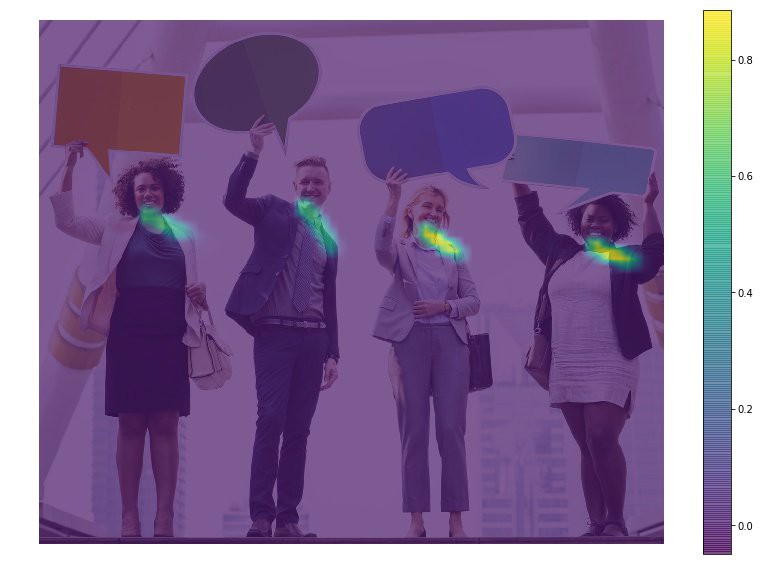
网络分支二预测 Part Affinities (PAF) 的2D 向量场(L, vector fields),其表示了两个关键点之间关联度(degree of association). 例如,关键点 Neck 和 Left Shoulder 之间的 Part Affinity, 如下图,属于同一个人体的关键点之间的 Affinity 值比较大.

总体来说,Confidence Maps 用于检测关键点位置;而 Affinity Maps 用于检测关键点之间的有效连接.
2. OpenPose 的 OpenCV DNN 实现
根据检测过程,主要涉及的函数有:getKeyponts() 、 getValidPairs() 和 getPersonwiseKeypoints() .
2.1. 模型加载
#!/usr/bin/python3
#!--*-- coding: utf-8 --*--
import cv2
import time
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
num_points = 18
keypointsMapping = ['Nose', 'Neck',
'R-Sho', 'R-Elb', 'R-Wr',
'L-Sho', 'L-Elb', 'L-Wr',
'R-Hip', 'R-Knee', 'R-Ank',
'L-Hip', 'L-Knee', 'L-Ank',
'R-Eye', 'L-Eye', 'R-Ear', 'L-Ear']
POSE_PAIRS = [[1,2], [1,5], [2,3], [3,4], [5,6], [6,7],
[1,8], [8,9], [9,10], [1,11], [11,12], [12,13],
[1,0], [0,14], [14,16], [0,15], [15,17],
[2,17], [5,16] ]
# index of pafs correspoding to the POSE_PAIRS
# e.g for POSE_PAIR(1,2), the PAFs are located at indices (31,32) of output, Similarly, (1,5) -> (39,40) and so on.
mapIdx = [[31,32], [39,40], [33,34], [35,36], [41,42], [43,44],
[19,20], [21,22], [23,24], [25,26], [27,28], [29,30],
[47,48], [49,50], [53,54], [51,52], [55,56],
[37,38], [45,46]]
colors = [[0,100,255], [0,100,255], [0,255,255],
[0,100,255], [0,255,255], [0,100,255],
[0,255,0], [255,200,100], [255,0,255],
[0,255,0], [255,200,100], [255,0,255],
[0,0,255], [255,0,0], [200,200,0],
[255,0,0], [200,200,0], [0,0,0]]
# dnn 加载模型
start = time.time()
prototxt = "./models/pose/coco/pose_deploy_linevec.prototxt"
caffemodel = "./models/pose/coco/pose_iter_440000.caffemodel"
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(prototxt, caffemodel)
print("[INFO]Time Taken in Model Loading: {}".format(time.time() - start))
# test img
img_cv2 = cv2.imread("test_image.jpg")
img_width, img_height = img_cv2.shape[1], img_cv2.shape[0]
# 根据长宽比,固定网路输入的 height,计算网络输入的 width.
net_height = 368
net_width = int((net_height/img_height)*img_width)
start = time.time()
in_blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(
img_cv2,
1.0 / 255,
(net_width, net_height),
(0, 0, 0),
swapRB=False,
crop=False)
net.setInput(in_blob)
output = net.forward()
print("[INFO]Time Taken in Forward pass: {}".format(time.time() - start))2.2. 关键点检测
2.2.1. getKeyponts( )函数
getKeyponts( )函数功能:对 Confidence Map 采用 NMS(Non Maximum Suppression) 来检测关键点.
