OpenCV 图像尺寸缩放时采用:
cv2.resize(src, dsize[, dst[, fx[, fy[, interpolation]]]])其中,
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| src | 【必需】原图像 |
| dsize | 【必需】输出图像所需大小 |
| fx | 【可选】沿水平轴的比例因子 |
| fy | 【可选】沿垂直轴的比例因子 |
| interpolation | 【可选】插值方式 |
插值方式可选:
| cv.INTER_NEAREST | 最近邻插值 |
|---|---|
| cv.INTER_LINEAR | 双线性插值(默认) |
| cv.INTER_CUBIC | 三次样条插值 |
| cv.INTER_AREA | 使用像素区域关系重新采样.它可能是图像抽取的首选方法,因为它可以提供无莫尔条纹的结果.但是当图像被缩放时,它类似于INTER_NEAREST方法. |
通常的,缩小使用cv.INTER_AREA,放缩使用cv.INTER_CUBIC(较慢)和cv.INTER_LINEAR(较快效果也不错).默认情况下,所有的放缩都使用cv.INTER_LINEAR.
1. OpenCV 最近邻插值
原文:Opencv 最邻近插值 - 2020.02.17
Opencv最近邻插值在图像放大时补充的像素取最临近的像素的值.由于方法简单,所以处理速度很快,但是放大图像画质劣化明显.
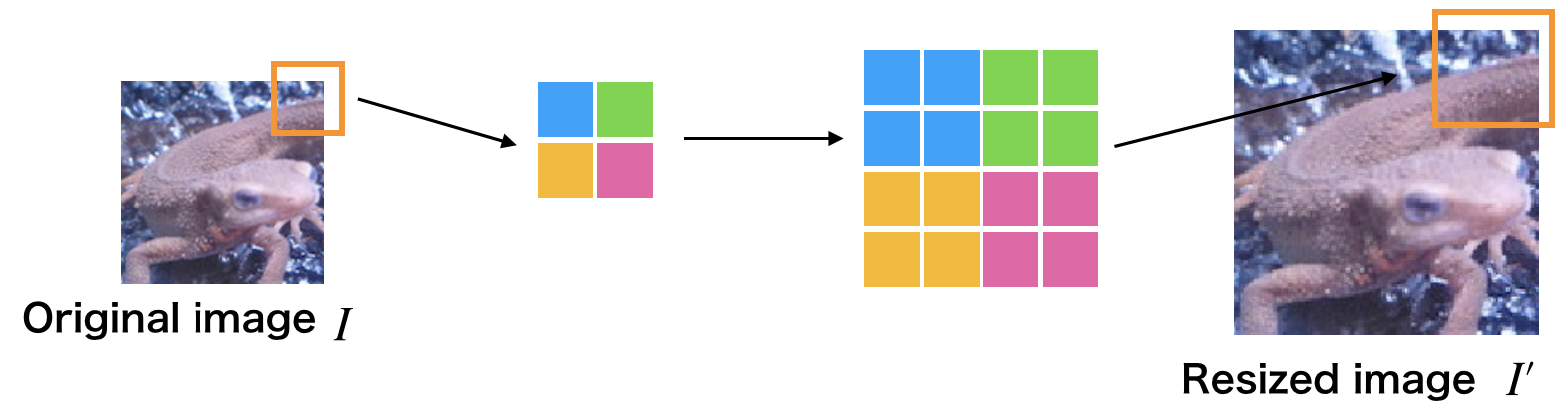
如图,原始图像 $I$ ,放大后图像 $I'$,假设放大率为 $\alpha$,则最近邻插值公式为:
$$ I' (x, y) = I([\frac{x}{\alpha}], [\frac{y}{a}]) $$
1.1. Python 实现
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Nereset Neighbor interpolation
def nn_interpolate(img, ax=1, ay=1):
H, W, C = img.shape
aH = int(ay * H)
aW = int(ax * W)
y = np.arange(aH).repeat(aW).reshape(aW, -1)
x = np.tile(np.arange(aW), (aH, 1))
y = np.round(y / ay).astype(np.int)
x = np.round(x / ax).astype(np.int)
out = img[y,x]
out = out.astype(np.uint8)
return out
# Read image
img = cv2.imread("test.jpg").astype(np.float)
# Nearest Neighbor
out = nn_interpolate(img, ax=1.5, ay=1.5)
# Save result
cv2.imshow("result", out)
cv2.imwrite("out.jpg", out)1.2. C++ 实现
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
// nearest nieghbor
cv::Mat nearest_neighbor(cv::Mat img, double rx, double ry){
