这篇博文主要是介绍如何基于 OpenCV 使用 Mask R-CNN.
Mask R-CNN 可以自动对图片中每个目标的进行分割,并构建像素级的 masks.
在博文 YOLOV3 - 基于 OpenCV 的 YOLO 目标检测 - AIUAI 中介绍了基于 OpenCV 的 YOLO 目标检测算法. 目标检测器,如 YOLO,Faster R-CNNs 和 SSDs,输出的是图片中每个目标物体的边界框的 (x, y) 坐标集合. 但是边界框缺乏一定的像素级信息,如 (1)哪些像素属于前景目标;(2) 哪些像素属于背景.
博文主要包括:
[1] - Mask R-CNN 概览
[2] - Mask R-CNN 图片
[3] - Mask R-CNN 视频流
1. Mask R-CNN 概览
1.1. 实例分割 vs. 语义分割
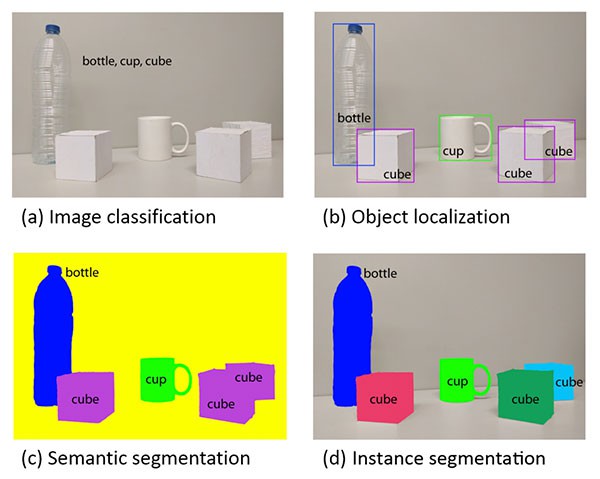
如下图,很好的说明了图像分类、目标检测、语义分割和实例分割之间的差异.
[1] - 图像分类,旨在预测能够刻画输入图像内容的标签集.
[2] - 目标检测,基于图像分类,但是同时会定位图片中目标的位置,则图像的刻画即包括两部分: (1) 每个目标的边界框(x,y) 坐标; (2) 对应每个边界框的相关类别标签.
[3] - 语义分割,预测输入图像的每个像素的类别标签(包括背景的类别标签.) 注:上图(c)中 cube 目标均是相同的颜色. 虽然语义分割算法能够对每个目标的像素进行分类,但是不能区分相同类别的两个目标.
[4] - 实例分割,即使图像中存在相同类别标签的目标,也能够预测图片中每个目标的像素级 mask. 如上图(d), 每个 cube 都是不同的颜色. 即:实例分割不仅能够定位每个独立的 cube,还能够预测其边界位置.
Mask R-CNN 是一种实例分割算法.
1.2. Mask R-CNN 简介
Mask R-CNN 算法是 He 等在论文 Mask R-CNN(2017) 中提出的.
Mask R-CNN 是基于 Girshick 等人在 R-CNN (2013), Fast R-CNN (2015) 和 Faster R-CNN (2015) 中的目标检测工作的.
为了更好的理解 Mask R-CNN 算法,这里简单回顾下 R-CNNs:
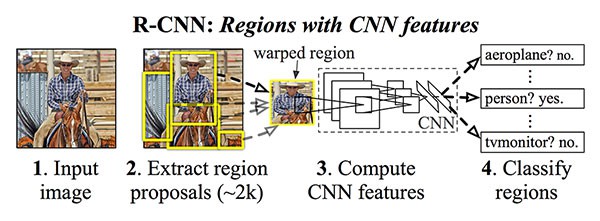
[1] - R-CNN
主要包括四步处理:
(1)-Step1: 输入一张图片到网络;
(2)-Step2: 提取区域候选框(region proposals),例如采用 Selective Search 算法得到的可能包含目标物体的图片区域.
(3)-Step3: 采用迁移学习,即特征提取部分,采用预训练的CNN计算每个候选框(ROI)的特征.