def getKeypoints(probMap, threshold=0.1):
mapSmooth = cv2.GaussianBlur(probMap,(3,3),0,0)
mapMask = np.uint8(mapSmooth>threshold)
keypoints = []
# 1. 找出对应于关键点的所有区域的轮廓(contours)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(
mapMask, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# for each blob find the maxima
# 对于每个关键点轮廓区域,找到最大值.
for cnt in contours:
# 2. 创建关键点的 mask;
blobMask = np.zeros(mapMask.shape)
blobMask = cv2.fillConvexPoly(blobMask, cnt, 1)
# 3. 提取关键点区域的 probMap
maskedProbMap = mapSmooth * blobMask
# 4. 提取关键点区域的局部最大值.
_, maxVal, _, maxLoc = cv2.minMaxLoc(maskedProbMap)
keypoints.append(maxLoc + (probMap[maxLoc[1], maxLoc[0]],))
return keypoints2.2.2. 关键点 mapMask
threshold = 0.1
part = 1
probMap = output[0, part, :,:]
mapSmooth = cv2.GaussianBlur(probMap, (3, 3), 0, 0)
mapMask = np.uint8(mapSmooth > threshold)
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.imshow(probMap)
plt.title("probMap")
plt.axis("off")
plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)
plt.imshow(mapSmooth)
plt.title("mapSmooth")
plt.axis("off")
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
plt.imshow(mapMask)
plt.title("mapMask")
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
2.2.3. 关键点坐标值
threshold = 0.1
part = 1
probMap = output[0, part, :,:]
probMap = cv2.resize(probMap, (img_cv2.shape[1], img_cv2.shape[0]))
mapSmooth = cv2.GaussianBlur(probMap, (3, 3), 0, 0)
mapMask = np.uint8(mapSmooth > threshold)
keypoints = []
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(mapMask, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
for cnt in contours:
blobMask = np.zeros(mapMask.shape)
blobMask = cv2.fillConvexPoly(blobMask, cnt, 1)
maskedProbMap = mapSmooth * blobMask
_, maxVal, _, maxLoc = cv2.minMaxLoc(maskedProbMap)
keypoints.append(maxLoc + (probMap[maxLoc[1], maxLoc[0]],))
img_cv2_copy = img_cv2.copy()
for keypoint in keypoints:
cv2.circle(img_cv2_copy, (keypoint[0], keypoint[1]), 5, (255, 0, 0), -1, cv2.LINE_AA)
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(img_cv2_copy[:, :, ::-1])
plt.title("Keypoints")
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()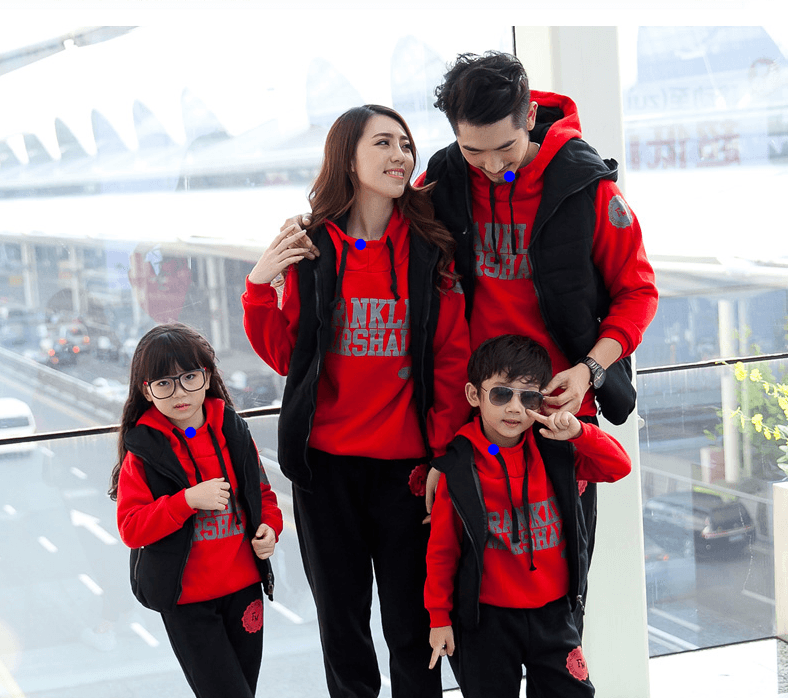
2.3. 有效关键点对检测
2.3.1. getValidPairs()函数
getValidPairs()函数功能:检测所有人体之间不同关键点之间的有效连接.
计算公式为:
$$ E = \int_{u=0}^{u=1} \mathbf{L}_c (\mathbf{p}(u)) \cdot \frac{\mathbf{d}_{j2} - \mathbf{d}_{j1}}{||\mathbf{d}_{j2} - \mathbf{d}_{j1}||_2} du $$
其中,$\mathbf{p}(u)$ 是对两个关键点 $\mathbf{d}_{j1}$ 和 $\mathbf{d}_{j2}$ 之间的位置进行插值:
$$ \mathbf{p}(u) = (1 - u)\mathbf{d}_{j1} + u\mathbf{d}_{j2} $$
$\mathbf{L}$ 是Part Affinity(PAF);
$\mathbf{d}$ 是两个关键点的向量.
