原文1 - 利用二维图像进行头部姿态估计 - 2017.10.23
原文2 - 人脸姿态估计 - 2018.04.17
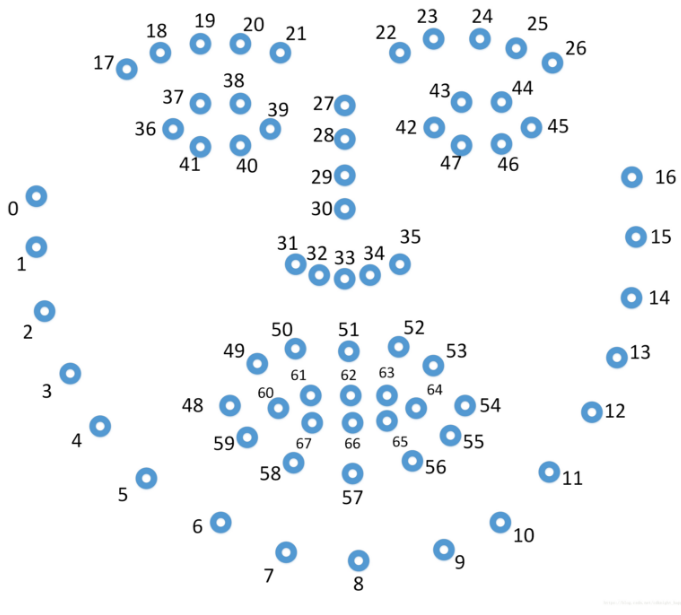
坐标变换:利用世界坐标系旋转、平移矩阵,将 3D点 从世界坐标系变换到相机坐标系中. 即:通过算法完成世界坐标系(3D)、2D landmark输入image、相机坐标系之间的映射转换和标定.
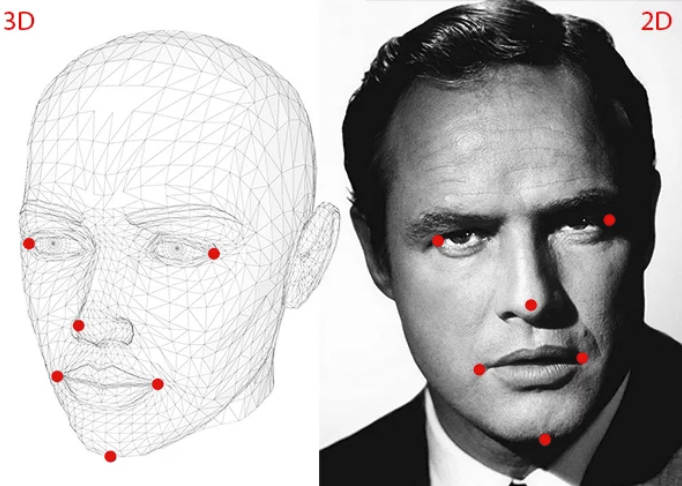
2D人脸特征点与3D世界坐标系的对应点
1. 计算旋转矩阵和平移矩阵
[基于OpenCV和Dlib的头部姿态估计[译] - AIUAI](https://www.aiuai.cn/aifarm909.html) - 10.2 Python 实现.
2. 旋转矩阵转换为欧拉角
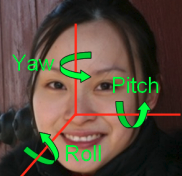
Yaw:摇头 左正右负
Pitch:点头 上负下正
Roll:摆头(歪头)左负 右正
// C++
static cv::Vec3d RotationMatrix2Euler(const cv::Matx33d& rotation_matrix)
{
double q0 = sqrt(1 + rotation_matrix(0, 0) + rotation_matrix(1, 1) + rotation_matrix(2, 2)) / 2.0;
double q1 = (rotation_matrix(2, 1) - rotation_matrix(1, 2)) / (4.0*q0);
double q2 = (rotation_matrix(0, 2) - rotation_matrix(2, 0)) / (4.0*q0);
double q3 = (rotation_matrix(1, 0) - rotation_matrix(0, 1)) / (4.0*q0);
double t1 = 2.0 * (q0*q2 + q1*q3);
double yaw = asin(2.0 * (q0*q2 + q1*q3));
double pitch = atan2(2.0 * (q0*q1 - q2*q3), q0*q0 - q1*q1 - q2*q2 + q3*q3);
double roll = atan2(2.0 * (q0*q3 - q1*q2), q0*q0 + q1*q1 - q2*q2 - q3*q3);
return cv::Vec3d(pitch, yaw, roll);
}% matlab
function [euler] = Rot2Euler(R)
q0 = sqrt( 1 + R(1,1) + R(2,2) + R(3,3) ) / 2;
q1 = (R(3,2) - R(2,3)) / (4*q0) ;
q2 = (R(1,3) - R(3,1)) / (4*q0) ;
q3 = (R(2,1) - R(1,2)) / (4*q0) ;
yaw = asin(2*(q0*q2 + q1*q3));
pitch= atan2(2*(q0*q1-q2*q3), q0*q0-q1*q1-q2*q2+q3*q3);
roll = atan2(2*(q0*q3-q1*q2), q0*q0+q1*q1-q2*q2-q3*q3);
euler = [pitch, yaw, roll];Python 实现:
# Python
class PnpHeadPoseEstimator:
"""
基于 OpenCV PnP 算法实现的头部姿态估计.
