论文:MoCov1 - Momentum Contrast for Unsupervised Visual Representation Learning - 2019
论文:MoCov2 - Improved Baselines with Momentum Contrastive Learning - 2020
Github - facebookresearch/moco
MoCo,Momentum Contrast,是一种无监督视觉表示学习算法.
MoCo 基于对比学习(contrastive learning) 的角度,将问题转换为字典查询(dictionary look-up),构建了基于队列的动态字典更新(dynamic dictionary with a queue)和滑动平均编码器(moving-averaged encoder)的算法.
1. MoCo
MoCo 基于的假设:可以通过覆盖大量负样本的大型字典来学习好的特征,且字典 keys 的编码器尽管在不断的更新,但仍应尽可能保持连续性.
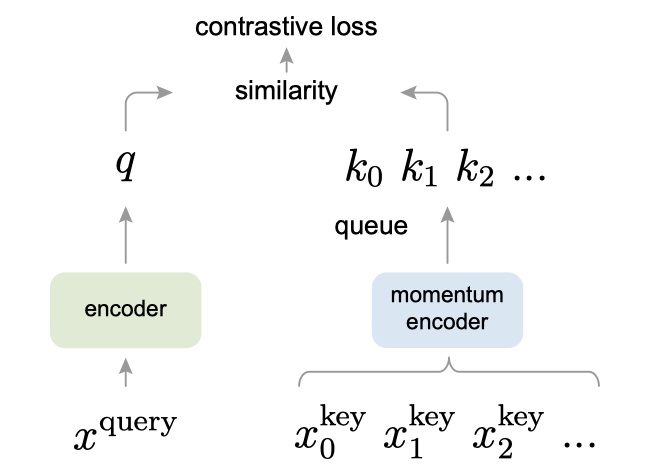
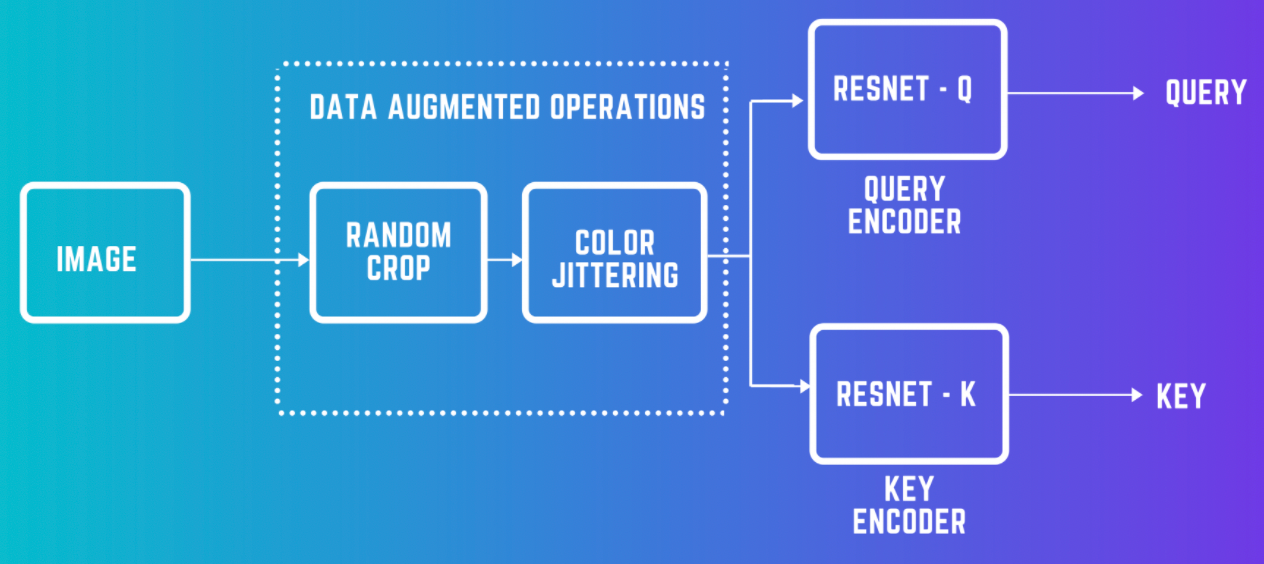
对于给定的一个样本x, 选择一个(或一批)正样本y(这里正样本对对于图像上的理解就是x的不同的data augmentation版本). 然后选择一批负样本(对于图像来说,就是除了x之外的图像), 然后设计loss function来将x与正样本之间的距离拉近,负样本之间的距离推开.