$\mathbf{p}$ 是两个关键点之间的插值点.
$\mathbf{E}$ 是通过计算 PAF $\mathbf{L}$ 和向量 $d_{ij}$ 之间的点积(dot product) 得到的.
# Find valid connections between the different
# joints of a all persons present
def getValidPairs(output):
valid_pairs = []
invalid_pairs = []
n_interp_samples = 10
paf_score_th = 0.1
conf_th = 0.7
# loop for every POSE_PAIR
for k in range(len(mapIdx)):
# A->B constitute a limb
pafA = output[0, mapIdx[k][0], :, :]
pafB = output[0, mapIdx[k][1], :, :]
pafA = cv2.resize(pafA, (imgWidth, imgHeight))
pafB = cv2.resize(pafB, (imgWidth, imgHeight))
# 检测第一个 limb 和第二个 limb 的关键点位置
candA = detected_keypoints[POSE_PAIRS[k][0]]
candB = detected_keypoints[POSE_PAIRS[k][1]]
nA = len(candA)
nB = len(candB)
# 如果检测到 joint-pair 的关键点位置,则,
# 检查 candA 和 candB 中每个 joint.
# 计算两个 joints 之间的距离向量(distance vector).
# 计算两个 joints 之间插值点集合的 PAF 值.
# 根据上述公式,计算 score 值,判断连接的有效性.
if( nA != 0 and nB != 0):
valid_pair = np.zeros((0,3))
for i in range(nA):
max_j=-1
maxScore = -1
found = 0
for j in range(nB):
# Find d_ij
d_ij = np.subtract(candB[j][:2], candA[i][:2])
norm = np.linalg.norm(d_ij)
if norm:
d_ij = d_ij / norm
else:
continue
# Find p(u)
interp_coord = list(
zip(np.linspace(candA[i][0],
candB[j][0],
num=n_interp_samples),
np.linspace(candA[i][1],
candB[j][1],
num=n_interp_samples)))
# Find L(p(u))
paf_interp = []
for k in range(len(interp_coord)):
paf_interp.append(
[pafA[int(round(interp_coord[k][1])),
int(round(interp_coord[k][0]))],
pafB[int(round(interp_coord[k][1])),
int(round(interp_coord[k][0]))]
])
# Find E
paf_scores = np.dot(paf_interp, d_ij)
avg_paf_score = sum(paf_scores)/len(paf_scores)
# 判断连接是否有效.
# 如果对应于 PAF 的插值向量值大于阈值,则连接有效.
if (len(np.where(paf_scores > paf_score_th)[0])/
n_interp_samples ) > conf_th :
if avg_paf_score > maxScore:
max_j = j
maxScore = avg_paf_score
found = 1
# Append the connection to the list
if found:
valid_pair = np.append(
valid_pair,
[[candA[i][3], candB[max_j][3], maxScore]],
axis=0)
# Append the detected connections to the global list
valid_pairs.append(valid_pair)
else: # If no keypoints are detected
print("No Connection : k = {}".format(k))
invalid_pairs.append(k)
valid_pairs.append([])
print(valid_pairs)
return valid_pairs, invalid_pairs2.3.2. 关键点对检测具体实现分析
有效的关键点对(joint pair) 是指两个关键点的连接,属于相同的人体.
最简单的方式是,计算一个关键点与其它所有可能的关键点之间的最小距离,来判断关键点对的有效性.
例如下图,可以计算 Nose 关键点与其它所有 Necks 关键点之间的距离,最小距离的 Neck 关键点,则对应于同一个人体.
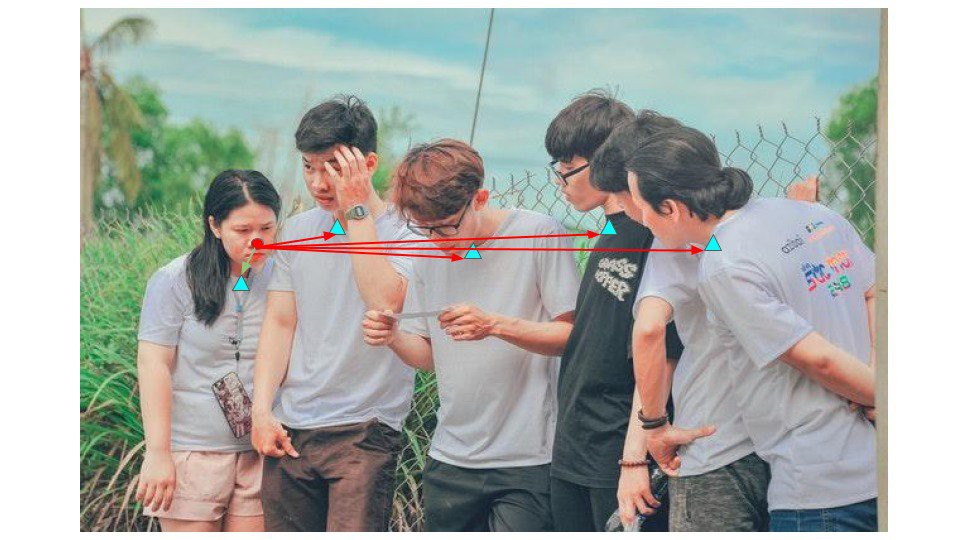
但是,这种方法不是对所有的关键点对都是有效的,尤其是对与图像中包含很多人体,或者有关键点缺失的时候.
