Github项目 - Mask R-CNN 的 Keras 实现 概括了整个项目.
这里分析 COCO 数据 - inspect_data.ipynb
这里根据源码里的次序, 逐步分析学习. 有利于深入了解 COCO 数据, 以及该项目的数据加载与处理过程.
- 导入相关库
##############################################################
# Mask R-CNN - Inspect Training Data 观察训练数据
# 数据加载和预处理的过程.
##############################################################
import os
import sys
import random
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
# 项目根目录
ROOT_DIR = os.path.abspath("../../")
# Import Mask RCNN 模块
sys.path.append(ROOT_DIR) # find local version of the library
from mrcnn import utils
from mrcnn import visualize
from mrcnn.visualize import display_images
import mrcnn.model as modellib
from mrcnn.model import log
- 配置 COCO 数据集
#########################################
# 配置数据集
# 选择 Shapes 数据集或者 COCO 数据集
#########################################
# Shapes toy dataset
# import shapes
# config = shapes.ShapesConfig()
# MS COCO Dataset
import coco
config = coco.CocoConfig()
COCO_DIR = "/data/datasets/COCO/"
# 加载数据集
if config.NAME == 'shapes':
dataset = shapes.ShapesDataset()
dataset.load_shapes(500, config.IMAGE_SHAPE[0], config.IMAGE_SHAPE[1])
elif config.NAME == "coco":
dataset = coco.CocoDataset()
dataset.load_coco(COCO_DIR, "train")
# Must call before using the dataset
dataset.prepare()
print("Image Count: {}".format(len(dataset.image_ids)))
print("Class Count: {}".format(dataset.num_classes))
for i, info in enumerate(dataset.class_info):
print("{:3}. {:50}".format(i, info['name']))
输出:
creating index...
index created!
Image Count: 82081
Class Count: 81
0. BG
1. person
2. bicycle
3. car
4. motorcycle
5. airplane
6. bus
7. train
8. truck
9. boat
10. traffic light
11. fire hydrant
12. stop sign
13. parking meter
14. bench
15. bird
16. cat
17. dog
18. horse
19. sheep
20. cow
21. elephant
22. bear
23. zebra
24. giraffe
25. backpack
26. umbrella
27. handbag
28. tie
29. suitcase
30. frisbee
31. skis
32. snowboard
33. sports ball
34. kite
35. baseball bat