MoCo 主要有如下特点:
1.1. InfoNCE 损失函数
[1] - 将对比学习问题转化为字典查询问题
损失函数(InfoNCE)形式如:
$$ L_q = -log \frac{exp(q \cdot k_+/ \tau)}{\sum_{i=0}^K exp(q \cdot k_i / \tau)} $$
另一种形式如,
$$ L_{q, k_+, \lbrace k_- \rbrace} = -log \frac{exp(q \cdot k_+/ \tau)}{exp(q \cdot k_+/ \tau) + \sum_{k_-} exp(q \cdot k_- / \tau)} $$
其中,$q$ 是查询的特征表示;$k_+$ 是正样本(相似)的特征表示,$\lbrace k_- \rbrace$ 是负样本(不相似)的特征表示;$\tau$ 是超参数.
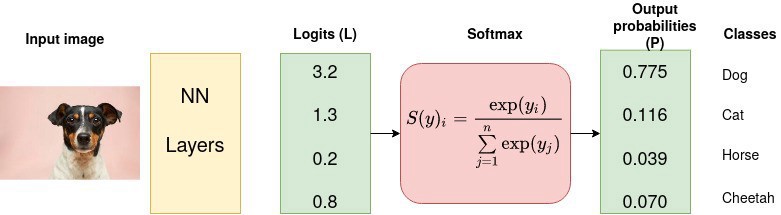
损失函数的求和,是对一个正样本和K个负样本进行的,其类似于 (K+1) Softmax 分类的 log 损失函数,其目标是将$q$ 分类为 $k_+$.
参考 SoftmaxEntropyCross 损失:
$$ L_{ce} = -log \frac{exp(x_i)}{\sum_j exp(x_j)} $$
或,
$$ L(x, class) = -log (\frac{exp(x[class])}{\sum_j exp(x[j])}) $$
1.2. 动量更新
记 $f_k$ 为 key 编码器;$f_q$ 为 q 查询编码器,$\theta_k$ 和 $\theta_q$ 分别为其参数,
MoCo 提出的 $\theta_k$ 动量更新方式如:
$$ \theta _k \leftarrow m \theta_k + (1 - m) \theta_q $$
其中,只有 $\theta_q$ 是需要 BP 梯度计算的. $m$ 为动量系数,实验证明,相对大的动量(如,m=0.999) 比相对小的动量(如,m=0.9) 的效果好很多.
1.3. 将字典作为队列
MoCo 的核心是,将字典维护为数据样本的队列. 有利于重用训练过程中的历史 mini-batches 的编码 keys.
基于队列的实现,可以将字典大小和 mini-batch size 解耦,且更大.
队列中的样本是渐进式被替代的. 当前 mini-batch 入队列;最老的 mini-batch 出队列.
字典 keys 一般都所有数据的部分采样子集.
1.4. Shuffling BN
MoCo 论文所述,在标准 ResNet 的 BN 层,会影响模型的训练. 因为模型可能在试图欺骗任务,并容易地找到loss值比较低的方案.
而,MoCo 采用的方式是 shuffling BN. 采用多个 GPU 进行训练,分别对每个 GPU 上的样本进行独立的进行BN.
即,对于 key 编码器 $f_k$,在将其分发到各 GPUs 上时,打乱当前 mini-batch 的采样次序;而查询编码器 $f_q$ 的mini-batch 的采样次序保持不变.
1.5. MoCo 实现伪代码

2. MoCoV2
MoCoV2 的提出源于 SimCLR - A Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Visual Representations,

SimCLR 是主要是有三方面的提升:
[1] - 较大的batchsize(如4k或8k),能够提供更多的负样本;
[2] - 将输出 fc 层 head 网络替换为 MLP head;
[3] - 更多的数据增强.