例如下图,对于关键点对, Left-Elbow -> Left Wrist,第三个人体的 wrist 关键点与第二个人体的 elbow 关键点的距离,比与其同一人体的 elbow 关键点的距离更小. 但该关键点对并不是有效的.
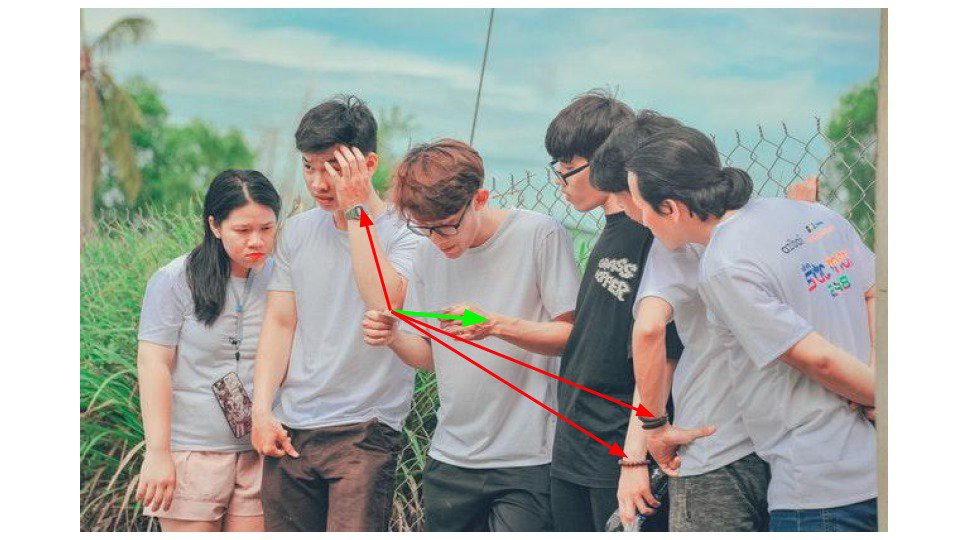

而 Part Affinity Maps 的作用是,给定沿着两个关键点对的仿射(affinity)的方向. 因此,有效的关键点对不仅具有最小的距离,其方向也应该顺着 PAF Heatmaps 方向.
例如,Left-Elbow -> Left Wrist 连接的 Heatmap,如下图,即使最小距离的关键点是错误的,但,由于 PAF 只能顺着 Elbow 和 Wrist 的单位向量,所以能正确检测有效的关键点对:

OpenPose 中采用的方法为:
[1] - 将关键点对的两个点之间的连线进行划分,得到该连线上的 n 个点(Divide the line joining the two points comprising the pair. Find n points on this line.);
[2] - 判断这些点上的 PAF 是否与连接该关键点的线的方向相同(Check if the PAF on these points have the same direction as that of the line joining the points for this pair);
[3] - 如果方向满足特定程度,则为有效的关键点对(If the direction matches to a certain extent, then it is valid pair.)