36. baseball glove
37. skateboard
38. surfboard
39. tennis racket
40. bottle
41. wine glass
42. cup
43. fork
44. knife
45. spoon
46. bowl
47. banana
48. apple
49. sandwich
50. orange
51. broccoli
52. carrot
53. hot dog
54. pizza
55. donut
56. cake
57. chair
58. couch
59. potted plant
60. bed
61. dining table
62. toilet
63. tv
64. laptop
65. mouse
66. remote
67. keyboard
68. cell phone
69. microwave
70. oven
71. toaster
72. sink
73. refrigerator
74. book
75. clock
76. vase
77. scissors
78. teddy bear
79. hair drier
80. toothbrush
- 随机显示图片样本
#########################################
# 显示数据集样本
#########################################
# 随机加载图片样本并显示
image_ids = np.random.choice(dataset.image_ids, 4)
for image_id in image_ids:
image = dataset.load_image(image_id)
mask, class_ids = dataset.load_mask(image_id)
visualize.display_top_masks(image, mask, class_ids, dataset.class_names)




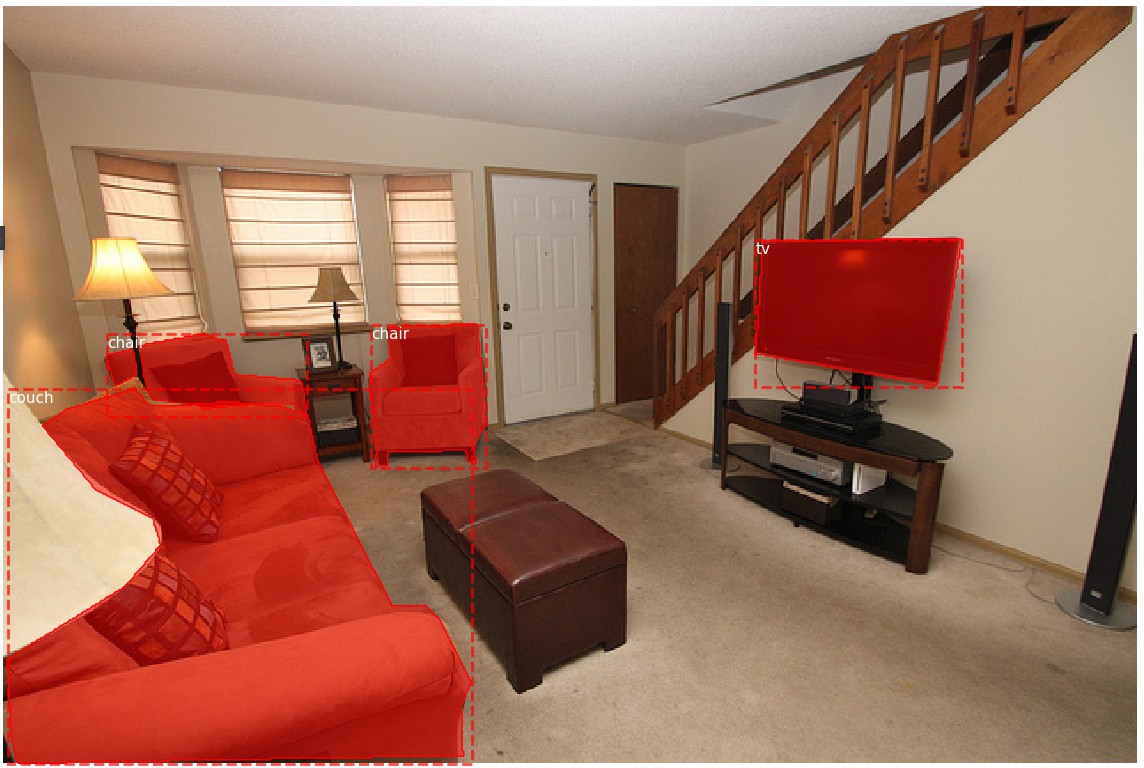
- 显示边界框 Bounding Boxes
#########################################
# 显示边界框 Bounding Boxes
# 这里的边界框是根据 masks 计算得到.
# 以便于图片 resize, rotate, crop 等.
# 只需要根据 masks 计算边界框即可,
# 而不是计算边界框的变换.
#########################################
# 随机加载一张图片和 mask
image_id = random.choice(dataset.image_ids)
image = dataset.load_image(image_id)
mask, class_ids = dataset.load_mask(image_id)
bbox = utils.extract_bboxes(mask) # Compute Bounding box
# Display image and additional stats
print("image_id ", image_id, dataset.image_reference(image_id))
log("image", image)
log("mask", mask)
log("class_ids", class_ids)
log("bbox", bbox)
# Display image and instances
visualize.display_instances(image, bbox, mask, class_ids, dataset.class_names)
('image_id ', 66646, 'http://cocodataset.org/#explore?id=367718')
image shape: (427, 640, 3) min: 0.00000 max: 255.00000 uint8
mask shape: (427, 640, 4) min: 0.00000 max: 1.00000 bool
class_ids shape: (4,) min: 57.00000 max: 63.00000 int32
bbox shape: (4, 4) min: 2.00000 max: 541.00000 int32

