手部关键点检测,旨在找出给定图片中手指上的关节点及指尖关节点. 其类似于面部关键点检测(Facial Landmark Detection) 和人体关键点检测(Human Body Pose Estimation);不同之处是,整个手部是作为一个目标物体的.

手部关键点检测的应用场景包括:
[1] - 手势识别
[2] - 手语识别与理解
[3] - 手部的行为识别等.
1. Background
主要是基于 CMU Perceptual Computing Lab 开源的手部关键点检测模型.
Github - OpenPose
手部关键点检测器的实现主要是基于论文:Hand Keypoint Detection in Single Images using Multiview Bootstrapping - CVPR2017.
其中,如下:
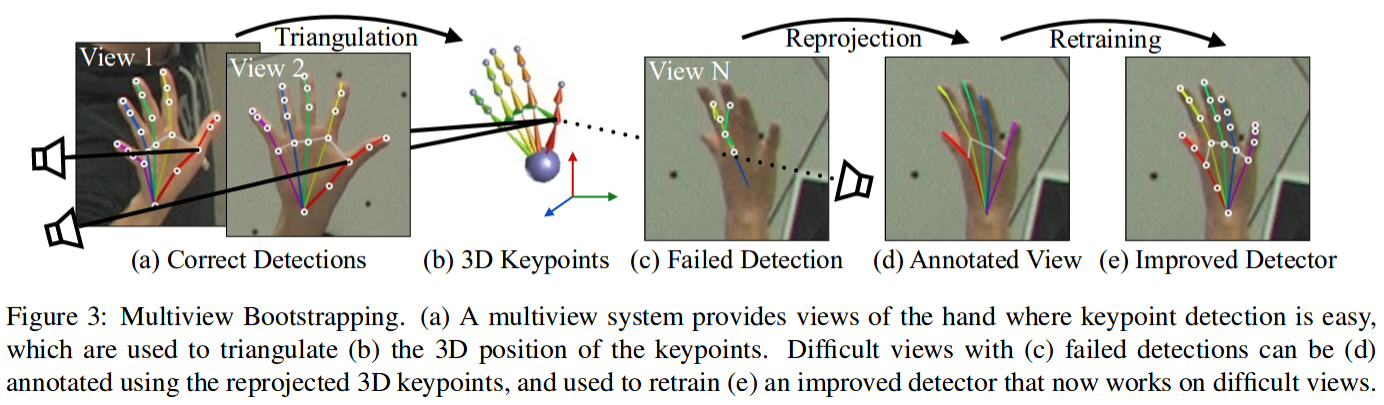
论文中,首先采用少量标注的人手部关键点图像数据集,训练类似于人体姿态关键点所使用的 CPM - Convolutional Pose Machines 网络,以得到手部关键点的粗略估计. 采用了 31个 HD 高清摄像头 从不同的视角对人手部进行拍摄.
然后,将拍摄图像送入手部关键点检测器,以初步得到许多粗略的关键点检测结果. 一旦有了同一手部的不同视角的关键点,则构建关键点测量(Keypoint triangulation),以得到关键点的 3D 位置. 关键点的 3D 位置被从 3D 重新投影到每一幅不同视角的 2D 图片,并采用 2D 图像和关键点,进一步训练网络.,以鲁棒的预测手部关键点位置. 这对于关键点难以预测的图片而言是尤其重要的. 采用这种方式,通过少量几次迭代,即可得到较为准确的手部关键点检测器.
总而言之,关键点检测器和多视角图像(multi-view images) 一起构建了较为准确的手部关键点检测模型. 采用的检测网络类似于人体关键点中所用的网络结构. 进度提升的主要因素是采用了多视角图片标注图片数据集.