It finds Roll, Pitch and Yaw of the head given a figure as input.
It uses the PnP algorithm and it requires the dlib library
"""
def __init__(self, cam_w, cam_h, dlib_shape_predictor_file_path):
"""
@param cam_w the camera width. If you are using a 640x480 resolution it is 640
@param cam_h the camera height. If you are using a 640x480 resolution it is 480
@dlib_shape_predictor_file_path path to the dlib file for shape prediction
(dlib/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat)
"""
if(IS_DLIB_INSTALLED == False):
raise ValueError('[DEEPGAZE] PnpHeadPoseEstimator: the dlib libray is not installed. \
Please install dlib if you want to use the PnpHeadPoseEstimator class.')
if(os.path.isfile(dlib_shape_predictor_file_path)==False):
raise ValueError('[DEEPGAZE] PnpHeadPoseEstimator: the files specified do not exist.')
# Defining the camera matrix.
# To have better result it is necessary to find the focal
# lenght of the camera.
# fx/fy are the focal lengths (in pixels)
# and cx/cy are the optical centres.
# These values can be obtained roughly by approximation,
# for example in a 640x480 camera:
# cx = 640/2 = 320
# cy = 480/2 = 240
# fx = fy = cx/tan(60/2 * pi / 180) = 554.26
c_x = cam_w / 2
c_y = cam_h / 2
f_x = c_x / np.tan(60/2 * np.pi / 180)
f_y = f_x
# Estimated camera matrix values.
self.camera_matrix = np.float32([[f_x, 0.0, c_x],
[0.0, f_y, c_y],
[0.0, 0.0, 1.0] ])
# These are the camera matrix values estimated on my webcam with
# the calibration code (see: src/calibration):
# camera_matrix = np.float32([[602.10618226, 0.0, 320.27333589],
# [ 0.0, 603.55869786, 229.7537026],
# [ 0.0, 0.0, 1.0] ])
# Distortion coefficients
self.camera_distortion = np.float32([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
# Distortion coefficients estimated by calibration in my webcam
# camera_distortion = np.float32([ 0.06232237, -0.41559805, 0.00125389, -0.00402566, 0.04879263])
if(DEBUG==True):
print("[DEEPGAZE] PnpHeadPoseEstimator: estimated camera matrix: \n" + str(self.camera_matrix) + "\n")
# Declaring the dlib shape predictor object
self._shape_predictor = dlib.shape_predictor(dlib_shape_predictor_file_path)
def _return_landmarks(self, inputImg, roiX, roiY, roiW, roiH, points_to_return=range(0,68)):
"""
Return the the roll pitch and yaw angles associated with the input image.
@param image It is a colour image. It must be >= 64 pixel.
@param radians When True it returns the angle in radians, otherwise in degrees.
"""
# Creating a dlib rectangle and finding the landmarks
dlib_rectangle = dlib.rectangle(left=int(roiX), top=int(roiY), right=int(roiW), bottom=int(roiH))
dlib_landmarks = self._shape_predictor(inputImg, dlib_rectangle)
# It selects only the landmarks that
# have been indicated in the input parameter "points_to_return".
# It can be used in solvePnP() to estimate the 3D pose.
landmarks = np.zeros((len(points_to_return),2), dtype=np.float32)
counter = 0 for point in points_to_return:
landmarks[counter] = [dlib_landmarks.parts()[point].x,
dlib_landmarks.parts()[point].y]
counter += 1
return landmarks
def return_roll_pitch_yaw(self, image, radians=False):
"""
Return the the roll pitch and yaw angles associated with the input image.
@param image It is a colour image. It must be >= 64 pixel.
@param radians When True it returns the angle in radians, otherwise in degrees.
