GPU 优化简介 原文 - An Introduction to GPU Optimization
采用 GPUs 加速简单的计算任务.
计算机处理的很多任务都会遇到大量的计算,耗时较多的问题;而且,随着数据集越来越大,耗时将更多. 解决方法之一是,使用线程(threads).
这里简单介绍 GPU 加速的工作模式,并通过 GPU 任务的一个简单 API 代码来说明其加速效果.
首先,看一个矩阵相乘的例子.
<h2>矩阵乘法 Matrix Multiplication</h2>
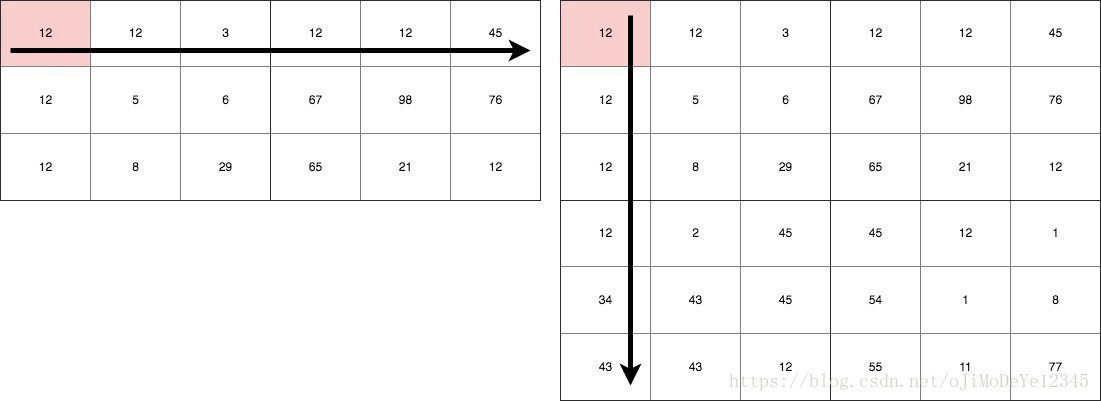
Figure 1. 矩阵乘法
假设有两个矩阵,其大小分别为:3 × 6 和 6 × 6. 两矩阵相乘得到的结果矩阵大小为 3 × 6. 结果矩阵的每个单元 cell 都有 6 次计算,因此,共有 3 × 6 × 6 次乘法计算.
即:计算的时间复杂度为 ${ O(mn^2) }$.
意味着,对于一个大小为 2000 × 2000 的矩阵而言,将进行的计算会达到 8, 000, 000, 000 次,会耗费 CPU 大量的时间!
<h2>GPUs 简介</h2>
GPUs 通常包含大量的处理核心(processing cores). 数量一般从 384 到上千个. 如图,NVIDIA 的部分显卡 GPUs.
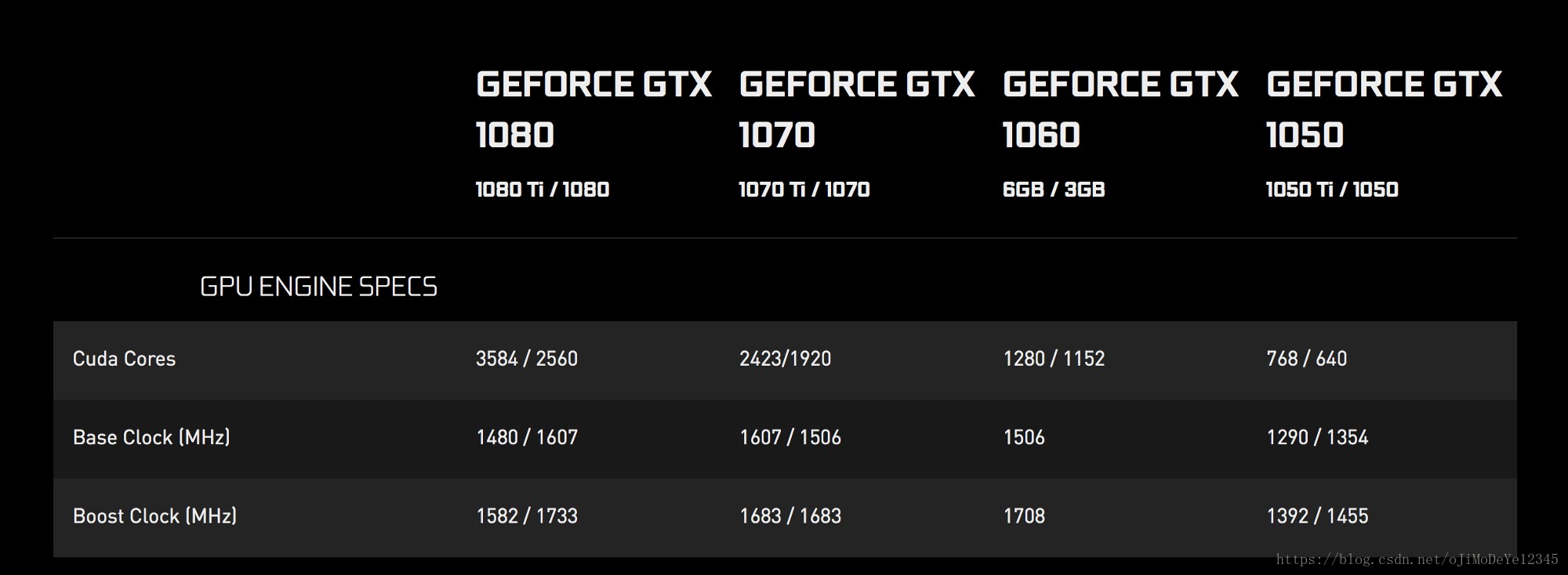