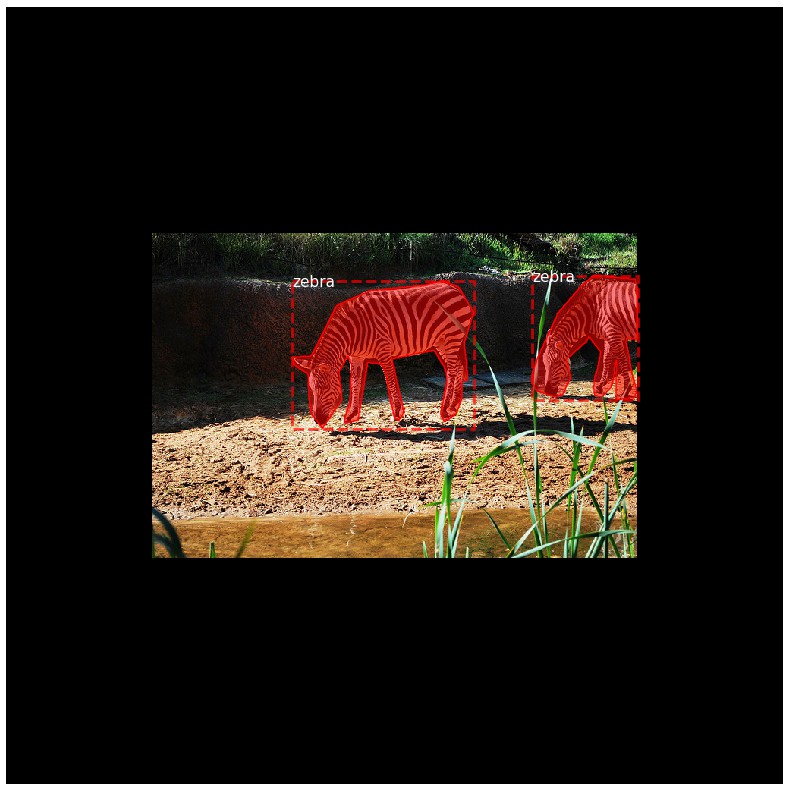
- 图片 Resize
#########################################
# 图片 Resize
#########################################
# Load random image and mask.
image_id = np.random.choice(dataset.image_ids, 1)[0]
image = dataset.load_image(image_id)
mask, class_ids = dataset.load_mask(image_id)
original_shape = image.shape
# Resize
image, window, scale, padding, _ = utils.resize_image(image,
min_dim=config.IMAGE_MIN_DIM,
max_dim=config.IMAGE_MAX_DIM,
mode=config.IMAGE_RESIZE_MODE)
mask = utils.resize_mask(mask, scale, padding)
bbox = utils.extract_bboxes(mask) # Compute Bounding box
# Display image and additional stats
print("image_id: ", image_id, dataset.image_reference(image_id))
print("Original shape: ", original_shape)
log("image", image)
log("mask", mask)
log("class_ids", class_ids)
log("bbox", bbox)
# Display image and instances
visualize.display_instances(image, bbox, mask, class_ids, dataset.class_names)
('image_id: ', 22573, 'http://cocodataset.org/#explore?id=558876')
('Original shape: ', (427, 640, 3))
image shape: (1024, 1024, 3) min: 0.00000 max: 255.00000 uint8
mask shape: (1024, 1024, 27) min: 0.00000 max: 1.00000 bool
class_ids shape: (27,) min: 1.00000 max: 25.00000 int32
bbox shape: (27, 4) min: 221.00000 max: 832.00000 int32

