多模态模型,这里主要是视觉和文本2个模态交互的模型。
一般的思路是,分别对文本和视觉进行特征提取,得到embedding,然后进行early或者late fusion,再根据预训练任务进行参数更新。
[1] - 视觉特征的提取
- 直接提取视觉向量;
- 目标检测,大多用的是Faster R-CNN,输出bounding box和对应位置;提取类别特征
- 潜在问题:提取的信息有冗余和噪音,对下游任务有益的视觉信息没有被有效提取,和对应的文本信息有语义鸿沟,不好做视觉-文本对齐等。
[2] - 文本特征的提取
- 文本一般会用BERT等做初始化,大规模训练集会从头开始训练。
Early fusion:特征提取后,一般是直接concat,进入transformer;
Late fusion:特征提取后,模态内部再进行深度学习,再做模态交互。
计算机视觉:计算机具有看到并理解其所看到的东西的能力,以类似于人类;
自然语言处理:计算机具有理解语言的能力,以类似于人类的方式。
CLIP 架起了计算机视觉与自然语言处理之间的桥梁.
CLIP
CLIP,Contrastive Language–Image Pre-training
[1] - 双流模型,文本和视觉分别进入transformer encoder,经过线性投影计算不同图文对的相似度;
[2] - 使用对比学习,将图片分类转换成图文匹配任务。
用4亿对来自网络的图文数据集,将文本作为图像标签,进行训练。进行下游任务时,只需要提供和图上的concepts对应的文本描述,就可以进行zero-shot transfer。
[3] - 输入图片到 CLIP 模型,可以返回与图片标题(描述)或摘要.
数据:4亿个网络公开的图文对。为覆盖到更多的视觉concepts, 用了50w个query在搜索引擎搜索图片,一个query差不多有2w张图片。
输入:一个batch有N个图像文本对;

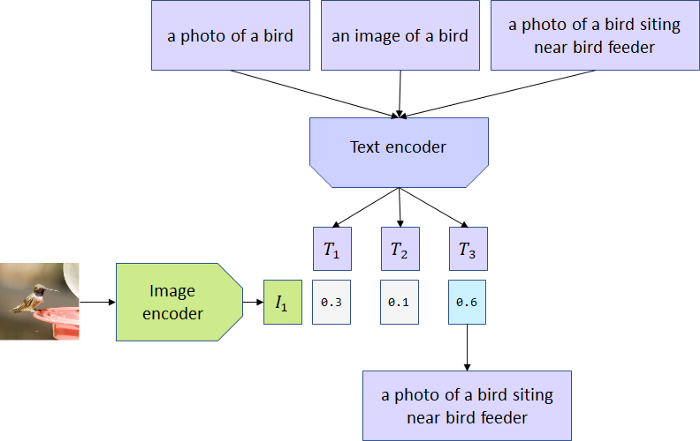
模型:对比学习,预测对图文数据,将图片分类任务转换成图文匹配任务:
[1] - 双流,2个encoder分别处理文本和图片数据,text encoder使用Transformer,image encoder用了2种模型,ResNet和Vision Transformer(ViT);
- 5种ResNet:ResNet-50, ResNet-101, EfficientNet-style的ResNet,包括RN50x4, RN50x16, RN50x64;
- 3种ViT:ViT-B/32, ViT-B/16, ViT-L/14;
[2] - encoder representation直接线性投影到multi-modal embedding space;
[3] - 计算2模态之间的cosine similarity,让N个匹配的图文对相似度最大,不匹配的图文对相似度最小;
[4] - 对称的cross-entropy loss;
[5] - 数据增强:对resized图片进行random square crop。
[6] - 将分类模型转换成图文匹配任务,用文本来弱监督图片分类。