代码实现与分析:
对于每个关键点对(body part pair, keypoints pair),
[1] - 选择属于同一个关键点对的关键点. 并分别存放在两个列表: candA 和 candB. candA 列表中的每个关键点可以与 candB 中的某些关键点相连接. 如下图,给出了 candA 和 candB 中的 Neck -> Right-Shoulder 关键点对的所有关键点:
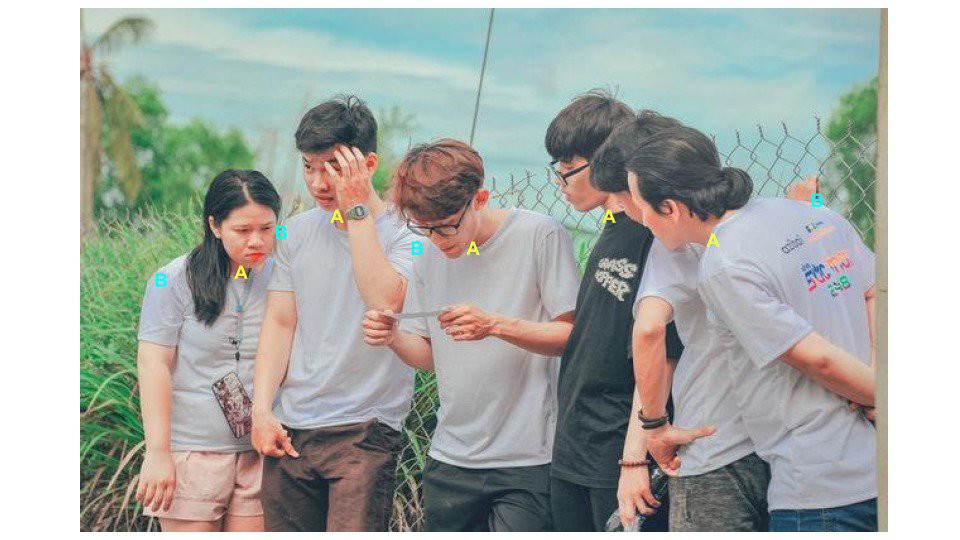

对应 Python 实现:
pafA = output[0, mapIdx[k][0], :, :]
pafB = output[0, mapIdx[k][1], :, :]
pafA = cv2.resize(pafA, (frameWidth, frameHeight))
pafB = cv2.resize(pafB, (frameWidth, frameHeight))
# Find the keypoints for the first and second limb
candA = detected_keypoints[POSE_PAIRS[k][0]]
candB = detected_keypoints[POSE_PAIRS[k][1]][2] - 计算两个关键点之间的单位向量,其给定了关节点之间连线的方向.
d_ij = np.subtract(candB[j][:2], candA[i][:2])
norm = np.linalg.norm(d_ij)
if norm:
d_ij = d_ij / norm[3] - 计算两个关键点之间连线的 10 个插值点.
# Find p(u)
interp_coord = list(zip(np.linspace(candA[i][0], candB[j][0], num=n_interp_samples),
np.linspace(candA[i][1], candB[j][1], num=n_interp_samples)))
# Find L(p(u))
paf_interp = []
for k in range(len(interp_coord)):
paf_interp.append(
[pafA[int(round(interp_coord[k][1])),
int(round(interp_coord[k][0]))],
pafB[int(round(interp_coord[k][1])),
int(round(interp_coord[k][0]))]
]) [4] - 计算插值点的 PAF 与单位向量 d_ij 之间的点积(dot product).
# Find E
paf_scores = np.dot(paf_interp, d_ij)
avg_paf_score = sum(paf_scores)/len(paf_scores)[5] - 如果这些插值点的 70% 的都满足判定标准,则该关键点对是有效的.
# Check if the connection is valid
# If the fraction of interpolated vectors
# aligned with PAF is higher then threshold -> Valid Pair
if (len(np.where(paf_scores > paf_score_th)[0])/n_interp_samples ) > conf_th :
if avg_paf_score > maxScore:
max_j = j
maxScore = avg_paf_score2.4. 同一人体关键点的组合
2.4.1. getPersonwiseKeypoints() 函数
getPersonwiseKeypoints()函数功能:计算得到属于每个人体的关键点集合.
对于每个检测到的有效 joint pair,分配属于一个人体的 joints.
def getPersonwiseKeypoints(valid_pairs, invalid_pairs):
# 每一行的最后一个值为 overall score.
personwiseKeypoints = -1 * np.ones((0, 19))
for k in range(len(mapIdx)):
if k not in invalid_pairs:
partAs = valid_pairs[k][:,0]
partBs = valid_pairs[k][:,1]
indexA, indexB = np.array(POSE_PAIRS[k])
for i in range(len(valid_pairs[k])):
found = 0
person_idx = -1
for j in range(len(personwiseKeypoints)):
if personwiseKeypoints[j][indexA] == partAs[i]:
person_idx = j
found = 1
break
if found:
personwiseKeypoints[person_idx][indexB] = partBs[i]
personwiseKeypoints[person_idx][-1] +=
keypoints_list[partBs[i].astype(int), 2] +
valid_pairs[k][i][2]
# if find no partA in the subset, create a new subset
elif not found and k < 17:
row = -1 * np.ones(19)
row[indexA] = partAs[i]
row[indexB] = partBs[i]
# add the keypoint_scores for the two keypoints and the paf_score
row[-1] = sum(
keypoints_list[valid_pairs[k][i,:2].astype(int), 2])
+ valid_pairs[k][i][2]
personwiseKeypoints = np.vstack([personwiseKeypoints, row])
return personwiseKeypoints2.4.2. 关键点组合的具体实现分析
计算得到所有关键点之间的关键点对后,可以将具有相同关键点检测候选值的关键点对,组合为多人的姿态估计.
代码实现具体分析
[1] - 首先创建保存每个人体的所有关键点的空列表.
然后对每个关键点对,判断 partA 是否已经在列表里, 如果已经在列表里,则表示该关键点对属于该列表,且 partB 也属于同一人体. 因此,添加该关键点对的 partB 到 partA 所在的列表.