"""
# The dlib shape predictor returns 68 points,
# we are interested only in a few of those
TRACKED_POINTS = (0, 4, 8, 12, 16, 17, 26, 27, 30, 33, 36, 39, 42, 45, 62)
# Antropometric constant values of the human head.
# Check the wikipedia EN page and:
# "Head-and-Face Anthropometric Survey of U.S. Respirator Users"
#
# X-Y-Z with X pointing forward and Y on the left and Z up.
# The X-Y-Z coordinates used are like the standard
# coordinates of ROS (robotic operative system)
# OpenCV uses the reference usually used in computer vision:
# X points to the right, Y down, Z to the front #
# The Male mean interpupillary distance is 64.7 mm
# (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Interpupillary_distance)
#
P3D_RIGHT_SIDE = np.float32([-100.0, -77.5, -5.0]) #0
P3D_GONION_RIGHT = np.float32([-110.0, -77.5, -85.0]) #4
P3D_MENTON = np.float32([0.0, 0.0, -122.7]) #8
P3D_GONION_LEFT = np.float32([-110.0, 77.5, -85.0]) #12
P3D_LEFT_SIDE = np.float32([-100.0, 77.5, -5.0]) #16
P3D_FRONTAL_BREADTH_RIGHT = np.float32([-20.0, -56.1, 10.0]) #17
P3D_FRONTAL_BREADTH_LEFT = np.float32([-20.0, 56.1, 10.0]) #26
P3D_SELLION = np.float32([0.0, 0.0, 0.0]) #27 This is the world origin
P3D_NOSE = np.float32([21.1, 0.0, -48.0]) #30
P3D_SUB_NOSE = np.float32([5.0, 0.0, -52.0]) #33
P3D_RIGHT_EYE = np.float32([-20.0, -32.35,-5.0]) #36
P3D_RIGHT_TEAR = np.float32([-10.0, -20.25,-5.0]) #39
P3D_LEFT_TEAR = np.float32([-10.0, 20.25,-5.0]) #42
P3D_LEFT_EYE = np.float32([-20.0, 32.35,-5.0]) #45
#P3D_LIP_RIGHT = np.float32([-20.0, 65.5,-5.0]) #48
#P3D_LIP_LEFT = np.float32([-20.0, 65.5,-5.0]) #54
P3D_STOMION = np.float32([10.0, 0.0, -75.0]) #62
# This matrix contains the 3D points of the
# 11 landmarks we want to find. It has been
# obtained from antrophometric measurement
# of the human head.
landmarks_3D = np.float32([P3D_RIGHT_SIDE,
P3D_GONION_RIGHT,
P3D_MENTON,
P3D_GONION_LEFT,
P3D_LEFT_SIDE,
P3D_FRONTAL_BREADTH_RIGHT,
P3D_FRONTAL_BREADTH_LEFT,
P3D_SELLION,
P3D_NOSE,
P3D_SUB_NOSE,
P3D_RIGHT_EYE,
P3D_RIGHT_TEAR,
P3D_LEFT_TEAR,
P3D_LEFT_EYE,
P3D_STOMION])
# Return the 2D position of our landmarks
img_h, img_w, img_d = image.shape landmarks_2D = self._return_landmarks(
inputImg=image,
roiX=0,
roiY=img_w,
roiW=img_w,
roiH=img_h,
points_to_return=TRACKED_POINTS)
# Print som red dots on the image
# for point in landmarks_2D:
# cv2.circle(frame,( point[0], point[1] ), 2, (0,0,255), -1)
# Applying the PnP solver to find the 3D pose
# of the head from the 2D position of the #landmarks.
# retval - bool
# rvec - Output rotation vector that, together with tvec, brings
# points from the world coordinate system to the camera coordinate system.
# tvec - Output translation vector. It is the position of the world origin (SELLION) in camera co-ords
retval, rvec, tvec = cv2.solvePnP(landmarks_3D,
landmarks_2D,
self.camera_matrix,
self.camera_distortion)
# Get as input the rotational vector
# Return a rotational matrix
rmat, _ = cv2.Rodrigues(rvec)
# euler_angles contain (pitch, yaw, roll)
# euler_angles = cv.DecomposeProjectionMatrix(
# projMatrix=rmat,
# cameraMatrix=camera_matrix,
# rotMatrix,
# transVect,
# rotMatrX=None,
# rotMatrY=None,
# rotMatrZ=None)
head_pose = [rmat[0,0], rmat[0,1], rmat[0,2], tvec[0],
rmat[1,0], rmat[1,1], rmat[1,2], tvec[1],
rmat[2,0], rmat[2,1], rmat[2,2], tvec[2],
0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0 ]
# print(head_pose) #TODO remove this line
return self.rotationMatrixToEulerAngles(rmat)
# Calculates rotation matrix to euler angles
# The result is the same as MATLAB except the order
# of the euler angles ( x and z are swapped ).
def rotationMatrixToEulerAngles(self, R) :
# assert(isRotationMatrix(R))
# To prevent the Gimbal Lock it is possible to use
# a threshold of 1e-6 for discrimination
sy = math.sqrt(R[0,0] * R[0,0] + R[1,0] * R[1,0])
singular = sy < 1e-6
if not singular :
x = math.atan2(R[2,1] , R[2,2])
y = math.atan2(-R[2,0], sy)
z = math.atan2(R[1,0], R[0,0])
else :
x = math.atan2(-R[1,2], R[1,1])
y = math.atan2(-R[2,0], sy)
z = 0
return np.array([x, y, z])上面 python 源码中是采用的 68 个人脸特征点.