而 MoCoV2 发现,MoCoV1 + MLP head + more data aug 也能取得更好的结果,而且还不需要大的训练 batchsize. 如图,从 batch 角度的理解, 基于 menmory queue 的机制,不需要很大的 batchsize,MoCo 也能提供更多的负样本进行对比学习.

3. MoCo Pytorch 实现
3.1. MoCo 构建
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class MoCo(nn.Module):
"""
Build a MoCo model with: a query encoder, a key encoder, and a queue
https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.05722
"""
def __init__(self, base_encoder, dim=128, K=65536, m=0.999, T=0.07, mlp=False):
"""
dim: 特征维度feature dimension (default: 128)
K: 队列大小queue size; 负样本keys数number of negative keys (default: 65536)
m: moco momentum of updating key encoder (default: 0.999)
T: softmax temperature (default: 0.07)
"""
super(MoCo, self).__init__()
self.K = K
self.m = m
self.T = T
# 创建编码器,这里是基于 resnet50
# num_classes:fc层输出的维度
self.encoder_q = base_encoder(num_classes=dim)
self.encoder_k = base_encoder(num_classes=dim)
if mlp: # hack: brute-force replacement; MoCov2
dim_mlp = self.encoder_q.fc.weight.shape[1]
self.encoder_q.fc = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(dim_mlp, dim_mlp), nn.ReLU(), self.encoder_q.fc)
self.encoder_k.fc = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(dim_mlp, dim_mlp), nn.ReLU(), self.encoder_k.fc)
for param_q, param_k in zip(self.encoder_q.parameters(), self.encoder_k.parameters()):
param_k.data.copy_(param_q.data) #初始化编码器k的参数
param_k.requires_grad = False #编码器k不需要梯度计算
#创建队列
self.register_buffer("queue", torch.randn(dim, K))
self.queue = nn.functional.normalize(self.queue, dim=0)
self.register_buffer("queue_ptr", torch.zeros(1, dtype=torch.long))
@torch.no_grad()
def _momentum_update_key_encoder(self):
"""
动量更新编码器 key 的参数
"""
for param_q, param_k in zip(self.encoder_q.parameters(), self.encoder_k.parameters()):
param_k.data = param_k.data * self.m + param_q.data * (1. - self.m)
@torch.no_grad()
def _dequeue_and_enqueue(self, keys):
#更新队列前,收集keys
keys = concat_all_gather(keys)
batch_size = keys.shape[0]
ptr = int(self.queue_ptr)
assert self.K % batch_size == 0 # for simplicity
#在 ptr 处替换 keys,出队列和入队列
self.queue[:, ptr:ptr + batch_size] = keys.T
ptr = (ptr + batch_size) % self.K # move pointer
self.queue_ptr[0] = ptr
@torch.no_grad()
def _batch_shuffle_ddp(self, x):
"""
Batch shuffle, for making use of BatchNorm.
*** Only support DistributedDataParallel (DDP) model. ***
"""
# gather from all gpus
batch_size_this = x.shape[0]
x_gather = concat_all_gather(x)
batch_size_all = x_gather.shape[0]
num_gpus = batch_size_all // batch_size_this
# random shuffle index
idx_shuffle = torch.randperm(batch_size_all).cuda()
# broadcast to all gpus
torch.distributed.broadcast(idx_shuffle, src=0)
# index for restoring
idx_unshuffle = torch.argsort(idx_shuffle)
# shuffled index for this gpu
gpu_idx = torch.distributed.get_rank()
idx_this = idx_shuffle.view(num_gpus, -1)[gpu_idx]
return x_gather[idx_this], idx_unshuffle
@torch.no_grad()
def _batch_unshuffle_ddp(self, x, idx_unshuffle):
"""
Undo batch shuffle.