# 空列表
personwiseKeypoints = -1 * np.ones((0, 19))for j in range(len(personwiseKeypoints)):
if personwiseKeypoints[j][indexA] == partAs[i]:
person_idx = j
found = 1
break
if found:
personwiseKeypoints[person_idx][indexB] = partBs[i][2] - 如果 partA 不在任一人体列表里,则表示该关键点对属于一个新出现的人体,故创建新的列表.
# if find no partA in the subset, create a new subset
elif not found and k < 17:
row = -1 * np.ones(19)
row[indexA] = partAs[i]
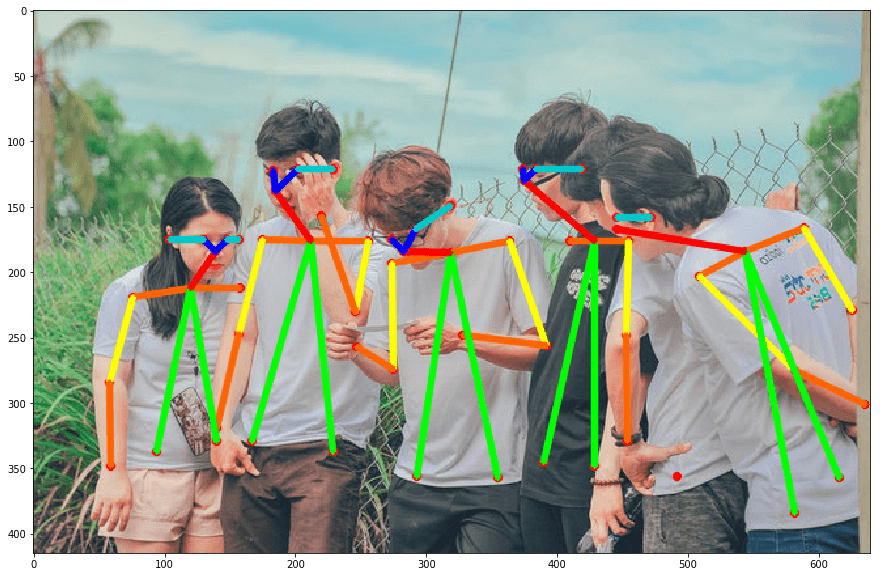
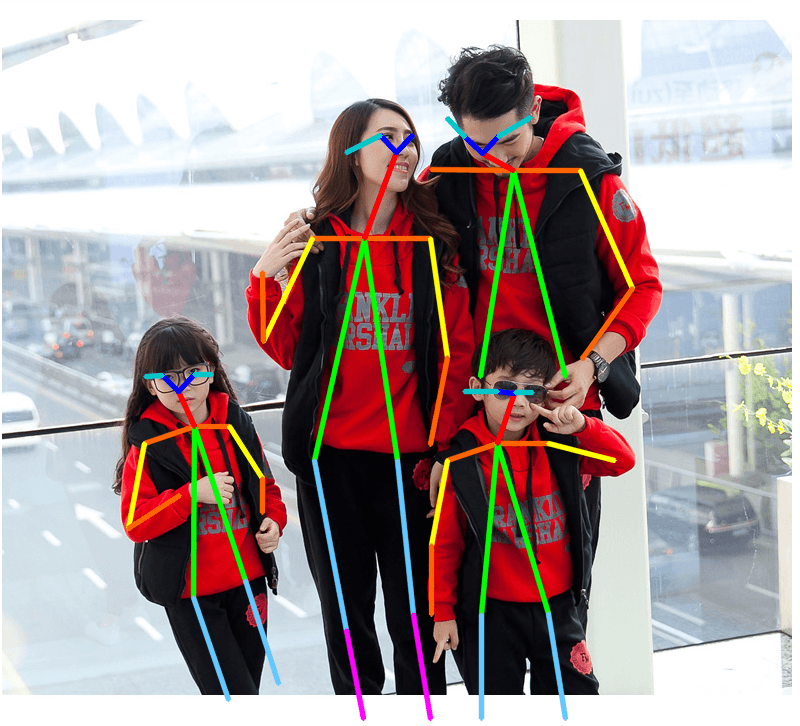
row[indexB] = partBs[i]2.5. 姿态检测结果可视化
##
img_cv2_copy = img_cv2.copy()
for i in range(num_points):
for j in range(len(detected_keypoints[i])):
cv2.circle(img_cv2_copy,
detected_keypoints[i][j][0:2],
5,
colors[i],
-1,
cv2.LINE_AA)
for i in range(17):
for n in range(len(personwiseKeypoints)):
index = personwiseKeypoints[n][np.array(POSE_PAIRS[i])]
if -1 in index:
continue
B = np.int32(keypoints_list[index.astype(int), 0])
A = np.int32(keypoints_list[index.astype(int), 1])
cv2.line(img_cv2_copy,
(B[0], A[0]), (B[1], A[1]),
colors[i],
3,
cv2.LINE_AA)
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(img_cv2_copy[:, :, ::-1])
plt.title("Results")
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()如:
3. 完整实现
模型下载:
COCO: http://posefs1.perception.cs.cmu.edu/OpenPose/models/pose/coco/pose_iter_440000.caffemodel
#!/usr/bin/python3
#!--*-- coding: utf-8 --*--
import os
import cv2
import time
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class general_mulitpose_model(object):
def __init__(self):
self.point_names = ['Nose', 'Neck',
'R-Sho', 'R-Elb', 'R-Wr',
'L-Sho', 'L-Elb', 'L-Wr',
'R-Hip', 'R-Knee', 'R-Ank',
'L-Hip', 'L-Knee', 'L-Ank',
'R-Eye', 'L-Eye', 'R-Ear', 'L-Ear']
self.point_pairs = [[1,2], [1,5], [2,3], [3,4], [5,6], [6,7],
[1,8], [8,9], [9,10], [1,11], [11,12], [12,13],
[1,0], [0,14], [14,16], [0,15], [15,17],
[2,17], [5,16] ]