(4)-Step4: 采用 SVM 对每个候选框的提取特征进行分类.
R-CNN 有效的原因在于 CNN 提取的鲁棒、判别性强的特征. 但,R-CNN 的问题在于其速度相当的慢. 此外,其并不是真正通过深度神经网络来学习定位目标,实际上只是构建了更高级的 HOG + Linear SVM detector 方法.
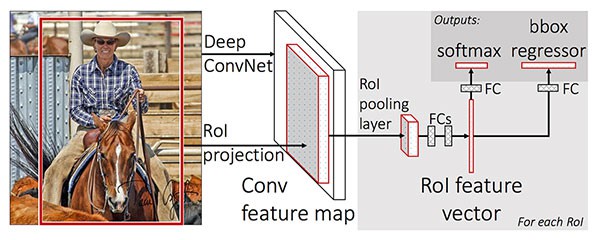
[2] - Fast R-CNN
类似于 R-CNN,Fast R-CNN 也采用了 Selective Search 算法来获得区域候选框;不过,其创新点在于 Region of Interest (ROI) Pooling 模块.
ROI Pooling 通过对 CNN 的输出的 feature map 提取固定尺寸的窗口(fixed-size window),并采用窗口内的特征得到最终的类别标签和边界框. Fast R-CNN 最重要的提升是,有效的实现了网络的 end-to-end 训练,其过程主要为:
(1)-给定输入图片及对应的 ground-truth 边界框;
(2)-提取特征图(feature map);
(3)-采用 ROI Pooling 处理,得到 ROI 特征向量;
(4)-最后,采用两个 FC 层,同时得到每个候选框的类别标签预测和边界框位置.
虽然 Fast R-CNN 是 end-to-end 训练的,但是由于依赖于 Selective Search 算法,其在预测推断时,速度明显受影响.
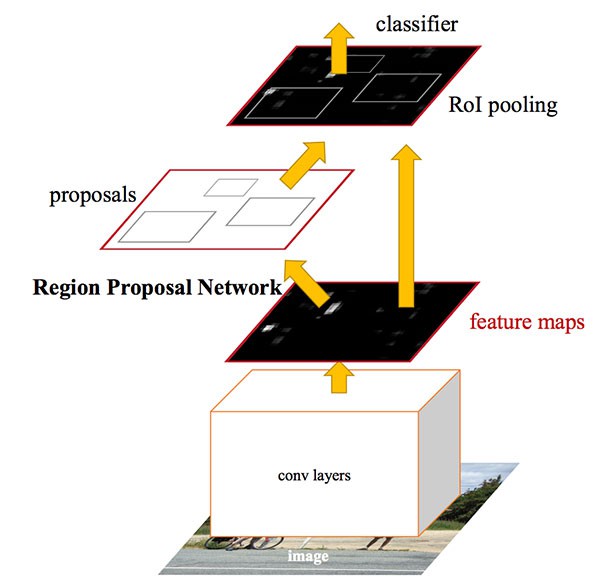
[3] - Faster R-CNN
为了进一步提升 R-CNN 结构的速度,Faster R-CNN 直接将区域候选框选取(region propoasal) 整合进网络结构中.
Faster R-CNN 提出 Region Proposal Network (RPN),以实现将区域候选框选取(region propoasal) 直接整合进网络中,取代 Selective Search 算法.
Faster R-CNN 结构能够取得 7-10 FPS 的速度,将基于深度学习的实时目标检测提升了一大步.
[4] - Mask R-CNN
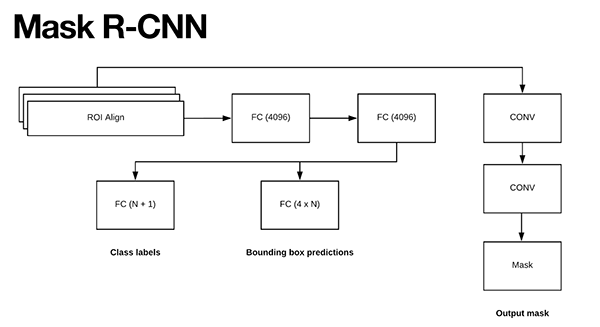
Mask R-CNN 是基于 Faster R-CNN 结构构建的,主要有两个创新:
(1)-将 ROI Pooling 模块替换为 ROI Align 模块;
(2)-在ROI Align 模块的输出端新增一个分支. 该分支的输入为 ROI Align 的输出,该分支的输出送入到两个 Conv 层. Conv 层的输出即为 mask.