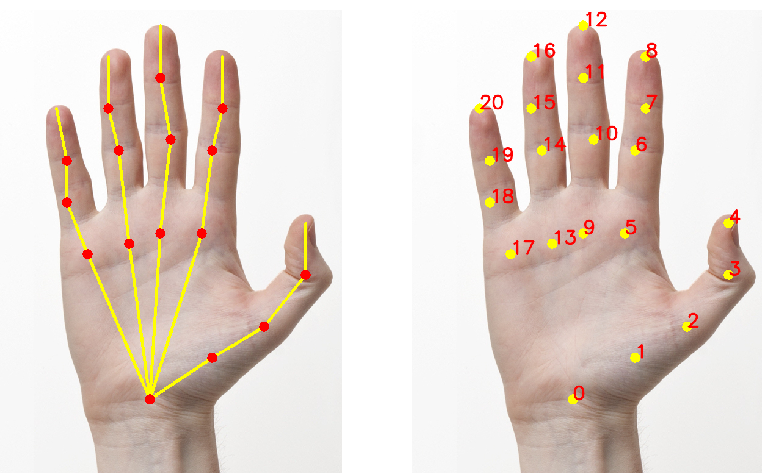
手部关键点检测模型共输出 22 个关键点,其中包括手部的 21 个点,第 22 个点表示背景. 如图:
Github 项目 - OpenPose 关键点输出格式 - AIUAI


2. 具体实现
2.1. 手部关键点检测模型下载
[1] - hand/pose_deploy.prototxt
[2] - hand/pose_iter_102000.caffemodel
2.2. Python 实现
#!/usr/bin/python3
#!--*-- coding: utf-8 --*--
from __future__ import division
import os
import cv2
import time
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class general_pose_model(object):
def __init__(self, modelpath):
self.num_points = 22
self.point_pairs = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],
[0,5],[5,6],[6,7],[7,8],
[0,9],[9,10],[10,11],[11,12],
[0,13],[13,14],[14,15],[15,16],
[0,17],[17,18],[18,19],[19,20]]
# self.inWidth = 368
self.inHeight = 368
self.threshold = 0.1
self.hand_net = self.get_hand_model(modelpath)
def get_hand_model(self, modelpath):
prototxt = os.path.join(modelpath, "hand/pose_deploy.prototxt")
caffemodel = os.path.join(modelpath, "hand/pose_iter_102000.caffemodel")
hand_model = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(prototxt, caffemodel)
return hand_model
def predict(self, imgfile):
img_cv2 = cv2.imread(imgfile)
img_height, img_width, _ = img_cv2.shape
aspect_ratio = img_width / img_height
inWidth = int(((aspect_ratio * self.inHeight) * 8) // 8)
inpBlob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(img_cv2, 1.0 / 255, (inWidth, self.inHeight), (0, 0, 0), swapRB=False, crop=False)
self.hand_net.setInput(inpBlob)
output = self.hand_net.forward()
# vis heatmaps
self.vis_heatmaps(imgfile, output)
#
points = []
for idx in range(self.num_points):
probMap = output[0, idx, :, :] # confidence map.
probMap = cv2.resize(probMap, (img_width, img_height))
# Find global maxima of the probMap.
minVal, prob, minLoc, point = cv2.minMaxLoc(probMap)
if prob > self.threshold:
points.append((int(point[0]), int(point[1])))
else:
points.append(None)
return points
def vis_heatmaps(self, imgfile, net_outputs):
img_cv2 = cv2.imread(imgfile)
plt.figure(figsize=[10, 10])
for pdx in range(self.num_points):
probMap = net_outputs[0, pdx, :, :]
probMap = cv2.resize(probMap, (img_cv2.shape[1], img_cv2.shape[0]))
plt.subplot(5, 5, pdx+1)
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_cv2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.imshow(probMap, alpha=0.6)
plt.colorbar()
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
def vis_pose(self, imgfile, points):
img_cv2 = cv2.imread(imgfile)
img_cv2_copy = np.copy(img_cv2)
for idx in range(len(points)):
if points[idx]:
cv2.circle(img_cv2_copy, points[idx], 8, (0, 255, 255), thickness=-1,
lineType=cv2.FILLED)
cv2.putText(img_cv2_copy, "{}".format(idx), points[idx], cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
1, (0, 0, 255), 2, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
# Draw Skeleton
for pair in self.point_pairs:
partA = pair[0]
partB = pair[1]
if points[partA] and points[partB]:
cv2.line(img_cv2, points[partA], points[partB], (0, 255, 255), 3)
cv2.circle(img_cv2, points[partA], 8, (0, 0, 255), thickness=-1, lineType=cv2.FILLED)
plt.figure(figsize=[10, 10])
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_cv2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.axis("off")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_cv2_copy, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
print("[INFO]Pose estimation.")
imgs_path = "/path/to/hand"
img_files = [os.path.join(imgs_path, img_file) for img_file in os.listdir(imgs_path)]