# index of pafs correspoding to the self.point_pairs
# e.g for point_pairs(1,2), the PAFs are located at indices (31,32) of output,
# Similarly, (1,5) -> (39,40) and so on.
self.map_idx = [[31,32], [39,40], [33,34], [35,36], [41,42], [43,44],
[19,20], [21,22], [23,24], [25,26], [27,28], [29,30],
[47,48], [49,50], [53,54], [51,52], [55,56],
[37,38], [45,46]]
self.colors = [[0,100,255], [0,100,255], [0,255,255],
[0,100,255], [0,255,255], [0,100,255],
[0,255,0], [255,200,100], [255,0,255],
[0,255,0], [255,200,100], [255,0,255],
[0,0,255], [255,0,0], [200,200,0],
[255,0,0], [200,200,0], [0,0,0]]
self.num_points = 18
self.pose_net = self.get_model()
def get_model(self):
prototxt = "./models/pose/coco/pose_deploy_linevec.prototxt"
caffemodel = "./models/pose/coco/pose_iter_440000.caffemodel"
coco_net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(prototxt, caffemodel)
return coco_net
def getKeypoints(self, probMap, threshold=0.1):
mapSmooth = cv2.GaussianBlur(probMap, (3, 3), 0, 0)
mapMask = np.uint8(mapSmooth > threshold)
keypoints = []
# find the blobs
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(mapMask,
cv2.RETR_TREE,
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# for each blob find the maxima
for cnt in contours:
blobMask = np.zeros(mapMask.shape)
blobMask = cv2.fillConvexPoly(blobMask, cnt, 1)
maskedProbMap = mapSmooth * blobMask
_, maxVal, _, maxLoc = cv2.minMaxLoc(maskedProbMap)
keypoints.append(maxLoc + (probMap[maxLoc[1], maxLoc[0]],))
return keypoints
def getValidPairs(self, output, detected_keypoints, img_width, img_height):
valid_pairs = []
invalid_pairs = []
n_interp_samples = 10
paf_score_th = 0.1
conf_th = 0.7
for k in range(len(self.map_idx)):
# A->B constitute a limb
pafA = output[0, self.map_idx[k][0], :, :]
pafB = output[0, self.map_idx[k][1], :, :]
pafA = cv2.resize(pafA, (img_width, img_height))
pafB = cv2.resize(pafB, (img_width, img_height))
# Find the keypoints for the first and second limb
candA = detected_keypoints[self.point_pairs[k][0]]
candB = detected_keypoints[self.point_pairs[k][1]]
nA = len(candA)
nB = len(candB)
if (nA != 0 and nB != 0):
valid_pair = np.zeros((0, 3))
for i in range(nA):
max_j = -1
maxScore = -1
found = 0
for j in range(nB):
# Find d_ij
d_ij = np.subtract(candB[j][:2], candA[i][:2])
norm = np.linalg.norm(d_ij)
if norm:
d_ij = d_ij / norm
else:
continue
# Find p(u)
interp_coord = list(
zip(np.linspace(candA[i][0], candB[j][0], num=n_interp_samples),
np.linspace(candA[i][1], candB[j][1], num=n_interp_samples)))
# Find L(p(u))
paf_interp = []
for k in range(len(interp_coord)):
paf_interp.append([pafA[int(round(interp_coord[k][1])), int(
round(interp_coord[k][0]))],
pafB[int(round(interp_coord[k][1])), int(
round(interp_coord[k][0]))]])
# Find E
paf_scores = np.dot(paf_interp, d_ij)
avg_paf_score = sum(paf_scores) / len(paf_scores)
# Check if the connection is valid
if (len(np.where(paf_scores > paf_score_th)[
0]) / n_interp_samples) > conf_th:
if avg_paf_score > maxScore:
max_j = j
maxScore = avg_paf_score
found = 1
# Append the connection to the list
if found:
valid_pair = np.append(valid_pair,
[[candA[i][3], candB[max_j][3], maxScore]], axis=0)
# Append the detected connections to the global list
valid_pairs.append(valid_pair)
else: # If no keypoints are detected
print("No Connection : k = {}".format(k))
invalid_pairs.append(k)
valid_pairs.append([])
return valid_pairs, invalid_pairs
def getPersonwiseKeypoints(self, valid_pairs, invalid_pairs, keypoints_list):
personwiseKeypoints = -1 * np.ones((0, 19))