Figure 2. NVIDIA GPUs CUDA 核心数
CUDA,Compute Unified Device Architecture. 其运行速度运行相对较慢,但通过利用大量的ALUs(Arithmetic and Logical Units),具有强大的并行化能力. 可参见 WHAT IS GPU-ACCELERATED COMPUTING?
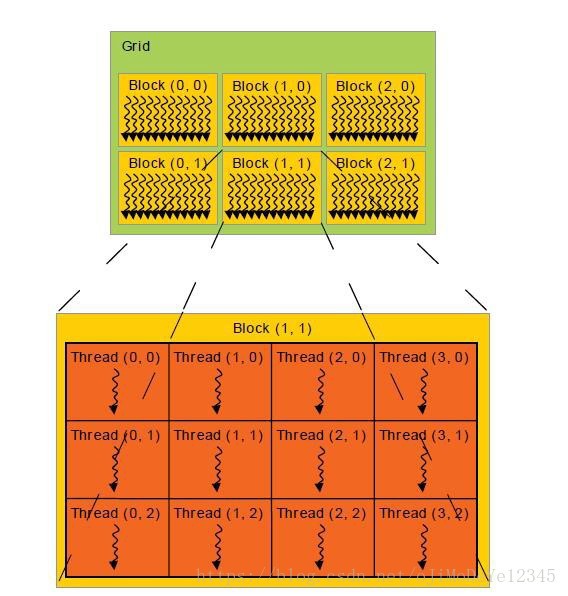
Figure 3. CUDA Thread Model
上图给出了 CUDA 的线程模型(AMD 也是差不多相同的结构).
为了便于说明,假设每个 CUDA 核心或一个 GPU 核心一次运行一个线程 thread. 如果数据集很大时,可以对数据集进行分片 pieces. 一个 方格Grid 包含多个 块 Blocks,Block 是一个矩阵,由与其大小相同数量的 线程 Threads 组成.
这里采用一个简单的 JAVA API 来说明 FIgure 3.
<h2>关于 GPU 的思考</h2>
正如前面所说,每个 GPU 核心能够运行分离的线程.
这里可以假设,矩阵的每个单元 cell 可以通过一个单独的 GPU 核心来计算. 而且,由于所有的核心是并行化运行的,那么所有的矩阵单元也可以并行化计算. 因此,计算的时间复杂度降到了 O(n).
