原文:Data Augmentation in SSD (Single Shot Detector) - 2018.06.28
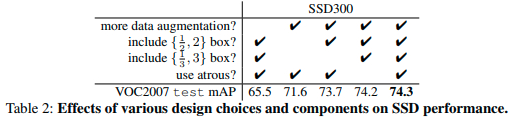
作者研究了 single shot 目标检测器 SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector 如何取得了比 Faster R-CNN 更佳的 mAP,且计算复杂度明显减少,实时运行效果更快. 这里将详细描述 SSD 所采用的数据增强策略. 根据论文所述,其数据增强策略取得了 8.8% 的 mAP 提升.
数据增强对于小目标检测的精度提升尤其重要,因为其对图像进行缩放(zoom),使得分类器能够识别更多图片中的目标物体. 数据增强对于图像中出现被遮挡物体(occluded objects)的处理,也很重要,通过对训练数据中的图像进行裁剪,使得只有部分物体是可见的.
1. 数据增强流程
采用的数据增强处理流程步骤如下:
- 光度变形(Photometric Distortions)
几何变换(Geometric Distortions)
- 图像扩展(ExpandImage)
- 随机裁剪(RandomCrop)
- 随机镜像(RandomMirror)
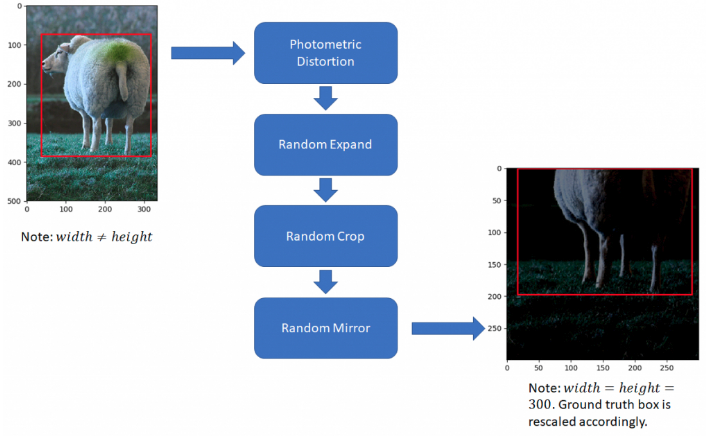
下面会详细介绍这些数据增强(包括相应的代码实现片段). 其中,每一数据变换都是概率随机的(一般 probability=0.5). 因此,不同的训练次数采用的是数据增强后的不同图像数据.
2. 光度变形(Photometric Distortions)
2.1. 随机调整亮度(Random Brightness)
以 probability=0.5 的 随机概率,随机对图像每个像素添加一个值,该添加值是从 [-delat, delta] 中随机选取的. 默认的 delta 值是 32.
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
if random.randint(2):
delta = random.uniform(-self.delta, self.delta)
image += delta
return image, boxes, labels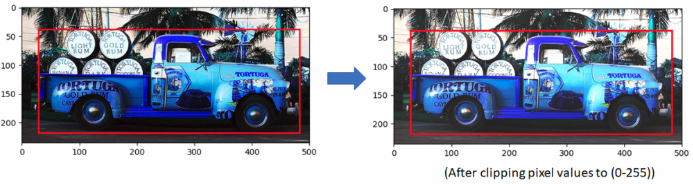
2.2. 随机调整对比度(Contrast), 色相(Hue) 和饱和度(Saturation)
亮度(Brightness)调整后,进行对比度,色相和饱和度的随机变换. 其顺序是随机的. 有两种选择,首先对比度处理,然后色相和饱和度;或者首先色相和饱和度处理,然后对比度处理. 每种选择都是随机的,probability=0.5.
