这里主要是对 基于 YOLOV3 和 OpenCV的目标检测(PythonC++)[译] Python 完整实现的整理.
OpenCV DNN支持图像分类、对象检测、图像分割常见通用网络模型.
1. YOLOV3 简述
YOLOV3 网络结构如图:
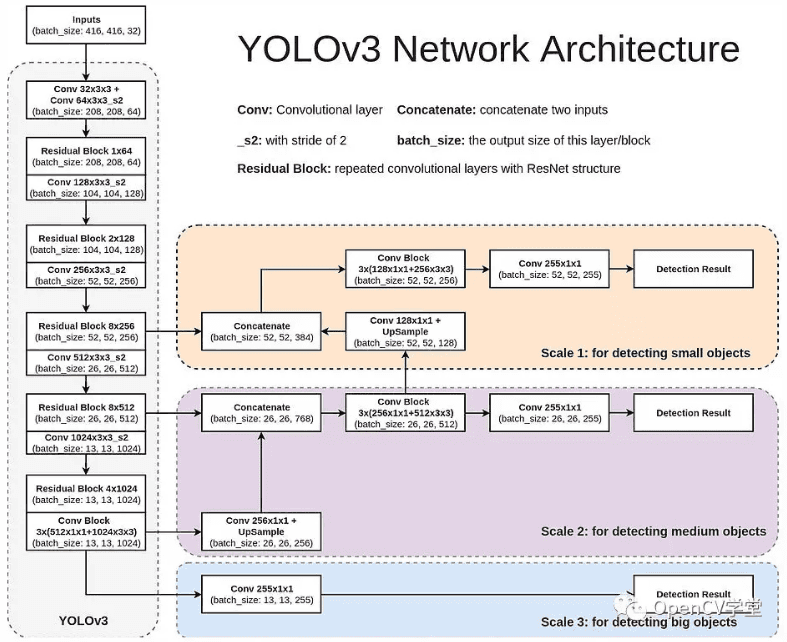
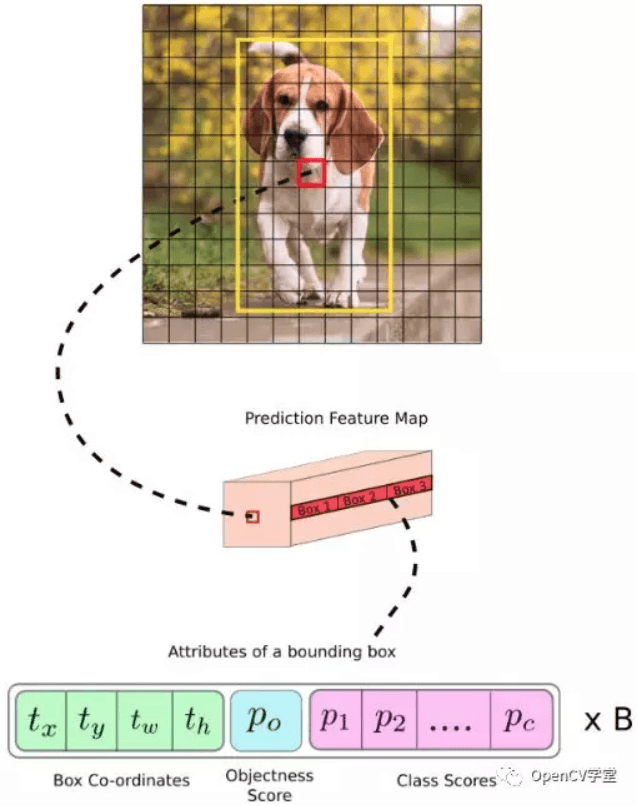
YOLOV3 采用全卷积结构,有效减少了模型参数总数,取消了softmax层,模型输出结构如图:
2. YOLOV3 DNN 实现
模型下载:
# coco.names
wget https://github.com/pjreddie/darknet/blob/master/data/coco.names?raw=true -O ./coco.names
# YOLOV3
wget https://github.com/pjreddie/darknet/blob/master/cfg/yolov3.cfg?raw=true -O ./yolov3.cfg
wget https://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolov3.weights
# YOLOV3-tiny
wget https://github.com/pjreddie/darknet/blob/master/cfg/yolov3-tiny.cfg
wget https://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolov3-tiny.weights完整实现:
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import sys
import numpy as np
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
class general_yolov3(object):
def __init__(self, modelpath, is_tiny=False):
self.conf_threshold = 0.5 # Confidence threshold
self.nms_threshold = 0.4 # NMS threshold
self.net_width = 416 # 网络输入图像宽度
self.net_height = 416 # 网络输入图像高度
self.classes = self.get_coco_names()
self.yolov3_model = self.get_yolov3_model(modelpath, is_tiny)
self.outputs_names = self.get_outputs_names()
def get_coco_names(self):
# COCO 物体类别名
classesFile = "/path/to/coco.names"
classes = None
with open(classesFile, 'rt') as f:
classes = f.read().rstrip('\n').split('\n')
return classes
def get_yolov3_model(self, modelpath, is_tiny):
if is_tiny:
cfg_file = os.path.join(modelpath, "yolov3-tiny.cfg")
weights_file = os.path.join(modelpath, "yolov3-tiny.weights")
else:
cfg_file = os.path.join(modelpath, "yolov3.cfg")
weights_file = os.path.join(modelpath, "yolov3.weights")
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromDarknet(cfg_file, weights_file)
net.setPreferableBackend(cv2.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_OPENCV)
net.setPreferableTarget(cv2.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CPU)
return net
def get_outputs_names(self):
# 所有网络层名
layersNames = self.yolov3_model.getLayerNames()
# 输出网络层名,如无连接输出的网络层.
return [layersNames[i[0] - 1] for i in
self.yolov3_model.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
def postprocess(self, img_cv2, outputs):
