原文:Unsupervised Learning with Python - 2018.05.12
作者:Vihar Kurama
无监督学习是机器学习技术的一类,其用于发现数据中的模式(patterns). 无监督算法的输入数据是无标签、未手工标注的,也就是说,对于无监督算法,其只需提供输入变量(X),而无需提供对应的输入变量(标签数据). 无监督学习算法自己去挖掘数据中有意义的结构信息.
Yan Lecun, director of AI research, explains that unsupervised learning —teaching machines to learn for themselves without having to be explicitly told if everything they do is right or wrong — is the key to “true” AI.
1. 监督学习与无监督学习
监督学习中,系统尝试从之前给出的例子中进行学习. 而,无监督学习中,系统尝试直接从给出的例子进行学习.
因此,如果数据集没有标签数据,那么其是一个无监督问题.
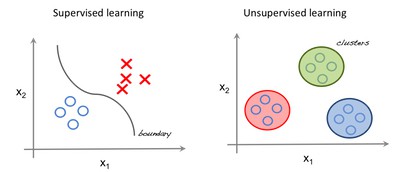
From [http://beta.cambridgespark.com/courses/jpm/01-module.html]
如上如,左图是监督学习,可以使用回归技术寻找特征之间的最佳拟合;右图是无监督学习,输入是特征分离的,预测是基于其归属的聚类进行的.
重要术语:
- 特征(Feature):用于进行预测的输入变量.
- 预测(Predictions):对于输入样本,模型预测的输出.
- 样本(Example):数据集的一行. 一个样本包含一个或多个特征,可能包含标签.
- 标签(Label):特征的结果.
2. 无监督学习的数据准备
这里采用 Iris (鸢尾花卉)数据集 为例. 该数据集包含 150 个记录样本集,有 5 个属性 - 花瓣长度(Petal Length),花瓣宽度(Petal Width),萼片长度(Sepal Length),萼片宽度(Sepal Width)和类别(Class). 类别包含三个:山鸢尾(Iris Setosa),维吉尼亚鸢尾(Iris Virginica) 和变色鸢尾(Iris Versicolor).
对于无监督学习算法,给出的鸢尾花的这四个特征, 并进行预测其类别.
这里采用 Python scikit-learn 库和 matplotlib 可视化库.
from sklearn import datasets
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Loading dataset
iris_df = datasets.load_iris()
# Available methods on dataset
print(dir(iris_df))
# Features
print(iris_df.feature_names)
# Targets
print(iris_df.target)
# Target Names
print(iris_df.target_names)
label = {0: 'red', 1: 'blue', 2: 'green'}
# Dataset Slicing
x_axis = iris_df.data[:, 0] # Sepal Length
y_axis = iris_df.data[:, 2] # Sepal Width
# Plotting
plt.scatter(x_axis, y_axis, c=iris_df.target)
plt.show()输入如:
['DESCR', 'data', 'feature_names', 'target', 'target_names']
['sepal length (cm)', 'sepal width (cm)', 'petal length (cm)', 'petal width (cm)']
[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2]
['setosa' 'versicolor' 'virginica']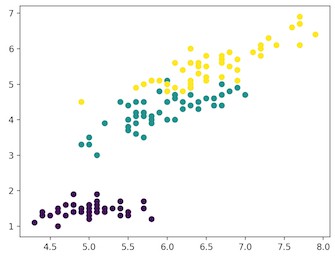
图1. 紫色:山鸢尾;绿色:维吉尼亚鸢尾;黄色:变色鸢尾
3. 聚类(Clustering)
聚类问题中,数据被分成几个组. 简单地说,其目的是将具有相似特征的组分开,并将特征组成聚类.
如图:
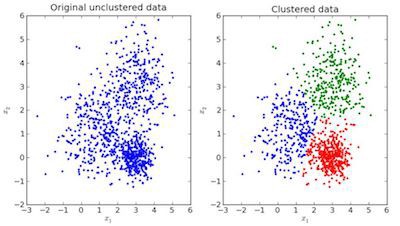
图 2. 聚类示例.
如上图中,左图为原始数据;右图为聚类结果(根据数据的特征聚类). 当给定输入样本时,根据其特征,检测其特征所归属的聚类,进行预测.