self.pd = [RandomContrast(),
ConvertColor(transform='HSV'),
RandomSaturation(),
RandomHue(),
ConvertColor(current='HSV', transform='BGR'),
RandomContrast() ]
im, boxes, labels = self.rand_brightness(im, boxes, labels)
if random.randint(2):
distort = Compose(self.pd[:-1])
else:
distort = Compose(self.pd[1:])
im, boxes, labels = distort(im, boxes, labels)其中,对比度是在 RGB 空间处理,色相和饱和度是在 HSV 空间. 因此,在进行每一步操作前需要先作对应的颜色空间转换. 对比度,色相和饱和度的调整类似于亮度调整,都是 probability=0.5 的随机进行. 通过随机在一个上界和下界区间内选择形变的值. 例如,饱和度调整:
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
if random.randint(2):
image[:, :, 1] *= random.uniform(self.lower, self.upper)
return image, boxes, labels
2.3. 随机光照噪声(RandomLightingNoise)
最后一种光度形变是随机光照噪声. 其包括随机颜色通道交换(color channel swap). 颜色变换定义为:
self.perms = ((0, 1, 2), (0, 2, 1),
(1, 0, 2), (1, 2, 0),
(2, 0, 1), (2, 1, 0))对于 RGB 图像,颜色通道变换(0 2 1) 则交换 green 和 blue 通道,保持 red 通道不变.

3. 几何变换
光度调整只会改变图像像素,而不会改变图像的尺寸大小. 而几何变换则会对图像尺寸和维度进行调整.
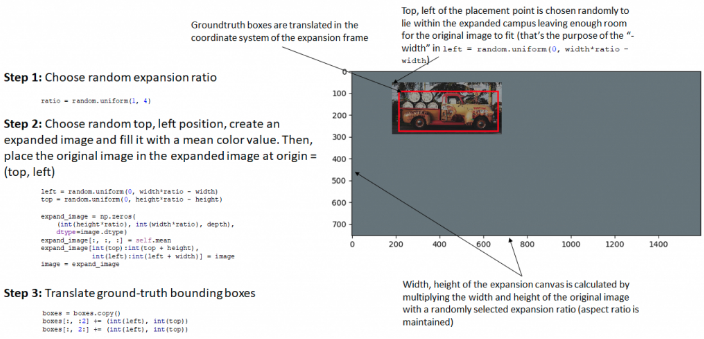
3.1. 随机扩展(RandomExpand)
3.2. 随机裁剪(RandomCrop)
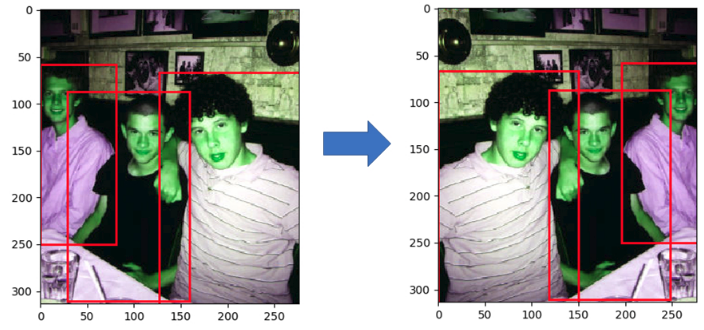
随机裁剪是对 ExpandImage 得到的图像裁剪出其中的一部分图像块,并确保该图像块至少一个 groundtruth box 有重叠,至少一个 groundtruth box 的中心(centroid) 位于该图像块中. 这样就可以避免不包含明显的前景目标的图像块不用于网络训练(只有包含明显的前景目标的图像块采用于网络训练.) 同时,保证只有部分前景目标可见的图片用于网络训练.
例如,下面图像中,Groundtruth box 表示为红色,裁剪的图像块表示为绿色. 由于是随机裁剪,因此有些图像是包含扩展的画布,有些则不包含.

3.3. 随机镜像(RandomMirror)
最后一步数据增强是随机镜像. 其仅是图像的左右翻转.在很多目标检测和图像分类张总均有采用.
 最后,类似于其它目标检测和图像分类任务,图像为 resize 到 300x300,groundtruth 坐标进行相应调整;并对图像进行归一化和减均值处理. 完整的数据增强脚本 - augmentations.py.