# 检测结果后处理
# 采用 NMS 移除低 confidence 的边界框
img_height, img_width, _ = img_cv2.shape
# 只保留高 confidence scores 的输出边界框
# 将最高 score 的类别标签作为边界框的类别标签
class_ids = []
confidences = []
boxes = []
for output in outputs:
for detection in output:
scores = detection[5:]
class_id = np.argmax(scores)
confidence = scores[class_id]
if confidence > self.conf_threshold:
center_x = int(detection[0] * img_width)
center_y = int(detection[1] * img_height)
width = int(detection[2] * img_width)
height = int(detection[3] * img_height)
left = int(center_x - width / 2)
top = int(center_y - height / 2)
class_ids.append(class_id)
confidences.append(float(confidence))
boxes.append([left, top, width, height])
# NMS 处理, 消除 lower confidences 的冗余重叠边界框
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes,
confidences,
self.conf_threshold,
self.nms_threshold)
results = []
for ind in indices:
res_box = {}
res_box["class_id"] = class_ids[ind[0]]
res_box["score"] = confidences[ind[0]]
box = boxes[ind[0]]
res_box["box"] = (box[0],
box[1],
box[0]+box[2],
box[1]+box[3])
results.append(res_box)
return results
def predict(self, img_file):
img_cv2 = cv2.imread(img_file)
# 创建网络输入的 4D blob.
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(
img_cv2, 1 / 255,
(self.net_width, self.net_height),
[0, 0, 0], 1, crop=False)
# 设置模型的输入 blob
self.yolov3_model.setInput(blob)
# 前向计算
outputs = self.yolov3_model.forward(self.outputs_names)
# 后处理
results = self.postprocess(img_cv2, outputs)
return results
def vis_res(self, img_file, results):
# 可视化检测结果
img_cv2 = cv2.imread(img_file)
for result in results:
left, top, right, bottom = result["box"]
cv2.rectangle(img_cv2,
(left, top),
(right, bottom),
(255, 178, 50), 3)
# 边界框的类别名和 confidence score
label = '%.2f' % result["score"]
class_id = result["class_id"]
if self.classes:
assert (result["class_id"] < len(self.classes))
label = '%s:%s' % (self.classes[class_id], label)
#
label_size, baseline = cv2.getTextSize(
label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
top = max(top, label_size[1])
cv2.rectangle(
img_cv2,
(left, top - round(1.5 * label_size[1])),
(left + round(1.5 * label_size[0]),
top + baseline), (255, 0, 0),
cv2.FILLED)
cv2.putText(img_cv2, label, (left, top),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.75, (0, 0, 0), 1)