// get height and width
int width = img.cols;
int height = img.rows;
int channel = img.channels();
// get resized shape
int resized_width = (int)(width * rx);
int resized_height = (int)(height * ry);
int x_before, y_before;
// output image
cv::Mat out = cv::Mat::zeros(resized_height, resized_width, CV_8UC3);
// nearest neighbor interpolation
for (int y = 0; y < resized_height; y++){
y_before = (int)round(y / ry);
y_before = fmin(y_before, height - 1);
for (int x = 0; x < resized_width; x++){
x_before = (int)round(x / rx);
x_before = fmin(x_before, width - 1);
// assign pixel to new position
for (int c = 0; c < channel; c++){
out.at<cv::Vec3b>(y, x)[c] = img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y_before, x_before)[c];
}
}
}
return out;
}
int main(int argc, const char* argv[]){
// read image
cv::Mat img = cv::imread("imori.jpg", cv::IMREAD_COLOR);
// nearest neighbor
cv::Mat out = nearest_neighbor(img, 1.5, 1.5);
//cv::imwrite("out.jpg", out);
cv::imshow("answer", out);
cv::waitKey(0);
cv::destroyAllWindows();
return 0;
}2. OpenCV 双线性插值
原文:Opencv 双线性插值- 2020.02.17
双线性插值考察4邻域的像素点,并根据距离设置权值.虽然计算量增大使得处理时间变长,但是可以有效抑制画质劣化.
[1] - 放大后图像坐标为 $(x', y')$,放大率为 $\alpha$,则对应的原图像坐标为 $([\frac{x'}{\alpha}], [\frac{y'}{\alpha}])$.
[2] - 求原图像的像素坐标 $([\frac{x'}{\alpha}], [\frac{y'}{\alpha}])$ 周围 4 邻域的像素坐标 $I(x, y), I(x+1, y), I(x, y+1), I(x+1, y+1)$:
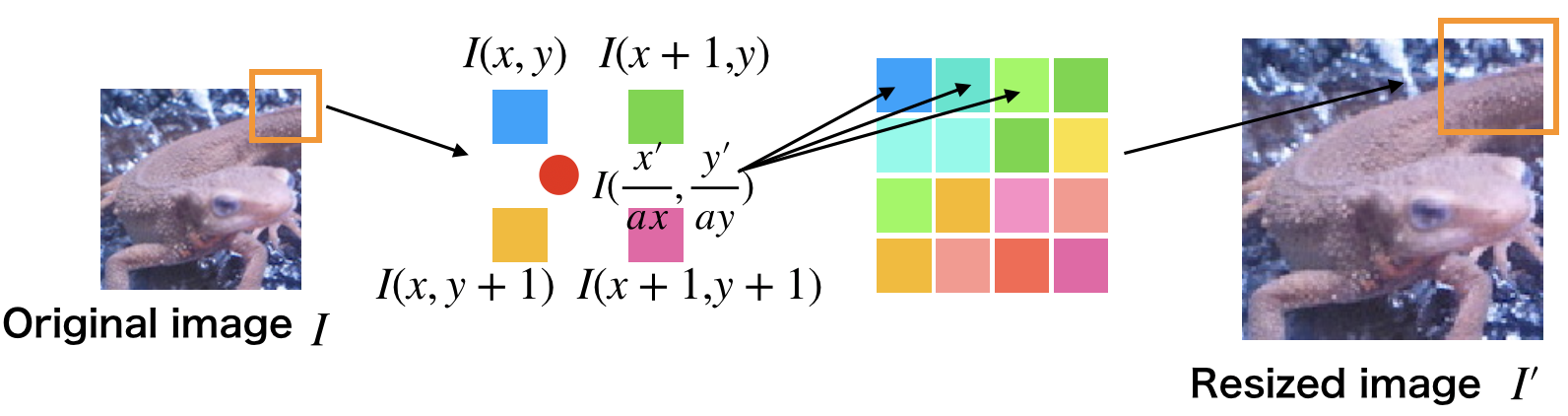
[3] - 分别求这 4 个点与 $([\frac{x'}{\alpha}], [\frac{y'}{\alpha}])$ 的距离,根据距离设置权重:$w = \frac{d}{\sum d}$.