3.1. KMeans 聚类
K-Means 是一种迭代聚类算法(iterative clustering algorithm),其旨在,在每次迭代中寻找局部最大值.
首先,需要给出初始化聚类数. 这里,由于已知数据集包含 3 个类别,因此,设置初始化聚类数量为 3,即 n_clusters=3.
然后,随机选择三个点(输入) 作为三个聚类(聚类中心). 基于各数据点之间的质心距离(centroid distance),判定下一个给定输入被分到的聚类;
接着,重新计算所有聚类的质心.
每个聚类的质心是特征值的集合,其定义了聚类生成的分组. 根据质心特征权重,可以定性地解释每个聚类所代表的分组类型.
基于 skearn 库的 KMeans 模型,拟合特征并进行预测.
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
# Loading dataset
iris_df = datasets.load_iris()
# Declaring Model
model = KMeans(n_clusters=3)
# Fitting Model
model.fit(iris_df.data)
# Predicitng a single input
predicted_label = model.predict([[7.2, 3.5, 0.8, 1.6]])
# Prediction on the entire data
all_predictions = model.predict(iris_df.data)
# Printing Predictions
print(predicted_label)
print(all_predictions)输出如下:
[0]
[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
2 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1
2 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 1 2]3.2. 分层聚类(Hierarchical Clustering)
分层聚类,顾名思义,是一种构建聚类层次的算法. 该算法首先从分配给自己一个聚类的所有数据开始. 然后,将最相近的两个聚类合并为同一个聚类. 最后,只剩下一个聚类时,结束算法.
分层聚类可以采用树状图(dendrogram) 进行表示.
from scipy.cluster.hierarchy import linkage, dendrogram
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
# Reading the DataFrame
seeds_df = pd.read_csv(
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/vihar/unsupervised-learning-with-python/master/seeds-less-rows.csv")
# Remove the grain species from the DataFrame, save for later
varieties = list(seeds_df.pop('grain_variety'))
# Extract the measurements as a NumPy array
samples = seeds_df.values
"""
Perform hierarchical clustering on samples using the
linkage() function with the method='complete' keyword argument.
Assign the result to mergings.
"""
mergings = linkage(samples, method='complete')
"""
Plot a dendrogram using the dendrogram() function on mergings,
specifying the keyword arguments labels=varieties, leaf_rotation=90,
and leaf_font_size=6.
"""
dendrogram(mergings,
labels=varieties,
leaf_rotation=90,
leaf_font_size=6,
)
plt.show()如图:
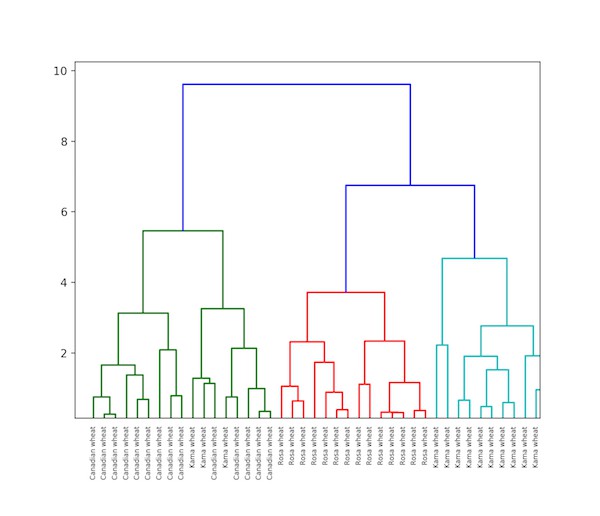
3.3. KMeans 聚类与分层聚类的区别
[1] - 分层聚类不能很好地处理大数据,但 KMeans聚类可以.
因为 KMeans 的时间复杂度是线性的,即O(n),而分层聚类的时间复杂度是二次的,即O(n2).
[2] - KMeans 聚类,采用随机初始化聚类中心,多次运行算法产生的结果可能会有所不同. 但分层聚类可以重现聚类结果.
[3] - 当聚类的形状是超球形时(如2D中的圆形,3D中的球形),KMeans 聚类更好.