*** Only support DistributedDataParallel (DDP) model. ***
"""
# gather from all gpus
batch_size_this = x.shape[0]
x_gather = concat_all_gather(x)
batch_size_all = x_gather.shape[0]
num_gpus = batch_size_all // batch_size_this
# restored index for this gpu
gpu_idx = torch.distributed.get_rank()
idx_this = idx_unshuffle.view(num_gpus, -1)[gpu_idx]
return x_gather[idx_this]
def forward(self, im_q, im_k):
"""
Input:
im_q: a batch of query images
im_k: a batch of key images
Output:
logits, targets
"""
# compute query features,计算查询特征
q = self.encoder_q(im_q) # queries: NxC
q = nn.functional.normalize(q, dim=1)
# compute key features
with torch.no_grad(): # no gradient to keys
self._momentum_update_key_encoder() # update the key encoder
# shuffle for making use of BN
im_k, idx_unshuffle = self._batch_shuffle_ddp(im_k)
k = self.encoder_k(im_k) # keys: NxC
k = nn.functional.normalize(k, dim=1)
# undo shuffle
k = self._batch_unshuffle_ddp(k, idx_unshuffle)
# compute logits
# Einstein sum is more intuitive
# positive logits: Nx1,正样本
l_pos = torch.einsum('nc,nc->n', [q, k]).unsqueeze(-1)
# negative logits: NxK,队列里都是负样本
l_neg = torch.einsum('nc,ck->nk', [q, self.queue.clone().detach()])
# logits: Nx(1+K)
logits = torch.cat([l_pos, l_neg], dim=1) #第0列是正样本
# apply temperature
logits /= self.T
# labels: positive key indicators
labels = torch.zeros(logits.shape[0], dtype=torch.long).cuda()
# https://github.com/facebookresearch/moco/issues/24
# dequeue and enqueue
self._dequeue_and_enqueue(k)
return logits, labels
# utils
@torch.no_grad()
def concat_all_gather(tensor):
"""
Performs all_gather operation on the provided tensors.
*** Warning ***: torch.distributed.all_gather has no gradient.
"""
tensors_gather = [torch.ones_like(tensor)
for _ in range(torch.distributed.get_world_size())]
torch.distributed.all_gather(tensors_gather, tensor, async_op=False)
output = torch.cat(tensors_gather, dim=0)
return output3.2. MoCo 训练
from PIL import ImageFilter
import random
class TwoCropsTransform:
"""
Take two random crops of one image as the query and key.
"""
def __init__(self, base_transform):
self.base_transform = base_transform
def __call__(self, x):
q = self.base_transform(x)
k = self.base_transform(x)
return [q, k]
class GaussianBlur(object):
"""
Gaussian blur augmentation in SimCLR https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.05709
"""
def __init__(self, sigma=[.1, 2.]):
self.sigma = sigma
def __call__(self, x):
sigma = random.uniform(self.sigma[0], self.sigma[1])
x = x.filter(ImageFilter.GaussianBlur(radius=sigma))
return x训练主函数:
#!/usr/bin/python3
#!--*-- coding: utf-8 --*--
import argparse
import builtins
import math
import os
import random
import shutil
import time
import warnings
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.parallel
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
import torch.distributed as dist
import torch.optim
import torch.multiprocessing as mp
import torch.utils.data
import torch.utils.data.distributed
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torchvision.datasets as datasets
import torchvision.models as models
import moco.loader #数据加载与增强辅助函数
import moco.builder #MoCo模型函数
model_names = sorted(name for name in models.__dict__
if name.islower() and not name.startswith("__")
and callable(models.__dict__[name]))
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch ImageNet Training')
parser.add_argument('data', metavar='DIR',
help='path to dataset')
parser.add_argument('-a', '--arch', metavar='ARCH', default='resnet50',
choices=model_names,
help='model architecture: ' +
' | '.join(model_names) +
' (default: resnet50)')
parser.add_argument('-j', '--workers', default=32, type=int, metavar='N',
help='number of data loading workers (default: 32)')
parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=200, type=int, metavar='N',
help='number of total epochs to run')
parser.add_argument('--start-epoch', default=0, type=int, metavar='N',
help='manual epoch number (useful on restarts)')
parser.add_argument('-b', '--batch-size', default=256, type=int,
metavar='N',
help='mini-batch size (default: 256), this is the total '
'batch size of all GPUs on the current node when '
'using Data Parallel or Distributed Data Parallel')
parser.add_argument('--lr', '--learning-rate', default=0.03, type=float,
metavar='LR', help='initial learning rate', dest='lr')