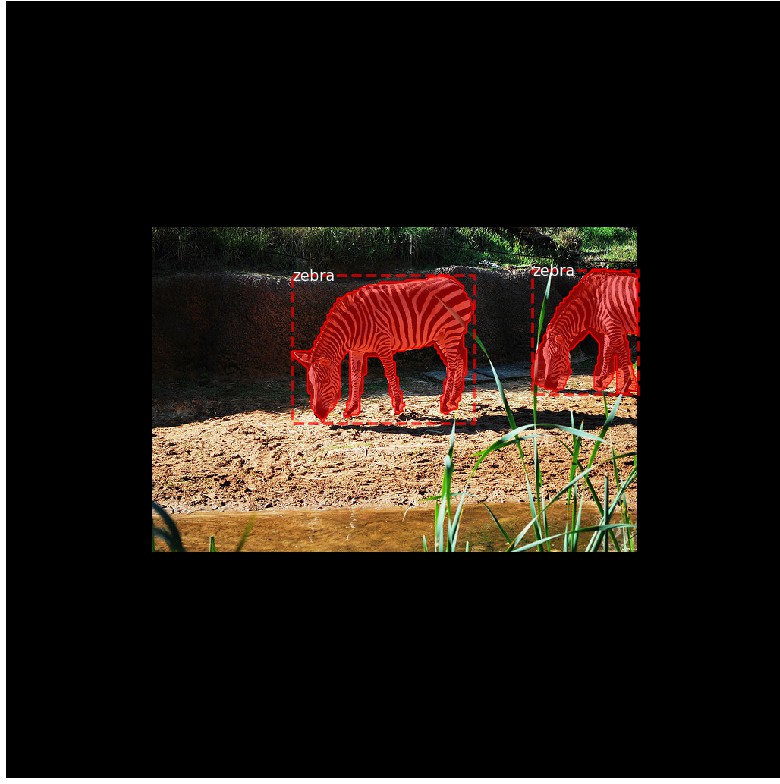
- Mini Masks
###############################################
# Mini Masks
# 对于高分辨率的图片, 其实例二值 masks 可能很大.
# 例如, 1024x1024 的图片, 单个实例 mask 需要 1MB 的内存
# (Numpy 采用 bytes 来表示 boolean 值.)
# 如果一张图片有 100 个实例, 将有 100MB 的 masks.
#
# 为了提高训练速率, 对 masks 进行优化:
# - 保存在物体边界框内的 mask 像素, 而不是整张图片保存为一个 mask.
# 大部分物体相对于图片尺寸比较小, 因此, 可以避免保存物体周围的很多 0 值,
# 以节省空间.
# - Resize mask 到更小的尺寸,(如 56x56).
# 对于物体大于设定尺寸的, 可能会损失一部分精度.
# 但,大部分物体标注开始是不很精确的, 在实际应用中可以忽略这部分损失.
# mini_mask 的尺寸可以在 config 类中定义.
#
# 根据示例,来测试 mask resizing 的效果.
###############################################
image_id = np.random.choice(dataset.image_ids, 1)[0]
image, image_meta, class_ids, bbox, mask = modellib.load_image_gt(dataset,
config,
image_id,
use_mini_mask=False)
log("image", image)
log("image_meta", image_meta)
log("class_ids", class_ids)
log("bbox", bbox)
log("mask", mask)
display_images([image]+[mask[:,:,i] for i in range(min(mask.shape[-1], 7))])
visualize.display_instances(image, bbox, mask, class_ids, dataset.class_names)
# Add augmentation and mask resizing.
image, image_meta, class_ids, bbox, mask = modellib.load_image_gt(dataset,
config,
image_id,
augment=True,
use_mini_mask=True)
log("mask", mask)
display_images([image]+[mask[:,:,i] for i in range(min(mask.shape[-1], 7))])
mask = utils.expand_mask(bbox, mask, image.shape)
visualize.display_instances(image, bbox, mask, class_ids, dataset.class_names)
image shape: (1024, 1024, 3) min: 0.00000 max: 255.00000 uint8
image_meta shape: (93,) min: 1.00000 max: 2910.00000 int64
class_ids shape: (2,) min: 23.00000 max: 23.00000 int32
bbox shape: (2, 4) min: 353.00000 max: 832.00000 int32
mask shape: (1024, 1024, 2) min: 0.00000 max: 1.00000 bool
mask shape: (56, 56, 2) min: 0.00000 max: 1.00000 bool