[4] - KMeans 聚类不允许嘈杂的数据,而分层聚类可以直接使用嘈杂的数据集进行聚类.
3.4. t-SNE 聚类
t-SNE 聚类是用于可视化的无监督学习方法之一.
t-SNE 表示 t分布的随机近邻嵌入(t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding).
t-SNE 将高维空间映射到可以可视化的2或3维空间.
具体而言,t-SNE 算法通过二维点或三维点对每个高维对象进行建模,使得相似样本由附近的点建模,而不相似样本很大概率由远离的点建模.
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Loading dataset
iris_df = datasets.load_iris()
# Defining Model
model = TSNE(learning_rate=100)
# Fitting Model
transformed = model.fit_transform(iris_df.data)
# Plotting 2d t-Sne
x_axis = transformed[:, 0]
y_axis = transformed[:, 1]
plt.scatter(x_axis, y_axis, c=iris_df.target)
plt.show()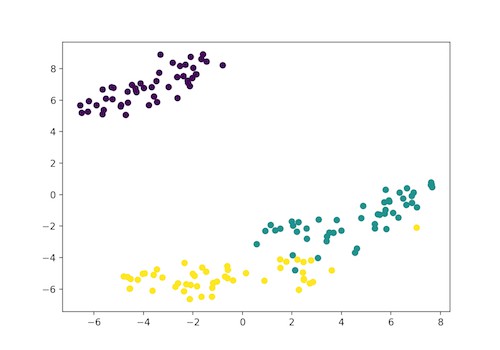
图. 紫色: Setosa; 绿色: Versicolor;黄色: Virginica
Iris 数据集包含 4 个特征,即 4d 的,通过 t-SNE 被变换为二维图像表示. 类似地,t-SNE 也可以用到 n 维特征的数据集.
3.5. DBSCAN 聚类
DBSCAN(Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise),即,具有噪声的基于密度的聚类方法,其是一种流行的聚类算法,用于预测分析中代替 KMeans. 它不要求初始化聚类数目,即可运行. 但必须调整其它两个参数.
scikit-learn 库实现提供了 eps 和 min_samples 参数的默认值,但这些参数往往需要调整. eps 参数是在同一邻域中考虑的两个数据点之间的最大距离. min_samples 参数是被认为是聚类的邻域中的数据点的最小量.
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.cluster import DBSCAN
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
# Load Dataset
iris = load_iris()
# Declaring Model
dbscan = DBSCAN()
# Fitting
dbscan.fit(iris.data)
# Transoring Using PCA
pca = PCA(n_components=2).fit(iris.data)
pca_2d = pca.transform(iris.data)
# Plot based on Class
for i in range(0, pca_2d.shape[0]):
if dbscan.labels_[i] == 0:
c1 = plt.scatter(pca_2d[i, 0], pca_2d[i, 1], c='r', marker='+')
elif dbscan.labels_[i] == 1:
c2 = plt.scatter(pca_2d[i, 0], pca_2d[i, 1], c='g', marker='o')
elif dbscan.labels_[i] == -1:
c3 = plt.scatter(pca_2d[i, 0], pca_2d[i, 1], c='b', marker='*')
plt.legend([c1, c2, c3], ['Cluster 1', 'Cluster 2', 'Noise'])
plt.title('DBSCAN finds 2 clusters and Noise')
plt.show()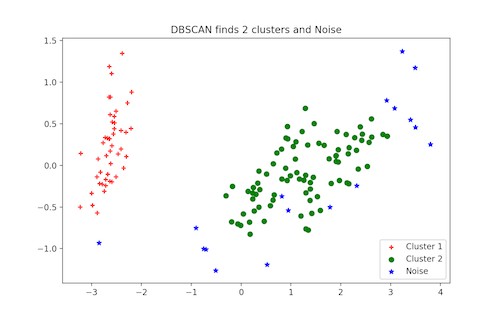
4. 更多无监督技术
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
- Anomaly detection
- Autoencoders
- Deep Belief Nets
- Hebbian Learning
- Generative Adversarial Networks(GANs)
- Self-Organizing maps
5. 相关链接
[1] - Supervised Learning In Python
[2] - Introduction To Machine Learning