parser.add_argument('--schedule', default=[120, 160], nargs='*', type=int,
help='learning rate schedule (when to drop lr by 10x)')
parser.add_argument('--momentum', default=0.9, type=float, metavar='M',
help='momentum of SGD solver')
parser.add_argument('--wd', '--weight-decay', default=1e-4, type=float,
metavar='W', help='weight decay (default: 1e-4)',
dest='weight_decay')
parser.add_argument('-p', '--print-freq', default=10, type=int,
metavar='N', help='print frequency (default: 10)')
parser.add_argument('--resume', default='', type=str, metavar='PATH',
help='path to latest checkpoint (default: none)')
parser.add_argument('--world-size', default=-1, type=int,
help='number of nodes for distributed training')
parser.add_argument('--rank', default=-1, type=int,
help='node rank for distributed training')
parser.add_argument('--dist-url', default='tcp://224.66.41.62:23456', type=str,
help='url used to set up distributed training')
parser.add_argument('--dist-backend', default='nccl', type=str,
help='distributed backend')
parser.add_argument('--seed', default=None, type=int,
help='seed for initializing training. ')
parser.add_argument('--gpu', default=None, type=int,
help='GPU id to use.')
parser.add_argument('--multiprocessing-distributed', action='store_true',
help='Use multi-processing distributed training to launch '
'N processes per node, which has N GPUs. This is the '
'fastest way to use PyTorch for either single node or '
'multi node data parallel training')
# moco specific configs:
parser.add_argument('--moco-dim', default=128, type=int,
help='feature dimension (default: 128)')
parser.add_argument('--moco-k', default=65536, type=int,
help='queue size; number of negative keys (default: 65536)')
parser.add_argument('--moco-m', default=0.999, type=float,
help='moco momentum of updating key encoder (default: 0.999)')
parser.add_argument('--moco-t', default=0.07, type=float,
help='softmax temperature (default: 0.07)')
# options for moco v2
parser.add_argument('--mlp', action='store_true',
help='use mlp head')
parser.add_argument('--aug-plus', action='store_true',
help='use moco v2 data augmentation')
parser.add_argument('--cos', action='store_true',
help='use cosine lr schedule')
def main():
args = parser.parse_args()
if args.seed is not None:
random.seed(args.seed)
torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
cudnn.deterministic = True
warnings.warn('You have chosen to seed training. '
'This will turn on the CUDNN deterministic setting, '
'which can slow down your training considerably! '
'You may see unexpected behavior when restarting '
'from checkpoints.')
if args.gpu is not None:
warnings.warn('You have chosen a specific GPU. This will completely '
'disable data parallelism.')
if args.dist_url == "env://" and args.world_size == -1:
args.world_size = int(os.environ["WORLD_SIZE"])
args.distributed = args.world_size > 1 or args.multiprocessing_distributed
ngpus_per_node = torch.cuda.device_count()
if args.multiprocessing_distributed:
# Since we have ngpus_per_node processes per node, the total world_size
# needs to be adjusted accordingly
args.world_size = ngpus_per_node * args.world_size
# Use torch.multiprocessing.spawn to launch distributed processes: the
# main_worker process function
mp.spawn(main_worker, nprocs=ngpus_per_node, args=(ngpus_per_node, args))
else:
# Simply call main_worker function
main_worker(args.gpu, ngpus_per_node, args)
def main_worker(gpu, ngpus_per_node, args):
args.gpu = gpu
# suppress printing if not master
if args.multiprocessing_distributed and args.gpu != 0:
def print_pass(*args):
pass
builtins.print = print_pass
if args.gpu is not None:
print("Use GPU: {} for training".format(args.gpu))
if args.distributed:
if args.dist_url == "env://" and args.rank == -1:
args.rank = int(os.environ["RANK"])
if args.multiprocessing_distributed:
# For multiprocessing distributed training, rank needs to be the
# global rank among all the processes
args.rank = args.rank * ngpus_per_node + gpu
dist.init_process_group(backend=args.dist_backend, init_method=args.dist_url,
world_size=args.world_size, rank=args.rank)
#创建 MoCo 模型
print("=> creating model '{}'".format(args.arch))
model = moco.builder.MoCo(
models.__dict__[args.arch],
args.moco_dim, args.moco_k, args.moco_m, args.moco_t, args.mlp)
print(model)
if args.distributed:
# For multiprocessing distributed, DistributedDataParallel constructor
# should always set the single device scope, otherwise,
# DistributedDataParallel will use all available devices.
if args.gpu is not None:
torch.cuda.set_device(args.gpu)
model.cuda(args.gpu)
# When using a single GPU per process and per
# DistributedDataParallel, we need to divide the batch size
# ourselves based on the total number of GPUs we have
args.batch_size = int(args.batch_size / ngpus_per_node)
args.workers = int((args.workers + ngpus_per_node - 1) / ngpus_per_node)
model = torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel(model, device_ids=[args.gpu])
else:
model.cuda()
# DistributedDataParallel will divide and allocate batch_size to all
# available GPUs if device_ids are not set
model = torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel(model)
elif args.gpu is not None:
torch.cuda.set_device(args.gpu)
model = model.cuda(args.gpu)
# comment out the following line for debugging
raise NotImplementedError("Only DistributedDataParallel is supported.")
else:
# AllGather implementation (batch shuffle, queue update, etc.) in
# this code only supports DistributedDataParallel.
raise NotImplementedError("Only DistributedDataParallel is supported.")
#定义损失函数(criterion)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda(args.gpu)#交叉熵损失函数
#定义优化器
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), args.lr,
momentum=args.momentum,
weight_decay=args.weight_decay)
# optionally resume from a checkpoint
if args.resume:
if os.path.isfile(args.resume):
print("=> loading checkpoint '{}'".format(args.resume))
if args.gpu is None:
checkpoint = torch.load(args.resume)
else:
# Map model to be loaded to specified single gpu.
loc = 'cuda:{}'.format(args.gpu)
checkpoint = torch.load(args.resume, map_location=loc)
args.start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch']
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
optimizer.load_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer'])
print("=> loaded checkpoint '{}' (epoch {})"
.format(args.resume, checkpoint['epoch']))
else:
print("=> no checkpoint found at '{}'".format(args.resume))
cudnn.benchmark = True
#数据加载
traindir = os.path.join(args.data, 'train')
normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
if args.aug_plus:
# MoCo v2's aug: similar to SimCLR https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.05709
augmentation = [
transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224, scale=(0.2, 1.)),
transforms.RandomApply([
transforms.ColorJitter(0.4, 0.4, 0.4, 0.1) # not strengthened
], p=0.8),
transforms.RandomGrayscale(p=0.2),
transforms.RandomApply([moco.loader.GaussianBlur([.1, 2.])], p=0.5),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
normalize
]
else:
# MoCo v1's aug: the same as InstDisc https://arxiv.org/abs/1805.01978
augmentation = [
transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224, scale=(0.2, 1.)),
transforms.RandomGrayscale(p=0.2),
transforms.ColorJitter(0.4, 0.4, 0.4, 0.4),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
normalize
]
#数据集加载,用的是 TwoCropsTransform
train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(
traindir,
moco.loader.TwoCropsTransform(transforms.Compose(augmentation)))
if args.distributed:
train_sampler = torch.utils.data.distributed.DistributedSampler(train_dataset)
else:
train_sampler = None
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
train_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=(train_sampler is None),
num_workers=args.workers, pin_memory=True, sampler=train_sampler, drop_last=True)
for epoch in range(args.start_epoch, args.epochs):
if args.distributed:
#用于 shuffling. 否则,每次处理都是相同的随机种子
train_sampler.set_epoch(epoch)
#学习率调整
adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch, args)