- Anchors
##########################################################################
# Anchors
# Anchors 的次序是很重要的. 训练和预测阶段采用相同的次序. 且必须保持卷积执行的次序.
# 对于 FPN 网络, Anchors 的次序配置方式, 应尽可能的使 anchors 与卷积层的输出相匹配.
# 卷积层的输出预测了 anchor 的 scores 和偏移 shifts.
# - 首先,根据金字塔层(pyramid level) 排序 anchors. 先是, 第一层所有的 anchors,
# 再是, 第二层所有的 anchors, 依次. 这样更容易根据层来分离 anchors.
# - 每一金字塔层内, 根据 feature map 处理顺序来排序 anchors. 典型地, 一个卷积层
# 是从左上角(top-left)开始对 feature map 处理, 一行一行地往右移动.
# - 对于每个 feature map 单元, 对具有不同比率(ratios) anchors 任意选择排序方式.
# 这里, 与传递到函数的 ratios 次序一致.
#
# Anchors Stride 步长
# 在 FPN 结构中, 前几层 feature map 的分辨率比较大. 例如, 如果输入图片是 1024x1024,
# 则, 第一层 feature map 的分辨率是 256x256, 能够生成大概 200K anchors(256x256x3)
# 这些 anchors 是 32x32 像素的, 其步长相对于图片是 4, 因此会有大量的重叠.
# 如果对 feature map 内的每个其它单元cell 生成 anchors,可以明显地减少工作量.
# 例如, 步长 2 会把 anchors 的数量减少 4 倍.
##########################################################################
# Generate Anchors
backbone_shapes = modellib.compute_backbone_shapes(config, config.IMAGE_SHAPE)
anchors = utils.generate_pyramid_anchors(config.RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES,
config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS,
backbone_shapes,
config.BACKBONE_STRIDES,
config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE)
# Print summary of anchors
num_levels = len(backbone_shapes)
anchors_per_cell = len(config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS)
print("Count: ", anchors.shape[0])
print("Scales: ", config.RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES)
print("ratios: ", config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS)
print("Anchors per Cell: ", anchors_per_cell)
print("Levels: ", num_levels)
anchors_per_level = []
for l in range(num_levels):
num_cells = backbone_shapes[l][0] * backbone_shapes[l][1]
anchors_per_level.append(anchors_per_cell * num_cells // config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE**2)
print("Anchors in Level {}: {}".format(l, anchors_per_level[l]))
# 可视化在某个特定层的 feature map 中心的单元格的 anchors.
# Load and draw random image
image_id = np.random.choice(dataset.image_ids, 1)[0]
image, image_meta, _, _, _ = modellib.load_image_gt(dataset, config, image_id)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, figsize=(10, 10))
ax.imshow(image)
levels = len(backbone_shapes)
for level in range(levels):
colors = visualize.random_colors(levels)
# 计算在图片中心的 anchors 的索引
level_start = sum(anchors_per_level[:level]) # 先前层的 anchors 相加和 sum of anchors of previous levels
level_anchors = anchors[level_start:level_start+anchors_per_level[level]]
print("Level {}. Anchors: {:6} Feature map Shape: {}".format(level, level_anchors.shape[0],