一个 2000 × 2000 的矩阵乘法,只需要 2000 次运行,对于计算机而言是很轻松的.
每一个线程thread,都有唯一的身份,即,线程在 Block 和 Grid 的位置. 也就是矩阵的单元所在位置.
另外,矩阵是加载在 GPU 的共享内存里的,可以根据其索引直接读取矩阵的单元数据,以并行化计算.
很简单吧,下面通过代码来说明.
<h2>基于 APARAPI 的 GPU 编程</h2>
APARAPI (A-PARallel-API) 是 OpenCL 的 JAVA 接口,是用于 GPUs 编程的开放式计算语言,其支持 CUDA 结构和 AMD 设备.
- pom.xml
</li> <li>MatrixMultiplication.java<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>cuda-aparapi</groupId> <artifactId>cuda</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>com.aparapi</groupId> <artifactId>aparapi</artifactId> <version>1.4.1</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
</li> </ul> 核Kernel是 GPU 执行代码的一部分, Kernel 可见的变量被复制到 GPU RAM. 以上代码中,GPUs 组织数据的形式是线性数组(linear array),而非 2D 数组的形式. 虽然,GPUs 不能处理 2D 数组,但其数据处理方式类似于数组维度.import com.aparapi.Kernel; import com.aparapi.Range; /** * Created by anuradhawick on 12/29/17. */ public class MatrixMultiplication { public static void main(String[] args) { // Width of the matrix final int SIZE = 5000; // We should use linear arrays as supported by the API final int[] a = new int[SIZE * SIZE]; final int[] b = new int[SIZE * SIZE]; int[] c = new int[SIZE * SIZE]; final int[] d = new int[SIZE * SIZE]; int val; // Creating random matrices for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { a[i SIZE + j] = (int) (Math.random() 100); b[i SIZE + j] = (int) (Math.random() 100); } } long time = System.currentTimeMillis(); // CPU multiplication System.out.println("Starting single threaded computation"); for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { val = 0; for (int k = 0; k < SIZE; k++) { val += a[i SIZE + k] b[k * SIZE + j]; } c[i * SIZE + j] = val; } } System.out.println("Task finished in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - time) + "ms"); // Kernel for multiplication Kernel kernel = new Kernel() { @Override public void run() { int row = getGlobalId() / SIZE; int col = getGlobalId() % SIZE; if (row > SIZE || col > SIZE) return; d[row * SIZE + col] = 0; for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { d[row SIZE + col] += a[row SIZE + i] b[i SIZE + col]; } } }; // Array size for GPU to know Range range = Range.create(SIZE * SIZE); System.out.println("Starting GPU computation"); time = System.currentTimeMillis(); kernel.execute(range); // Running the Kernel System.out.println("Task finished in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - time) + "ms"); // Verifying the result for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < SIZE; j++) { if (c[i SIZE + j] != d[i SIZE + j]) { System.out.println("ERROR"); return; } } } } }Range range = Range.create(SIZE * SIZE);分配 GPU 内存,GPU 最多会运行 SIZE × SIZE 个线程.
int row = getGlobalId() / SIZE; int col = getGlobalId() % SIZE;从线程的专有内存(private memory) 获取线程 Id. 根据 Id 即可确定线程的单元格位置.
对于每个单元格,计算
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) { d[row SIZE + col] += a[row SIZE + i] b[i SIZE + col]; }仅仅是对两个矩阵对应单元格的计算结果进行相加.
只需采用线程索引定义单个线程的 Kernel. 所有线程并行化运行.
GPU 计算的速度会有多快呢,以上代码的输出为:
// 1200 x 1200 Starting single threaded computation Task finished in 25269ms Starting GPU computation Task finished in 1535ms相差很大!
由于 CPU 耗时较久,以下仅为 GPU 计算耗时:
// 2000 x 2000 Task finished in 3757ms // 5000 x 5000 Task finished in 5402ms<h2>Related</h2>