for k in range(len(self.map_idx)):
if k not in invalid_pairs:
partAs = valid_pairs[k][:, 0]
partBs = valid_pairs[k][:, 1]
indexA, indexB = np.array(self.point_pairs[k])
for i in range(len(valid_pairs[k])):
found = 0
person_idx = -1
for j in range(len(personwiseKeypoints)):
if personwiseKeypoints[j][indexA] == partAs[i]:
person_idx = j
found = 1
break
if found:
personwiseKeypoints[person_idx][indexB] = partBs[i]
personwiseKeypoints[person_idx][-1] += keypoints_list[
partBs[i].astype(int), 2] + \
valid_pairs[k][i][2]
# if find no partA in the subset, create a new subset
elif not found and k < 17:
row = -1 * np.ones(19)
row[indexA] = partAs[i]
row[indexB] = partBs[i]
# add the keypoint_scores for the two keypoints and the paf_score
row[-1] = sum(keypoints_list[valid_pairs[k][i, :2].astype(int), 2]) + \
valid_pairs[k][i][2]
personwiseKeypoints = np.vstack([personwiseKeypoints, row])
return personwiseKeypoints
def predict(self, inputparam):
img_cv2 = cv2.imread(inputparam["filename"])
img_width, img_height = img_cv2.shape[1], img_cv2.shape[0]
net_height = 368
net_width = int((net_height / img_height) * img_width)
start = time.time()
in_blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(
img_cv2,
1.0 / 255,
(net_width, net_height),
(0, 0, 0),
swapRB=False,
crop=False)
self.pose_net.setInput(in_blob)
output = self.pose_net.forward()
print("[INFO]Time Taken in Forward pass: {}".format(time.time() - start))
detected_keypoints = []
keypoints_list = np.zeros((0, 3))
keypoint_id = 0
threshold = 0.1
for part in range(self.num_points):
probMap = output[0, part, :, :]
probMap = cv2.resize(probMap, (img_cv2.shape[1], img_cv2.shape[0]))
keypoints = self.getKeypoints(probMap, threshold)
print("Keypoints - {} : {}".format(self.point_names[part], keypoints))
keypoints_with_id = []
for i in range(len(keypoints)):
keypoints_with_id.append(keypoints[i] + (keypoint_id,))
keypoints_list = np.vstack([keypoints_list, keypoints[i]])
keypoint_id += 1
detected_keypoints.append(keypoints_with_id)
valid_pairs, invalid_pairs = \
self.getValidPairs(output,
detected_keypoints,
img_width,
img_height)
personwiseKeypoints = \
self.getPersonwiseKeypoints(valid_pairs,
invalid_pairs,
keypoints_list)
return personwiseKeypoints, keypoints_list
def vis_pose(self, img_file, personwiseKeypoints, keypoints_list):
img_cv2 = cv2.imread(img_file)
for i in range(17):
for n in range(len(personwiseKeypoints)):
index = personwiseKeypoints[n][np.array(self.point_pairs[i])]
if -1 in index:
continue
B = np.int32(keypoints_list[index.astype(int), 0])
A = np.int32(keypoints_list[index.astype(int), 1])
cv2.line(img_cv2, (B[0], A[0]), (B[1], A[1]), self.colors[i], 3, cv2.LINE_AA)
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(img_cv2[:, :, ::-1])
plt.title("Results")
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
print("[INFO]MultiPose estimation.")
img_file = "multipose_test_image.jpg"
start = time.time()
multipose_model = general_mulitpose_model()
print("[INFO]Time Taken in Model Loading: {}".\
format(time.time() - start))
personwiseKeypoints, keypoints_list = \
multipose_model.predict(inputparam)
multipose_model.vis_pose(img_file,
personwiseKeypoints,
keypoints_list)
print(personwiseKeypoints)
print(keypoints_list)
print("[INFO]Done.")如:

4. 参考资料
[1] - Multi-Person Pose Estimation in OpenCV using OpenPose - 2018.09.11
5 comments
倒数第7行inputparam有错
对应的是图片文件名.
C++版的 openpose caffe的模型太大了
我想跑那个mobilenet_thin的姿态检测模型 但是需要pbtxt文件。。不知道怎么搞了
mobilenet_thin 这个基于 tensorflow 的实现,没尝试过转换为 dnn 可调用的形式.
这个看起来很有意思啊