最后,类似于其它目标检测和图像分类任务,图像为 resize 到 300x300,groundtruth 坐标进行相应调整;并对图像进行归一化和减均值处理. 完整的数据增强脚本 - augmentations.py.
import torch
from torchvision import transforms
import cv2
import numpy as np
import types
from numpy import random
def intersect(box_a, box_b):
max_xy = np.minimum(box_a[:, 2:], box_b[2:])
min_xy = np.maximum(box_a[:, :2], box_b[:2])
inter = np.clip((max_xy - min_xy), a_min=0, a_max=np.inf)
return inter[:, 0] * inter[:, 1]
def jaccard_numpy(box_a, box_b):
"""Compute the jaccard overlap of two sets of boxes. The jaccard overlap
is simply the intersection over union of two boxes.
E.g.:
A ∩ B / A ∪ B = A ∩ B / (area(A) + area(B) - A ∩ B)
Args:
box_a: Multiple bounding boxes, Shape: [num_boxes,4]
box_b: Single bounding box, Shape: [4]
Return:
jaccard overlap: Shape: [box_a.shape[0], box_a.shape[1]]
"""
inter = intersect(box_a, box_b)
area_a = ((box_a[:, 2]-box_a[:, 0]) *
(box_a[:, 3]-box_a[:, 1])) # [A,B]
area_b = ((box_b[2]-box_b[0]) *
(box_b[3]-box_b[1])) # [A,B]
union = area_a + area_b - inter
return inter / union # [A,B]
class Compose(object):
"""Composes several augmentations together.
Args:
transforms (List[Transform]): list of transforms to compose.
Example:
>>> augmentations.Compose([
>>> transforms.CenterCrop(10),
>>> transforms.ToTensor(),
>>> ])
"""
def __init__(self, transforms):
self.transforms = transforms
def __call__(self, img, boxes=None, labels=None):
for t in self.transforms:
img, boxes, labels = t(img, boxes, labels)
return img, boxes, labels
class Lambda(object):
"""Applies a lambda as a transform."""
def __init__(self, lambd):
assert isinstance(lambd, types.LambdaType)
self.lambd = lambd
def __call__(self, img, boxes=None, labels=None):
return self.lambd(img, boxes, labels)
class ConvertFromInts(object):
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
return image.astype(np.float32), boxes, labels
class SubtractMeans(object):
def __init__(self, mean):
self.mean = np.array(mean, dtype=np.float32)
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
image = image.astype(np.float32)
image -= self.mean
return image.astype(np.float32), boxes, labels
class ToAbsoluteCoords(object):
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
height, width, channels = image.shape
boxes[:, 0] *= width
boxes[:, 2] *= width
boxes[:, 1] *= height
boxes[:, 3] *= height
return image, boxes, labels
class ToPercentCoords(object):
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
height, width, channels = image.shape
boxes[:, 0] /= width
boxes[:, 2] /= width
boxes[:, 1] /= height
boxes[:, 3] /= height
return image, boxes, labels
class Resize(object):
def __init__(self, size=300):
self.size = size
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
image = cv2.resize(image, (self.size,
self.size))
return image, boxes, labels
class RandomSaturation(object):
def __init__(self, lower=0.5, upper=1.5):
self.lower = lower
self.upper = upper
assert self.upper >= self.lower, "contrast upper must be >= lower."
assert self.lower >= 0, "contrast lower must be non-negative."
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
if random.randint(2):
image[:, :, 1] *= random.uniform(self.lower, self.upper)
return image, boxes, labels
class RandomHue(object):
def __init__(self, delta=18.0):
assert delta >= 0.0 and delta <= 360.0
self.delta = delta
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
if random.randint(2):
image[:, :, 0] += random.uniform(-self.delta, self.delta)
image[:, :, 0][image[:, :, 0] > 360.0] -= 360.0
image[:, :, 0][image[:, :, 0] < 0.0] += 360.0
return image, boxes, labels
class RandomLightingNoise(object):
def __init__(self):
self.perms = ((0, 1, 2), (0, 2, 1),
(1, 0, 2), (1, 2, 0),
(2, 0, 1), (2, 1, 0))
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
if random.randint(2):
swap = self.perms[random.randint(len(self.perms))]
shuffle = SwapChannels(swap) # shuffle channels
image = shuffle(image)
return image, boxes, labels
class ConvertColor(object):
def __init__(self, current='BGR', transform='HSV'):
self.transform = transform
self.current = current
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
if self.current == 'BGR' and self.transform == 'HSV':
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
elif self.current == 'HSV' and self.transform == 'BGR':
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR)
else:
raise NotImplementedError
return image, boxes, labels
class RandomContrast(object):
def __init__(self, lower=0.5, upper=1.5):
self.lower = lower
self.upper = upper
assert self.upper >= self.lower, "contrast upper must be >= lower."