如图:
正如在 Faster R-CNN/Mask R-CNN 结构中,采用RPN 网络来生成图片中可能包含物体的区域候选框. 每个候选区域根据其"目标分数(objectness score)" 进行排名(如,表征了给定区域可能包含目标的可能性), 然后保留 top N 个最可能包含目标的区域.
在 Faster R-CNN 论文中,Girshick 等人设置 N=2000. 但实际上,可以采用较小的 N 值,如 N=(10, 100, 200, 300),仍能得到比较好的结果.
在 Mask R-CNN 论文中,He 等设置 N=300,这里也采用该设置.
所选择的 300 个 ROIs 被送入到三个并行的网络分支:
- (1)类别标签预测
- (2)边界框预测
- (3)Mask 预测
在 Mask R-CNN 预测阶段,所选择的 300 个 ROIs 先送入 NMS( non-maxima suppression) 处理,并只保留 top 100 的检测框,最终得到 100xLx15x15 的 4D Tensor. 其中,L 是数据集中类别标签的总数,15x15 是每个 mask 的尺寸.
以 COCO dataset 为例,L=90 个目标物体类别标签,mask 预测分支得到的结果为 100x90x15x15.
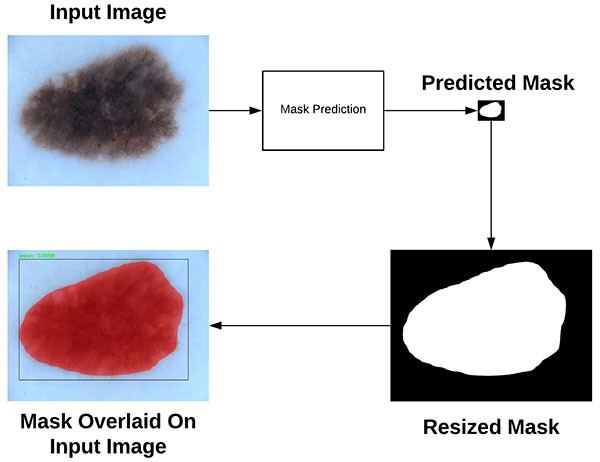
Mask R-CNN 预测 mask 的过程如图:
更多细节参考:
[1] - Mask R-CNN
2. Mask R-CNN 图片实例分割
具体实现如下 - mask_rcnn.py:
#!/usr/bin/python3
#--*-- coding:utf-8 --*--
import numpy as np
import argparse
import random
import time
import cv2
import os
#参数配置
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-i", "--image", required=True,
help="path to input image")
ap.add_argument("-m", "--mask-rcnn", required=True,
help="base path to mask-rcnn directory")
ap.add_argument("-v", "--visualize", type=int, default=0,
help="whether or not we are going to visualize each instance")
ap.add_argument("-c", "--confidence", type=float, default=0.5,
help="minimum probability to filter weak detections")
ap.add_argument("-t", "--threshold", type=float, default=0.3,
help="minimum threshold for pixel-wise mask segmentation")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
#加载 COCO 类别标签
labelsPath = os.path.sep.join([args["mask_rcnn"],
"object_detection_classes_coco.txt"])
LABELS = open(labelsPath).read().strip().split("\n")
#加载用于可视化给定实例分割的颜色集合
colorsPath = os.path.sep.join([args["mask_rcnn"], "colors.txt"])
COLORS = open(colorsPath).read().strip().split("\n")
COLORS = [np.array(c.split(",")).astype("int") for c in COLORS]
COLORS = np.array(COLORS, dtype="uint8")
#Mask R-CNN 权重路径及模型配置文件
weightsPath = os.path.sep.join([args["mask_rcnn"],
"frozen_inference_graph.pb"])
configPath = os.path.sep.join([args["mask_rcnn"],
"mask_rcnn_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28.pbtxt"])
#加载预训练的 Mask R-CNN 模型(90 classes)
print("[INFO] loading Mask R-CNN from disk...")