实验
Zero-shot Transfer
图片分类的zero-shot指的是对未知类别进行推理。
本文的zero-shot指的是对未知任务进行推理,通过zero-shot transfer衡量任务学习的能力。
Visual N-Grams (Li et al., 2017) 是第一个将zero-shot transfer应用到图片分类任务上的模型。模型用于学习长度为1~5grams的共142806个visual n-grams,对输入的图片,最大化对应的n-grams的probability。
同样的,CLIP在进行zero-shot transfer时,将数据集中的类别标签转换为文字描述,主要步骤如下:
- 输入:一张图片 + 所有类别转换的文本(100个类别就是100个文本描述);
- 转换向量:经过2个encoder,分别输出image和text的feature embedding;
- 计算cosine similarity;
- 预测类别:multinomial logistic regression classifier。
zero-shot prediction 代码
zero-shot prediction
基于输入的图片,在类别描述中检索,找到最合适的类别。
"Ref:https://github.com/openai/CLIP"
import os
import clip
import torch
from torchvision.datasets import CIFAR100
# Load the model
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
model, preprocess = clip.load('ViT-B/32', device)
# Download the dataset
cifar100 = CIFAR100(root=os.path.expanduser("~/.cache"), download=True, train=False)
# Prepare the inputs
image, class_id = cifar100[3637]
image_input = preprocess(image).unsqueeze(0).to(device)
text_inputs = torch.cat([clip.tokenize(f"a photo of a {c}") for c in cifar100.classes]).to(device)
#cifar每个类别,输入图片,检索匹配的类别
# Calculate features
with torch.no_grad():
image_features = model.encode_image(image_input)
text_features = model.encode_text(text_inputs)
# Pick the top 5 most similar labels for the image
image_features /= image_features.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
text_features /= text_features.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
similarity = (100.0 * image_features @ text_features.T).softmax(dim=-1)
values, indices = similarity[0].topk(5)
# Print the result
print("\nTop predictions:\n")
for value, index in zip(values, indices):
print(f"{cifar100.classes[index]:>16s}: {100 * value.item():.2f}%")
"""
Top predictions:
snake: 65.31%
turtle: 12.29%
sweet_pepper: 3.83%
lizard: 1.88%
crocodile: 1.75%
"""Linear-probe evaluation
将 pretraining 的模型视作特征提取器,增加一个分类头,只训练这个分类头。第二种方式的直觉在于“一个好的特征应该能够区分不同的类”,除此之外,fine-tune 效果好有可能是因为架构很适合下游任务,但是 linear-probe 只取决于特征质量。
通过CLIP的image_encoder得到视觉向量,结合标签做Logistic Regression。
"Ref:https://github.com/openai/CLIP"
import os
import clip
import torch
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision.datasets import CIFAR100
from tqdm import tqdm
# Load the model
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
model, preprocess = clip.load('ViT-B/32', device)
# Load the dataset
root = os.path.expanduser("~/.cache")
train = CIFAR100(root, download=True, train=True, transform=preprocess)
test = CIFAR100(root, download=True, train=False, transform=preprocess)
def get_features(dataset):
all_features = []
all_labels = []
with torch.no_grad():
for images, labels in tqdm(DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=100)):
features = model.encode_image(images.to(device))
all_features.append(features)
all_labels.append(labels)
return torch.cat(all_features).cpu().numpy(), torch.cat(all_labels).cpu().numpy()
# Calculate the image features
train_features, train_labels = get_features(train)
test_features, test_labels = get_features(test)
# Perform logistic regression
classifier = LogisticRegression(random_state=0, C=0.316, max_iter=1000, verbose=1) # c自定义
classifier.fit(train_features, train_labels)
# Evaluate using the logistic regression classifier
predictions = classifier.predict(test_features)
accuracy = np.mean((test_labels == predictions).astype(np.float)) * 100.
print(f"Accuracy = {accuracy:.3f}")CLIP 局限
[1] - 不是和SOTA的比较:以上的数据分析,都是和a linear classifier on top of ResNet-50 features进行比较,大部分的数据集,都有对应的SOTA模型。为了达到SOTA,zero-shot CLIP估计要提高1000x的算力,当前情况不支持;
[2] - 在部分fine-grained分类上表现不佳:
- 前面实验分析发现,模型不能很好的区分cars,species of flowers, 以及variants of aircraft;
- abstract和systematic任务表现不好,比如统计图上object的数量;
- 在训练集中基本不会出现的比较novel的任务,表现欠佳,比如classifying
- distance to the nearest car in a photo;
[3] - 训练集中没有出现的图片类型(out-of-distribution),表现不好,比如OCR识别数字效果可以,但是MNIST的准确率只有88%;
其余
Align before Fuse: Vision and Language Representation Learning with Momentum Distillation
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2107.07651.pdf
https://github.com/salesforce/ALBEF
提取的视觉token和文本token不对齐,做图文特征交叉是个难点。
之前的模型,使用bounding box提取region feature,本文提出ALBEF,通过cross-modal attention,实现图文表征学习。且为了从noisy的web数据上提升模型效果,提出momentum distillation,这是一种self-training method,学习pseudo-targets。实验结果显示,模型在多个下游任务上,达到SOTA。