# 计算速率信息
# getPerfProfile() 函数返回模型的推断总时间以及
# 每一网络层的耗时(in layersTimes).
t, _ = self.yolov3_model.getPerfProfile()
label = 'Inference time: %.2f ms' % \
(t * 1000.0 / cv2.getTickFrequency())
cv2.putText(img_cv2, label, (0, 15),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 255))
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.imshow(img_cv2[:,:,::-1])
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
print("[INFO]Yolov3 object detection in OpenCV.")
img_file = "test.jpg"
start = time.time()
modelpath = "/path/to/yolov3_models/"
yolov3_model = general_yolov3(modelpath, is_tiny=True)
print("[INFO]Model loads time: ", time.time() - start)
start = time.time()
results = yolov3_model.predict(img_file)
print("[INFO]Model predicts time: ", time.time() - start)
yolov3_model.vis_res(img_file, results)
print("[INFO]Done.")如:
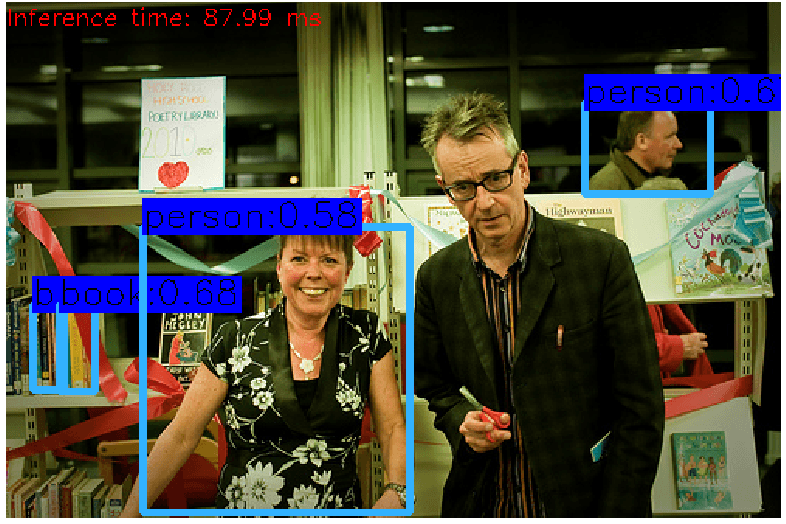
yolov3-tiny 模型:

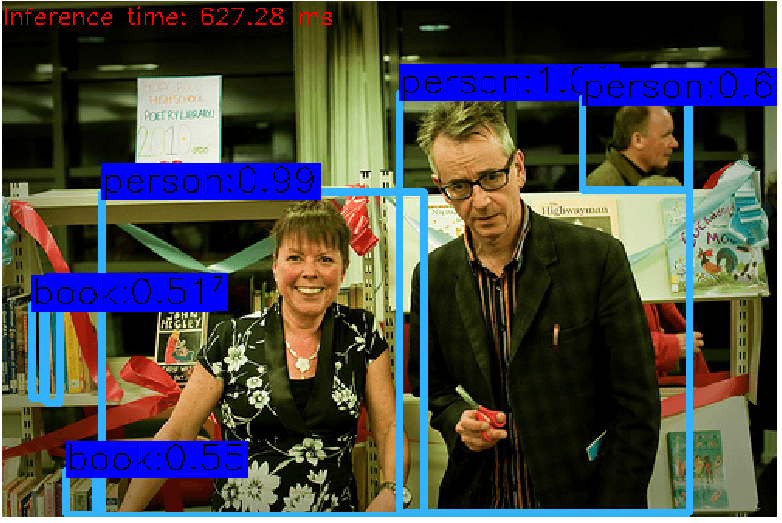
yolov3 模型:

3. 参考资料
[1] - OpenCV4.0如何跑YOLOv3对象检测模型 - OpenCV学堂