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromTensorflow(weightsPath, configPath)
#读取图片
image = cv2.imread(args["image"])
(H, W) = image.shape[:2]
#构建输入图片 blob
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(image, swapRB=True, crop=False)
net.setInput(blob)
start = time.time()
#forward 计算,输出图片中目标的边界框坐标以及每个目标的像素级分割
(boxes, masks) = net.forward(["detection_out_final", "detection_masks"])
end = time.time()
# Mask R-CNN 的时间统计
print("[INFO] Mask R-CNN took {:.6f} seconds".format(end - start))
print("[INFO] boxes shape: {}".format(boxes.shape))
print("[INFO] masks shape: {}".format(masks.shape))
# loop over the number of detected objects
for i in range(0, boxes.shape[2]):
#检测的 class ID 及对应的置信度(概率)
classID = int(boxes[0, 0, i, 1])
confidence = boxes[0, 0, i, 2]
#过滤低置信度预测结果
if confidence > args["confidence"]:
# 用于可视化
clone = image.copy()
#将边界框坐标缩放回相对于图片的尺寸,然后计算边界框的width和height
box = boxes[0, 0, i, 3:7] * np.array([W, H, W, H])
(startX, startY, endX, endY) = box.astype("int")
boxW = endX - startX
boxH = endY - startY
#提取目标的像素级分割
mask = masks[i, classID]
#resize mask以保持与边界框的维度一致
mask = cv2.resize(mask, (boxW, boxH),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
#根据设定阈值,得到二值化mask.
mask = (mask > args["threshold"])
#提取图片的 ROI
roi = clone[startY:endY, startX:endX]
#可视化
if args["visualize"] > 0:
#将二值mask转换为:0和255
visMask = (mask * 255).astype("uint8")
instance = cv2.bitwise_and(roi, roi, mask=visMask)
#可视化提取的 ROI、mask 以及对应的分割实例
cv2.imshow("ROI", roi)
cv2.imshow("Mask", visMask)
cv2.imshow("Segmented", instance)
#只提取 ROI 的 masked 区域
roi = roi[mask]
#随机选择一种颜色,用于可视化特定的实例分割
color = random.choice(COLORS)
#通过融合选择的颜色和 ROI 进行融合,创建透明覆盖图
blended = ((0.4 * color) + (0.6 * roi)).astype("uint8")
#替换原始图片的融合 ROI 区域
clone[startY:endY, startX:endX][mask] = blended
#画出图片中实例的边界框
color = [int(c) for c in color]
cv2.rectangle(clone, (startX, startY), (endX, endY), color, 2)
#画出预测的类别标签以及对应的实例概率
text = "{}: {:.4f}".format(LABELS[classID], confidence)
cv2.putText(clone, text, (startX, startY - 5),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, color, 2)
#show
cv2.imshow("Output", clone)
cv2.waitKey(0)运行,如:
python mask_rcnn.py --mask-rcnn mask-rcnn-coco --image images/example_01.jpg
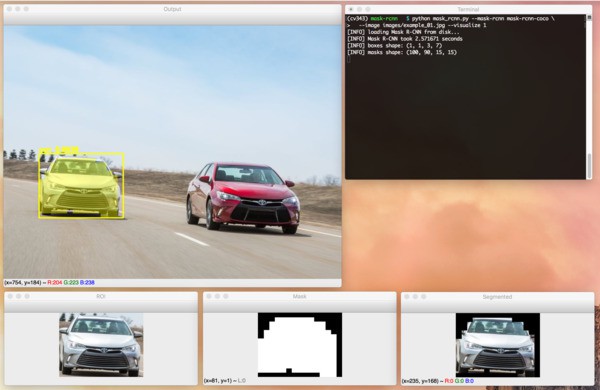
python mask_rcnn.py --mask-rcnn mask-rcnn-coco --image images/example_03.jpg --visualize 1输出如:
中间输入如:
3. Mask R-CNN 视频流实例分割
具体实现如下 - mask_rcnn_video.py:
import numpy as np
import argparse
import imutils
import time
import cv2
import os
#
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-i", "--input", required=True,
help="path to input video file")
ap.add_argument("-o", "--output", required=True,
help="path to output video file")
ap.add_argument("-m", "--mask-rcnn", required=True,
help="base path to mask-rcnn directory")
ap.add_argument("-c", "--confidence", type=float, default=0.5,
help="minimum probability to filter weak detections")
ap.add_argument("-t", "--threshold", type=float, default=0.3,
help="minimum threshold for pixel-wise mask segmentation")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