#
start = time.time()
modelpath = "/path/to/hand_models"
pose_model = general_pose_model(modelpath)
print("[INFO]Model loads time: ", time.time() - start)
for img_file in img_files:
start = time.time()
res_points = pose_model.predict(img_file)
print("[INFO]Model predicts time: ", time.time() - start)
pose_model.vis_pose(img_file, res_points)
print("[INFO]Done.")示例如图:
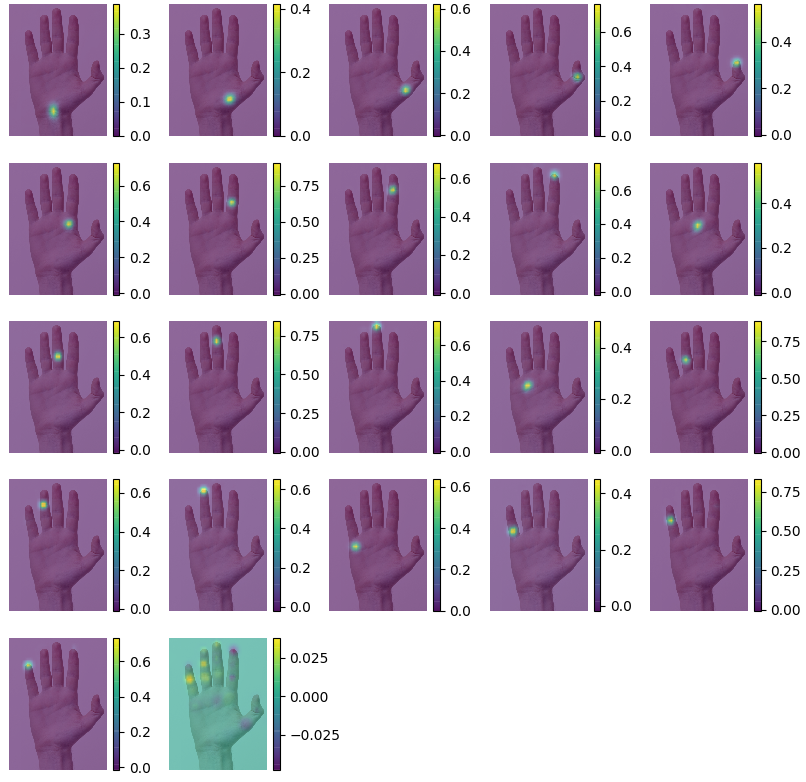
各手部关键点的 heatmap:

2.3. C++ 实现
#include <opencv2/dnn.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::dnn;
const int POSE_PAIRS[20][2] =
{
{0,1}, {1,2}, {2,3}, {3,4}, // thumb
{0,5}, {5,6}, {6,7}, {7,8}, // index
{0,9}, {9,10}, {10,11}, {11,12}, // middle
{0,13}, {13,14}, {14,15}, {15,16}, // ring
{0,17}, {17,18}, {18,19}, {19,20} // small
};
string protoFile = "hand/pose_deploy.prototxt";
string weightsFile = "hand/pose_iter_102000.caffemodel";
int nPoints = 22;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
cout << "USAGE : ./handPoseImage <imageFile> " << endl;
string imageFile = "right-frontal.jpg";
// Take arguments from commmand line
if (argc == 2)
{
imageFile = argv[1];
}
float thresh = 0.01;
Mat frame = imread(imageFile);
Mat frameCopy = frame.clone();
int frameWidth = frame.cols;
int frameHeight = frame.rows;
float aspect_ratio = frameWidth/(float)frameHeight;
int inHeight = 368;
int inWidth = (int(aspect_ratio*inHeight) * 8) / 8;
cout << "inWidth = " << inWidth << " ; inHeight = " << inHeight << endl;
double t = (double) cv::getTickCount();
Net net = readNetFromCaffe(protoFile, weightsFile);
Mat inpBlob = blobFromImage(frame, 1.0 / 255, Size(inWidth, inHeight), Scalar(0, 0, 0), false, false);
net.setInput(inpBlob);
Mat output = net.forward();
int H = output.size[2];
int W = output.size[3];
// find the position of the body parts
vector<Point> points(nPoints);
for (int n=0; n < nPoints; n++)
{
// Probability map of corresponding body's part.
Mat probMap(H, W, CV_32F, output.ptr(0,n));
resize(probMap, probMap, Size(frameWidth, frameHeight));
Point maxLoc;
double prob;
minMaxLoc(probMap, 0, &prob, 0, &maxLoc);
if (prob > thresh)
{
circle(frameCopy, cv::Point((int)maxLoc.x, (int)maxLoc.y), 8, Scalar(0,255,255), -1);
cv::putText(frameCopy, cv::format("%d", n), cv::Point((int)maxLoc.x, (int)maxLoc.y), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 1, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2);
}
points[n] = maxLoc;
}
int nPairs = sizeof(POSE_PAIRS)/sizeof(POSE_PAIRS[0]);
for (int n = 0; n < nPairs; n++)
{
// lookup 2 connected body/hand parts
Point2f partA = points[POSE_PAIRS[n][0]];
Point2f partB = points[POSE_PAIRS[n][1]];
if (partA.x<=0 || partA.y<=0 || partB.x<=0 || partB.y<=0)
continue;
line(frame, partA, partB, Scalar(0,255,255), 8);
circle(frame, partA, 8, Scalar(0,0,255), -1);
circle(frame, partB, 8, Scalar(0,0,255), -1);
}
t = ((double)cv::getTickCount() - t)/cv::getTickFrequency();
cout << "Time Taken = " << t << endl;
imshow("Output-Keypoints", frameCopy);
imshow("Output-Skeleton", frame);
imwrite("Output-Skeleton.jpg", frame);
waitKey();
return 0;
}3. 参考
[1] - Hand Keypoint Detection using Deep Learning and OpenCV - 2018.10.08
[2] - Github - spmallick/learnopencv/HandPose
[3] - Stackoverflow - how-can-i-use-smoothing-techniques-to-remove-jitter-in-pose-estimation - 关键点平滑
7 条评论
如何找到掌纹的坐标点呢
输出的 res_points 里是各手部点的坐标吧.
你好,请问如何才能够实现掌纹的定位
你好 你这边掌纹识别实现了吗 新手不知道怎么弄 有没有文章参考
掌纹是说手掌的纹路吗,这种的话可能更适合用分割.
学习了,巧了,我们最近也在用这个项目
赞