assert self.lower >= 0, "contrast lower must be non-negative."
# expects float image
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
if random.randint(2):
alpha = random.uniform(self.lower, self.upper)
image *= alpha
return image, boxes, labels
class RandomBrightness(object):
def __init__(self, delta=32):
assert delta >= 0.0
assert delta <= 255.0
self.delta = delta
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
if random.randint(2):
delta = random.uniform(-self.delta, self.delta)
image += delta
return image, boxes, labels
class ToCV2Image(object):
def __call__(self, tensor, boxes=None, labels=None):
return tensor.cpu().numpy().astype(np.float32).transpose((1, 2, 0)), boxes, labels
class ToTensor(object):
def __call__(self, cvimage, boxes=None, labels=None):
return torch.from_numpy(cvimage.astype(np.float32)).permute(2, 0, 1), boxes, labels
class RandomSampleCrop(object):
"""Crop
Arguments:
img (Image): the image being input during training
boxes (Tensor): the original bounding boxes in pt form
labels (Tensor): the class labels for each bbox
mode (float tuple): the min and max jaccard overlaps
Return:
(img, boxes, classes)
img (Image): the cropped image
boxes (Tensor): the adjusted bounding boxes in pt form
labels (Tensor): the class labels for each bbox
"""
def __init__(self):
self.sample_options = (
# using entire original input image
None,
# sample a patch s.t. MIN jaccard w/ obj in .1,.3,.4,.7,.9
(0.1, None),
(0.3, None),
(0.7, None),
(0.9, None),
# randomly sample a patch
(None, None),
)
def __call__(self, image, boxes=None, labels=None):
height, width, _ = image.shape
while True:
# randomly choose a mode
mode = random.choice(self.sample_options)
if mode is None:
return image, boxes, labels
min_iou, max_iou = mode
if min_iou is None:
min_iou = float('-inf')
if max_iou is None:
max_iou = float('inf')
# max trails (50)
for _ in range(50):
current_image = image
w = random.uniform(0.3 * width, width)
h = random.uniform(0.3 * height, height)
# aspect ratio constraint b/t .5 & 2
if h / w < 0.5 or h / w > 2:
continue
left = random.uniform(width - w)
top = random.uniform(height - h)
# convert to integer rect x1,y1,x2,y2
rect = np.array([int(left), int(top), int(left+w), int(top+h)])
# calculate IoU (jaccard overlap) b/t the cropped and gt boxes
overlap = jaccard_numpy(boxes, rect)
# is min and max overlap constraint satisfied? if not try again
if overlap.min() < min_iou and max_iou < overlap.max():
continue
# cut the crop from the image
current_image = current_image[rect[1]:rect[3], rect[0]:rect[2],
:]
# keep overlap with gt box IF center in sampled patch
centers = (boxes[:, :2] + boxes[:, 2:]) / 2.0
# mask in all gt boxes that above and to the left of centers
m1 = (rect[0] < centers[:, 0]) * (rect[1] < centers[:, 1])
# mask in all gt boxes that under and to the right of centers
m2 = (rect[2] > centers[:, 0]) * (rect[3] > centers[:, 1])
# mask in that both m1 and m2 are true
mask = m1 * m2
# have any valid boxes? try again if not
if not mask.any():
continue
# take only matching gt boxes
current_boxes = boxes[mask, :].copy()
# take only matching gt labels
current_labels = labels[mask]