#
labelsPath = os.path.sep.join([args["mask_rcnn"],
"object_detection_classes_coco.txt"])
LABELS = open(labelsPath).read().strip().split("\n")
#
np.random.seed(42)
COLORS = np.random.randint(0, 255, size=(len(LABELS), 3),
dtype="uint8")
#
weightsPath = os.path.sep.join([args["mask_rcnn"],
"frozen_inference_graph.pb"])
configPath = os.path.sep.join([args["mask_rcnn"],
"mask_rcnn_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28.pbtxt"])
#
print("[INFO] loading Mask R-CNN from disk...")
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromTensorflow(weightsPath, configPath)
#读取视频流
vs = cv2.VideoCapture(args["input"])
writer = None
#计算视频流总帧数
try:
prop = cv2.cv.CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT if imutils.is_cv2() \
else cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT
total = int(vs.get(prop))
print("[INFO] {} total frames in video".format(total))
except:
print("[INFO] could not determine # of frames in video")
total = -1
# loop over frames from the video file stream
while True:
# read the next frame from the file
(grabbed, frame) = vs.read()
if not grabbed:
break
#
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, swapRB=True, crop=False)
net.setInput(blob)
start = time.time()
(boxes, masks) = net.forward(["detection_out_final",
"detection_masks"])
end = time.time()
# loop over the number of detected objects
for i in range(0, boxes.shape[2]):
classID = int(boxes[0, 0, i, 1])
confidence = boxes[0, 0, i, 2]
if confidence > args["confidence"]:
(H, W) = frame.shape[:2]
box = boxes[0, 0, i, 3:7] * np.array([W, H, W, H])
(startX, startY, endX, endY) = box.astype("int")
boxW = endX - startX
boxH = endY - startY
#
mask = masks[i, classID]
mask = cv2.resize(mask, (boxW, boxH),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
mask = (mask > args["threshold"])
#
roi = frame[startY:endY, startX:endX][mask]
#
color = COLORS[classID]
blended = ((0.4 * color) + (0.6 * roi)).astype("uint8")
#
frame[startY:endY, startX:endX][mask] = blended
#
color = [int(c) for c in color]
cv2.rectangle(frame, (startX, startY), (endX, endY),
color, 2)
#
text = "{}: {:.4f}".format(LABELS[classID], confidence)
cv2.putText(frame, text, (startX, startY - 5),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, color, 2)
# check if the video writer is None
if writer is None:
# initialize our video writer
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"MJPG")
writer = cv2.VideoWriter(args["output"], fourcc, 30,
(frame.shape[1], frame.shape[0]), True)
# some information on processing single frame
if total > 0:
elap = (end - start)
print("[INFO] single frame took {:.4f} seconds".format(elap))
print("[INFO] estimated total time to finish: {:.4f}".format(
elap * total))
# write the output frame to disk
writer.write(frame)
# release the file pointers
print("[INFO] cleaning up...")
writer.release()
vs.release()运行,如:
python mask_rcnn_video.py --input videos/cats_and_dogs.mp4 \ --output output/cats_and_dogs_output.avi \ --mask-rcnn mask-rcnn-coco



One comment
非常好的翻译,比csdn那帮有用!!!感谢,如果有怎么训练自己的模型就更好了