在语义分割和实例分割数据集中,标注数据一般给定的是分割图 - mask 或 rle.
从分割标注数据中提取矩形框(bounding boxes)信息.
1. RLE 标注数据
1.1. binary mask to rle
https://www.kaggle.com/paulorzp/run-length-encode-and-decode
import numpy as np
def rle_encode(binary_mask):
'''
binary_mask: numpy array, 1 - mask, 0 - background
Returns run length as string formated
'''
pixels = binary_mask.T.flatten()
pixels = np.concatenate([[0], pixels, [0]])
runs = np.where(pixels[1:] != pixels[:-1])[0] + 1
runs[1::2] -= runs[::2]
return ' '.join(str(x) for x in runs)1.2. rle to binary mask
def rle_decode(rle_mask, shape=(768, 768)):
'''
rle_mask: run-length as string formated (start length)
shape: (height,width) of array to return
Returns numpy array, 1 - mask, 0 - background
'''
s = rle_mask.split()
starts, lengths = [np.asarray(x, dtype=int) for x in (s[0:][::2], s[1:][::2])]
starts -= 1
ends = starts + lengths
binary_mask = np.zeros(shape[0]*shape[1], dtype=np.uint8)
for lo, hi in zip(starts, ends):
binary_mask[lo:hi] = 1
return binary_mask.reshape(shape).T # Needed to align to RLE direction1.3. rle masks to mask
# 将各个独立的 masks 合并到单个 mask array
def masks_as_image(rle_masks_list, all_masks=None):
if all_masks is None:
all_masks = np.zeros((768, 768), dtype = np.int16)
assert isinstance(rle_masks_list, list):
for rle_mask in rle_masks_list:
if isinstance(rle_mask, str):
all_masks += rle_decode(rle_mask)
return np.expand_dims(all_masks, -1)1.4. rle to bounding boxes
RLE 标注数据提取矩形边界框(bounding box) 主要包含如下步骤:
[1] - 采用 masks_as_image 将 RLE mask 转换为 Binary numpy array ;
[2] - 采用 skimage.measure.label 获取 mask 的连通区域(connected regions);
[3] - 采用 skimage.measure.regionprops 度量连通区域的形态学特征(morphological properties) 并得到矩形框(bounding box). 对于每个连通区域的矩形框格式为:(min_row, min_col, max_row, max_col).
如:
from skimage.measure import label as sk_label
from skimage.measure import regionprops as sk_regions
# rle masks.
mask = masks_as_image(rle_masks)
#
sk_mask = sk_label(mask)
regions = sk_regions(sk_mask)
for region in regions:
print('[INFO]bbox: ', region.bbox)
top, left, bottom, right = region.bbox注: 这里可能会将互相重叠的主体 masks 误处理为一个,得到错误的矩形框. 可以采用逐个连通区域来处理.
如:
from skimage.measure import regionprops as sk_regions
# rle masks.
for rle_mask in rle_mask:
binary_mask = rle_decode(rle_mask)
regions = sk_regions(binary_mask)
if len(regions) < 1:
continue
for region in regions:
print('[INFO]bbox: ', region.bbox)
top, left, bottom, right = region.bbox2. Mask 标注数据
如图:
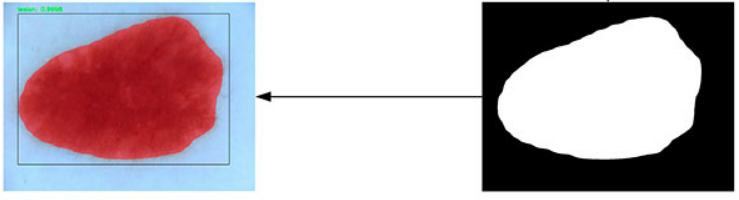
2.1. cv2.findContours
import numpy as np
import cv2 # opencv 4.x
def binary_mask_to_box(binary_mask):
binary_mask = np.array(binary_mask, np.uint8)
contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(
binary_mask, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
areas = []
for cnt in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(cnt)
areas.append(area)
# 取最大面积的连通区域
idx = areas.index(np.max(areas))
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contours[idx])
bounding_box = [x, y, x+w, y+h]
return bounding_box2.2. skimage.measure.regionprops
如:
# from skimage.measure import label as sk_label
from skimage.measure import regionprops as sk_region
regions = sk_region(binary_mask)
if len(regions) < 1:
continue
lefts, tops, rights, bottoms = [], [], [], []
for region in regions:
top, left, bottom, right = region.bbox
lefts.append(left)
tops.append(top)
rights.append(right)
bottoms.append(bottom)
#
bounding_box = [min(lefts), min(tops), max(rights), max(bottoms)]2.3. polygon
import numpy as np
from skimage import measure
def binary_mask_to_polygon(binary_mask, tolerance=0):
"""Converts a binary mask to COCO polygon representation
Args:
binary_mask: a 2D binary numpy array where '1's represent the object
tolerance: Maximum distance from original points of polygon to approximated
polygonal chain. If tolerance is 0, the original coordinate array is returned.
"""
polygons = []
# pad mask to close contours of shapes which start and end at an edge
padded_binary_mask = np.pad(binary_mask, pad_width=1, mode='constant', constant_values=0)
contours = measure.find_contours(padded_binary_mask, 0.5)
contours = np.subtract(contours, 1)
for contour in contours:
contour = close_contour(contour)
contour = measure.approximate_polygon(contour, tolerance)
if len(contour) < 3:
continue
contour = np.flip(contour, axis=1)
segmentation = contour.ravel().tolist()
# after padding and subtracting 1 we may get -0.5 points in our segmentation
segmentation = [0 if i < 0 else i for i in segmentation]
polygons.append(segmentation)
return polygons
#
def close_contour(contour):
if not np.array_equal(contour[0], contour[-1]):
contour = np.vstack((contour, contour[0]))
return contour
#
def binary_mask_to_xy(binary_mask):
polygons = binary_mask_to_polygon(binary_mask, tolerance=2)
#
xs = []
ys = []
for polygon in polygons:
for tdx in range(0, len(polygon), 2):
xs.append(polygon[tdx])
ys.append(polygon[tdx + 1])
return xs, ys
#
xs, ys = binary_mask_to_xy(binary_mask)
if len(xs) < 1 or len(ys) < 1:
continue
# left, top, right, bottom
bounding_box = [int(min(xs)), int(min(ys)), int(max(xs)), int(max(ys))]