应用
1. CLIP-Art
CLIP-Art: Contrastive Pre-training for Fine-Grained Art Classification-CVPR2021
解决两个问题:
- 实例检索(instance retrieval)
- 细粒度艺术属性识别(fine-grained artwork attribute recognition)

- 将给定图片的噪声细粒度类别标注转为自然语言文本;iMet 数据集,每张图片生成了超过 15 的文本描述
- 微调 ViT-B/32 CLIP 模型,InfoNCE loss(使正样本对之间的互信息最大,使负样本对之间的互信息最小)
- 域适应$CLIP_{art}$ 以进一步微调到细粒度艺术识别任务
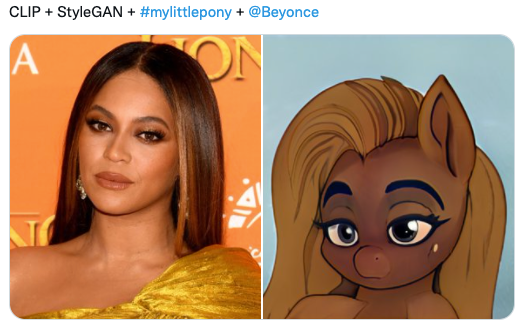
2. CLIP + StyleGAN
https://github.com/vipermu/StyleCLIP
used CLIP and StyleGAN to generate portraits in the style of "My Little Pony."
A pony that looks like Elvis Presley




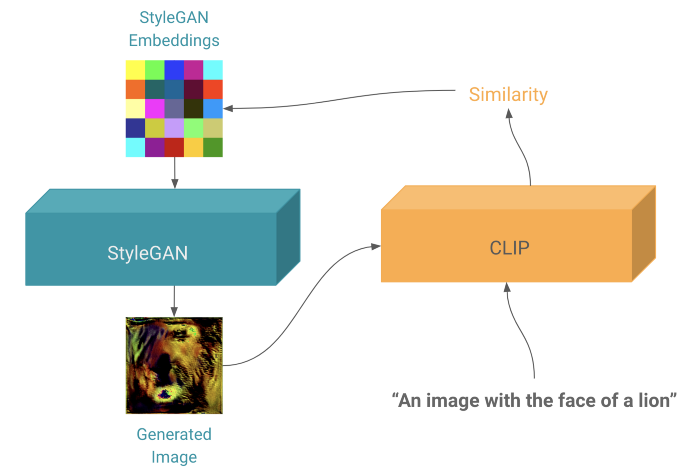
Generating Images from Prompts using CLIP and StyleGAN