# train for one epoch
train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch, args)
if not args.multiprocessing_distributed or (args.multiprocessing_distributed
and args.rank % ngpus_per_node == 0):
save_checkpoint({
'epoch': epoch + 1,
'arch': args.arch,
'state_dict': model.state_dict(),
'optimizer' : optimizer.state_dict(),
}, is_best=False, filename='checkpoint_{:04d}.pth.tar'.format(epoch))
def train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch, args):
batch_time = AverageMeter('Time', ':6.3f')
data_time = AverageMeter('Data', ':6.3f')
losses = AverageMeter('Loss', ':.4e')
top1 = AverageMeter('Acc@1', ':6.2f')
top5 = AverageMeter('Acc@5', ':6.2f')
progress = ProgressMeter(
len(train_loader),
[batch_time, data_time, losses, top1, top5],
prefix="Epoch: [{}]".format(epoch))
# switch to train mode
model.train()
end = time.time()
for i, (images, _) in enumerate(train_loader):
# measure data loading time
data_time.update(time.time() - end)
if args.gpu is not None:
images[0] = images[0].cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
images[1] = images[1].cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
# compute output,对比学习,输入是两张图片
output, target = model(im_q=images[0], im_k=images[1])
loss = criterion(output, target)
# acc1/acc5 are (K+1)-way contrast classifier accuracy
# measure accuracy and record loss
acc1, acc5 = accuracy(output, target, topk=(1, 5))
losses.update(loss.item(), images[0].size(0))
top1.update(acc1[0], images[0].size(0))
top5.update(acc5[0], images[0].size(0))
# compute gradient and do SGD step
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# measure elapsed time
batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
end = time.time()
if i % args.print_freq == 0:
progress.display(i)
def save_checkpoint(state, is_best, filename='checkpoint.pth.tar'):
torch.save(state, filename)
if is_best:
shutil.copyfile(filename, 'model_best.pth.tar')
class AverageMeter(object):
"""Computes and stores the average and current value"""
def __init__(self, name, fmt=':f'):
self.name = name
self.fmt = fmt
self.reset()
def reset(self):
self.val = 0
self.avg = 0
self.sum = 0
self.count = 0
def update(self, val, n=1):
self.val = val
self.sum += val * n
self.count += n
self.avg = self.sum / self.count
def __str__(self):
fmtstr = '{name} {val' + self.fmt + '} ({avg' + self.fmt + '})'
return fmtstr.format(**self.__dict__)
class ProgressMeter(object):
def __init__(self, num_batches, meters, prefix=""):
self.batch_fmtstr = self._get_batch_fmtstr(num_batches)
self.meters = meters
self.prefix = prefix
def display(self, batch):
entries = [self.prefix + self.batch_fmtstr.format(batch)]
entries += [str(meter) for meter in self.meters]
print('\t'.join(entries))
def _get_batch_fmtstr(self, num_batches):
num_digits = len(str(num_batches // 1))
fmt = '{:' + str(num_digits) + 'd}'
return '[' + fmt + '/' + fmt.format(num_batches) + ']'
#学习率调整策略
def adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch, args):
"""
Decay the learning rate based on schedule
"""
lr = args.lr
if args.cos: # cosine lr schedule
# cos lr
lr *= 0.5 * (1. + math.cos(math.pi * epoch / args.epochs))
else: # stepwise lr schedule
for milestone in args.schedule:
lr *= 0.1 if epoch >= milestone else 1.
for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
param_group['lr'] = lr
def accuracy(output, target, topk=(1,)):
"""
Computes the accuracy over the k top predictions for the specified values of k
"""
with torch.no_grad():
maxk = max(topk)
batch_size = target.size(0)
_, pred = output.topk(maxk, 1, True, True)
pred = pred.t()
correct = pred.eq(target.view(1, -1).expand_as(pred))
res = []
for k in topk:
correct_k = correct[:k].view(-1).float().sum(0, keepdim=True)
res.append(correct_k.mul_(100.0 / batch_size))
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()