[4] - 根据下面公式求得放大后图像 $(x', y')$ 处的像素值:
$$ d_x = \frac{x'}{\alpha} -x $$
$$ d_y = \frac{y'}{\alpha} - y $$
$$ I'(x', y') = (1 - d_x)(1 - d_y) I(x, y) + d_x(1 - d_y) I(x+1, y) + (1 - d_x)d_y I(x, y+1) + d_x d_y I(x+1, y+1) $$
2.1. Python 实现
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Bi-Linear interpolation
def bl_interpolate(img, ax=1., ay=1.):
H, W, C = img.shape
aH = int(ay * H)
aW = int(ax * W)
# get position of resized image
y = np.arange(aH).repeat(aW).reshape(aW, -1)
#y = np.tile(np.arange(aH), (aW, 1)).transpose()
x = np.tile(np.arange(aW), (aH, 1)) #
# get position of original position
y = (y / ay)
x = (x / ax)
ix = np.floor(x).astype(np.int)
iy = np.floor(y).astype(np.int)
ix = np.minimum(ix, W-2)
iy = np.minimum(iy, H-2)
# get distance
dx = x - ix
dy = y - iy
dx = np.repeat(np.expand_dims(dx, axis=-1), 3, axis=-1)
dy = np.repeat(np.expand_dims(dy, axis=-1), 3, axis=-1)
# interpolation
out = (1-dx) * (1-dy) * img[iy, ix] + dx * (1 - dy) * img[iy, ix+1] + (1 - dx) * dy * img[iy+1, ix] + dx * dy * img[iy+1, ix+1]
out = np.clip(out, 0, 255)
out = out.astype(np.uint8)
return out
# Read image
img = cv2.imread("imori.jpg").astype(np.float)
# Bilinear interpolation
out = bl_interpolate(img, ax=1.5, ay=1.5)
# Save result
cv2.imshow("result", out)
cv2.imwrite("out.jpg", out)2.2. C++ 实现
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
// bilinear
cv::Mat bilinear(cv::Mat img, double rx, double ry){
// get height and width
int width = img.cols;
int height = img.rows;
int channel = img.channels();
// get resized shape
int resized_width = (int)(width * rx);
int resized_height = (int)(height * ry);
int x_before, y_before;
double dx, dy;
double val;
// output image
cv::Mat out = cv::Mat::zeros(resized_height, resized_width, CV_8UC3);
// bi-linear interpolation
for (int y = 0; y < resized_height; y++){
y_before = (int)floor(y / ry);
y_before = fmin(y_before, height - 1);
dy = y / ry - y_before;
for (int x = 0; x < resized_width; x++){
x_before = (int)floor(x / rx);
x_before = fmin(x_before, width - 1);
dx = x / rx - x_before;
// compute bi-linear
for (int c = 0; c < channel; c++){
val = (1. - dx) * (1. - dy) * img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y_before, x_before)[c] +
dx * (1. - dy) * img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y_before, x_before + 1)[c] +
(1. - dx) * dy * img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y_before + 1, x_before)[c] +
dx * dy * img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y_before + 1, x_before)[c];
// assign pixel to new position
out.at<cv::Vec3b>(y, x)[c] = (uchar)val;
}
}
}
return out;
}
int main(int argc, const char* argv[]){
// read image
cv::Mat img = cv::imread("imori.jpg", cv::IMREAD_COLOR);
// bilinear
cv::Mat out = bilinear(img, 1.5, 1.5);
//cv::imwrite("out.jpg", out);
cv::imshow("answer", out);
cv::waitKey(0);
cv::destroyAllWindows();
return 0;
}