3. 语义搜索



4. 跨模态搜索
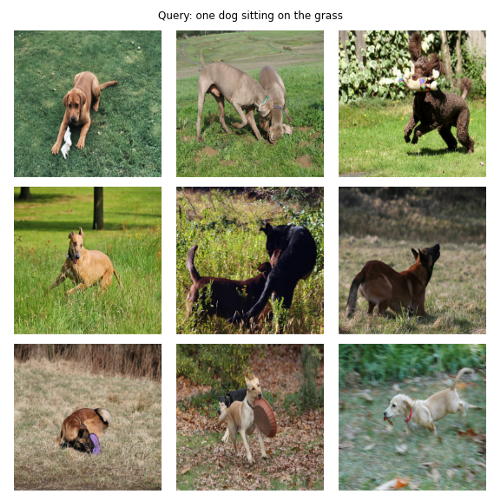





5. 图像分类

6. StyleGAN-NADA
StyleGAN-NADA: CLIP-Guided Domain Adaptation of Image Generators
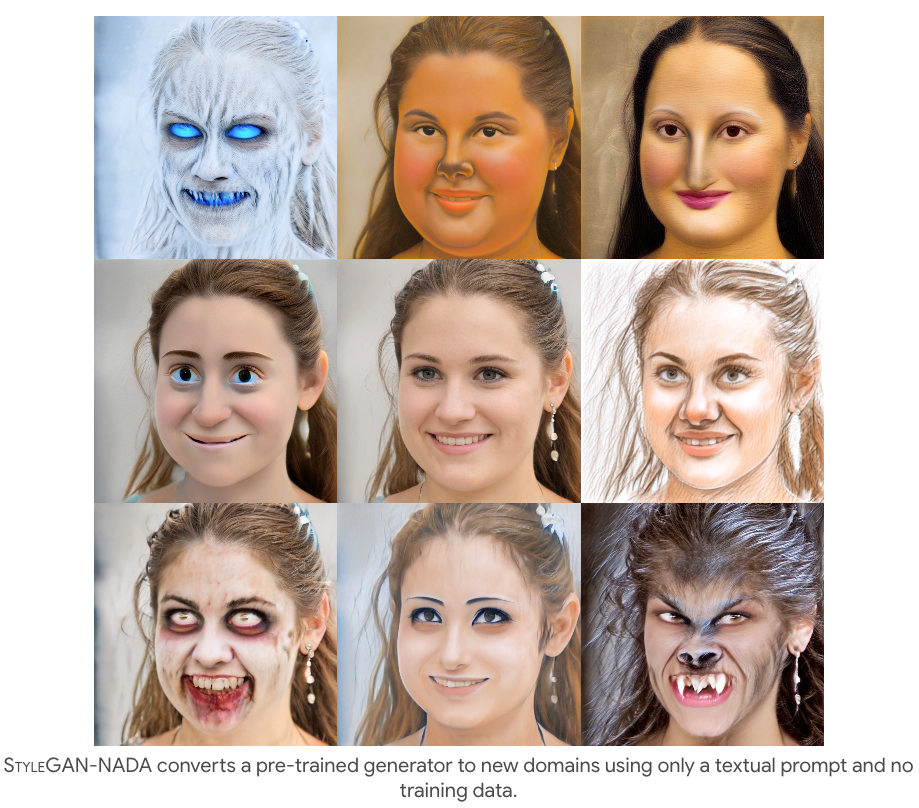