# should we use the box left and top corner or the crop's
current_boxes[:, :2] = np.maximum(current_boxes[:, :2],
rect[:2])
# adjust to crop (by substracting crop's left,top)
current_boxes[:, :2] -= rect[:2]
current_boxes[:, 2:] = np.minimum(current_boxes[:, 2:],
rect[2:])
# adjust to crop (by substracting crop's left,top)
current_boxes[:, 2:] -= rect[:2]
return current_image, current_boxes, current_labels
class Expand(object):
def __init__(self, mean):
self.mean = mean
def __call__(self, image, boxes, labels):
if random.randint(2):
return image, boxes, labels
height, width, depth = image.shape
ratio = random.uniform(1, 4)
left = random.uniform(0, width*ratio - width)
top = random.uniform(0, height*ratio - height)
expand_image = np.zeros(
(int(height*ratio), int(width*ratio), depth),
dtype=image.dtype)
expand_image[:, :, :] = self.mean
expand_image[int(top):int(top + height),
int(left):int(left + width)] = image
image = expand_image
boxes = boxes.copy()
boxes[:, :2] += (int(left), int(top))
boxes[:, 2:] += (int(left), int(top))
return image, boxes, labels
class RandomMirror(object):
def __call__(self, image, boxes, classes):
_, width, _ = image.shape
if random.randint(2):
image = image[:, ::-1]
boxes = boxes.copy()
boxes[:, 0::2] = width - boxes[:, 2::-2]
return image, boxes, classes
class SwapChannels(object):
"""Transforms a tensorized image by swapping the channels in the order
specified in the swap tuple.
Args:
swaps (int triple): final order of channels
eg: (2, 1, 0)
"""
def __init__(self, swaps):
self.swaps = swaps
def __call__(self, image):
"""
Args:
image (Tensor): image tensor to be transformed
Return:
a tensor with channels swapped according to swap
"""
# if torch.is_tensor(image):
# image = image.data.cpu().numpy()
# else:
# image = np.array(image)
image = image[:, :, self.swaps]
return image
class PhotometricDistort(object):
def __init__(self):
self.pd = [
RandomContrast(),
ConvertColor(transform='HSV'),
RandomSaturation(),
RandomHue(),
ConvertColor(current='HSV', transform='BGR'),
RandomContrast()
]
self.rand_brightness = RandomBrightness()
self.rand_light_noise = RandomLightingNoise()
def __call__(self, image, boxes, labels):
im = image.copy()
im, boxes, labels = self.rand_brightness(im, boxes, labels)
if random.randint(2):
distort = Compose(self.pd[:-1])
else:
distort = Compose(self.pd[1:])
im, boxes, labels = distort(im, boxes, labels)
return self.rand_light_noise(im, boxes, labels)
class SSDAugmentation(object):
def __init__(self, size=300, mean=(104, 117, 123)):
self.mean = mean
self.size = size
self.augment = Compose([
ConvertFromInts(),
ToAbsoluteCoords(),
PhotometricDistort(),
Expand(self.mean),
RandomSampleCrop(),
RandomMirror(),
ToPercentCoords(),
Resize(self.size),
SubtractMeans(self.mean)
])
def __call__(self, img, boxes, labels):
return self.augment(img, boxes, labels)
10 comments
resize函数里 为什么不用对坐标框的坐标进行处理呢??
ToPercentCoords 中已经处理过了.
SubtractMeans(self.mean),这会不会出现负像素的问题
会出现.
您好,我对随机裁剪的bbox坐标有一些疑问,让的gt bbox的坐标值控制在裁剪区域里,但是这样不会造成框的不准确吗,如果我只对gt bbox的坐标减去裁剪区域的左上角坐标可不可以呢
请问怎么读图片和存储图片和xml文件?
是说三个问题吗,(1)读取图片;(2)存储图片;(3)xml文件处理吗.
是的,请问有博客可以做参考么
今天正好在看ssd的数据增强,浏览你的博客,看到这篇文章,感觉豁然开朗.
也是跟着大神们的成果学习.