7. StyleCLIP
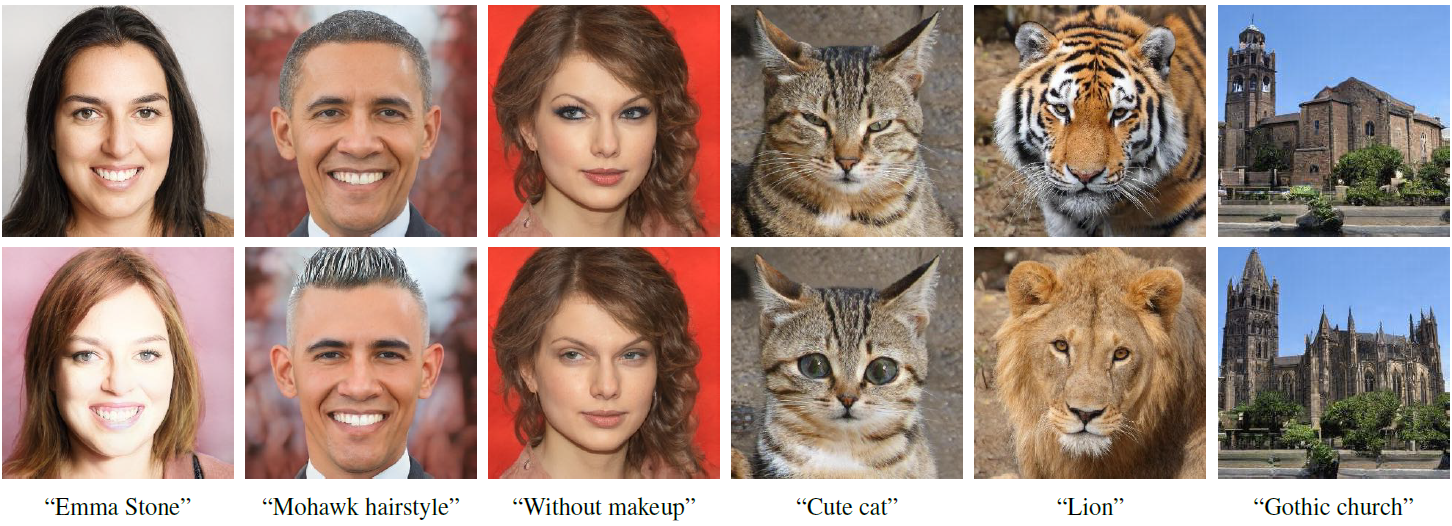

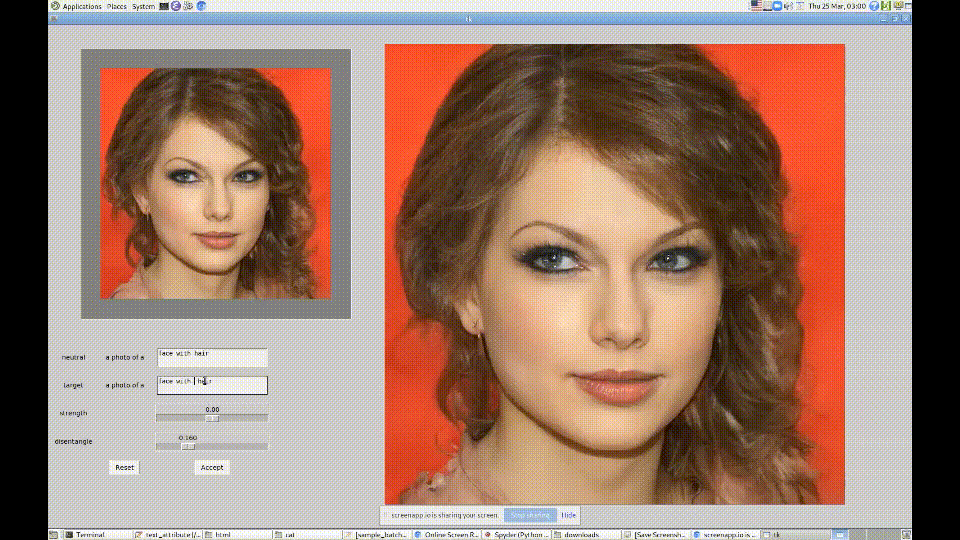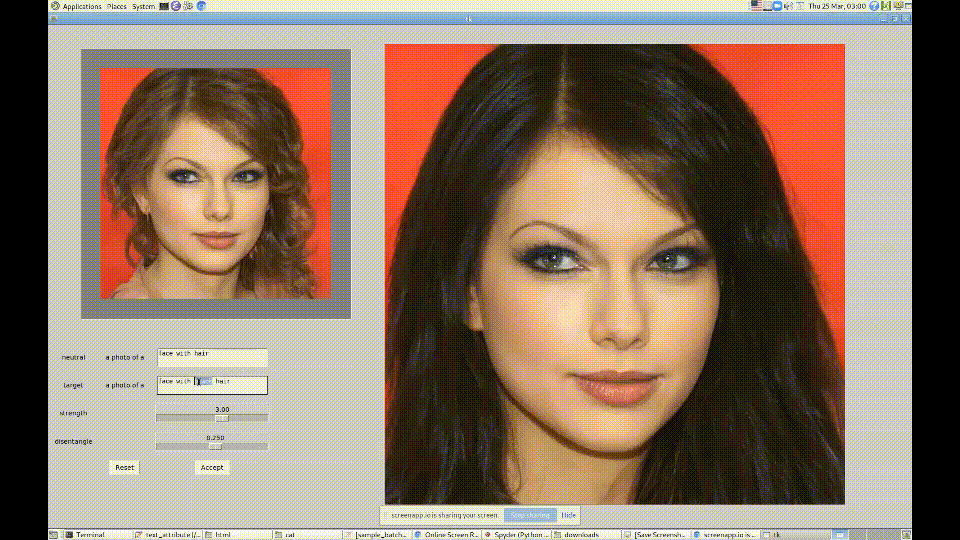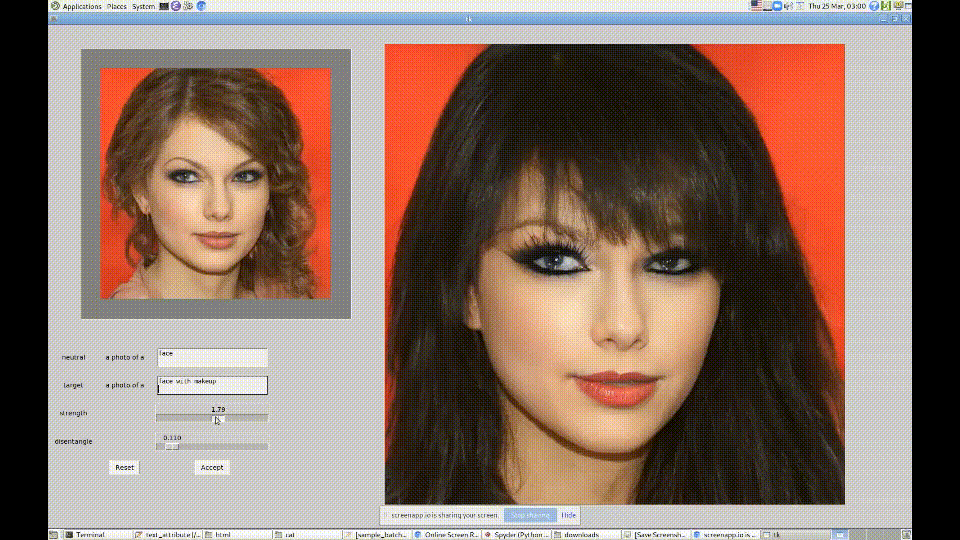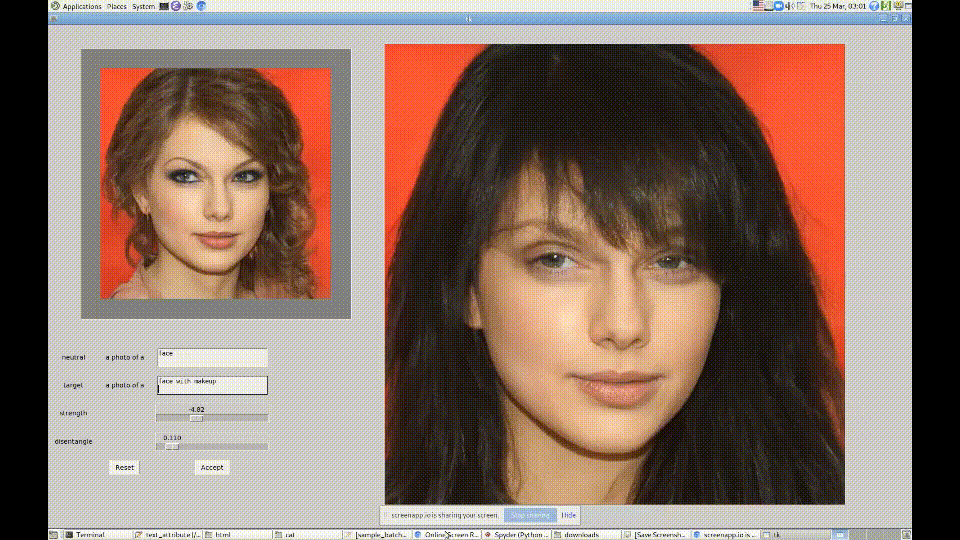
材料
[1] - A Beginner’s Guide to the CLIP Model
[2] - CLIP from OpenAI: what is it and how you can try it out yourself
[3] - Simple Implementation of OpenAI CLIP model: A Tutorial
[4] - Generating Images from Prompts using CLIP and StyleGAN
2 comments
大家好,我们在github开源了中文Chinese-CLIP模型,有多个模型规模可选,下游效果也还不错,附带详细的技术报告和demo https://github.com/OFA-Sys/Chinese-CLIP 希望大家多多试用 & star,多提宝贵意见~
有关注到过,达摩院,赞!