backbone_shapes[level]))
center_cell = backbone_shapes[level] // 2
center_cell_index = (center_cell[0] * backbone_shapes[level][1] + center_cell[1])
level_center = center_cell_index * anchors_per_cell
center_anchor = anchors_per_cell * (
(center_cell[0] * backbone_shapes[level][1] / config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE**2) \
+ center_cell[1] / config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE)
level_center = int(center_anchor)
# 画出 anchors.
# Brightness show the order in the array, dark to bright.
for i, rect in enumerate(level_anchors[level_center:level_center+anchors_per_cell]):
y1, x1, y2, x2 = rect
p = patches.Rectangle((x1, y1), x2-x1, y2-y1, linewidth=2, facecolor='none',
edgecolor=(i+1)*np.array(colors[level]) / anchors_per_cell)
ax.add_patch(p)
('Count: ', 261888)
('Scales: ', (32, 64, 128, 256, 512))
('ratios: ', [0.5, 1, 2])
('Anchors per Cell: ', 3)
('Levels: ', 5)
Anchors in Level 0: 196608
Anchors in Level 1: 49152
Anchors in Level 2: 12288
Anchors in Level 3: 3072
Anchors in Level 4: 768
Level 0. Anchors: 196608 Feature map Shape: [256 256]
Level 1. Anchors: 49152 Feature map Shape: [128 128]
Level 2. Anchors: 12288 Feature map Shape: [64 64]
Level 3. Anchors: 3072 Feature map Shape: [32 32]
Level 4. Anchors: 768 Feature map Shape: [16 16]



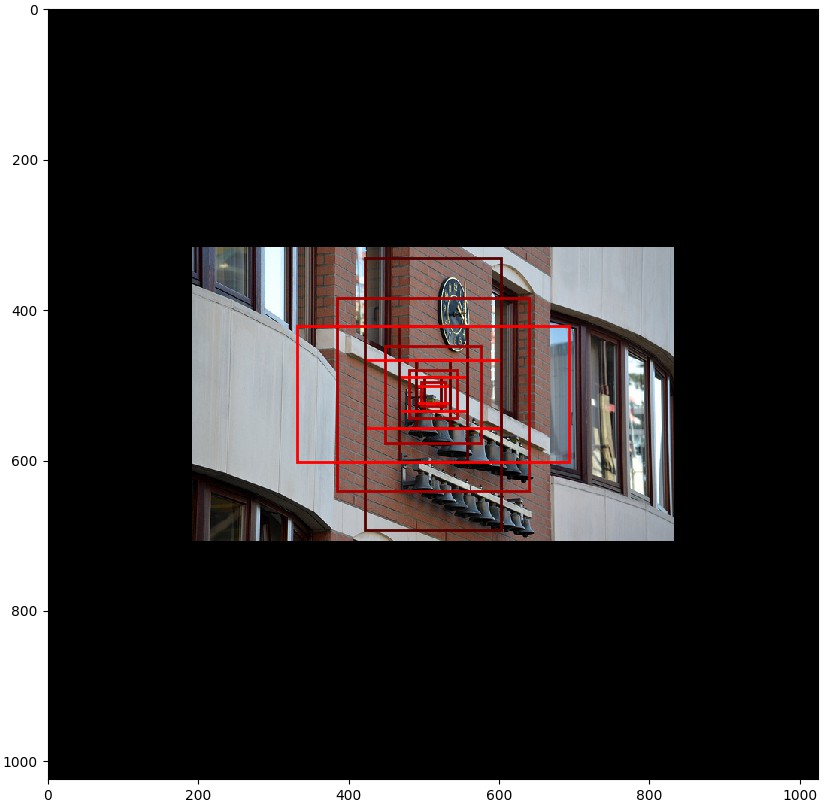
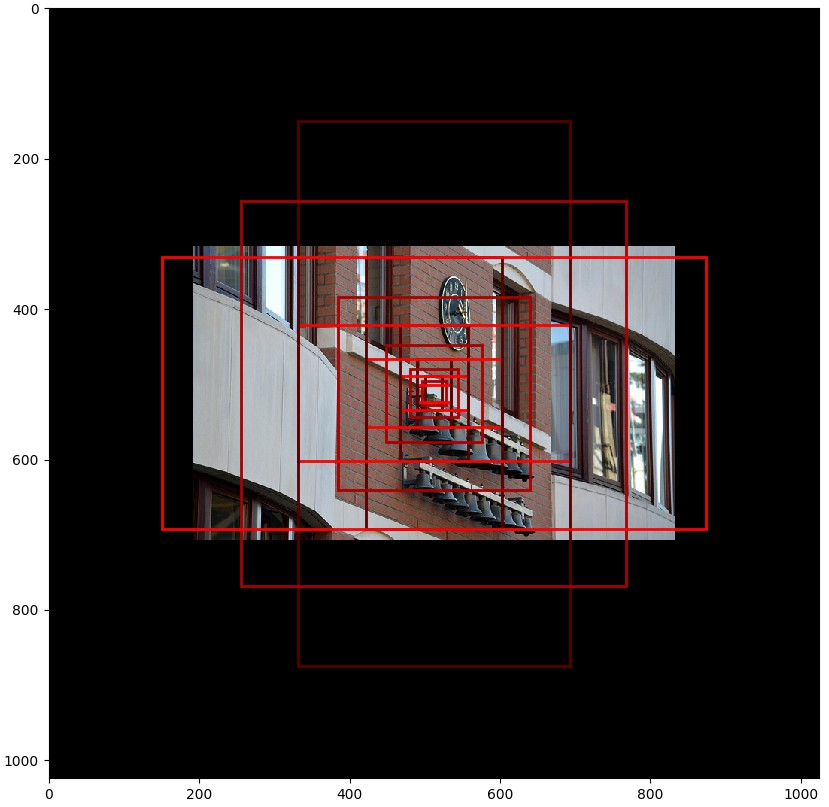
- Data Generator 数据生成
###############################################
# Data Generator 数据生成
###############################################
# Create data generator
random_rois = 2000
g = modellib.data_generator(dataset, config, shuffle=True, random_rois=random_rois,
batch_size=4, detection_targets=True)
# Uncomment to run the generator through a lot of images
# to catch rare errors
# for i in range(1000):
# print(i)
# _, _ = next(g)
# Get Next Image
if random_rois:
[normalized_images, image_meta, rpn_match, rpn_bbox, gt_class_ids, gt_boxes,
gt_masks, rpn_rois, rois], [mrcnn_class_ids, mrcnn_bbox, mrcnn_mask] = next(g)
log("rois", rois)
log("mrcnn_class_ids", mrcnn_class_ids)
log("mrcnn_bbox", mrcnn_bbox)
log("mrcnn_mask", mrcnn_mask)
else:
[normalized_images, image_meta, rpn_match, rpn_bbox, gt_boxes, gt_masks], _ = next(g)
log("gt_class_ids", gt_class_ids)
log("gt_boxes", gt_boxes)
log("gt_masks", gt_masks)
log("rpn_match", rpn_match, )
log("rpn_bbox", rpn_bbox)
image_id = modellib.parse_image_meta(image_meta)["image_id"][0]
print("image_id: ", image_id, dataset.image_reference(image_id))
# Remove the last dim in mrcnn_class_ids. It's only added
# to satisfy Keras restriction on target shape.
mrcnn_class_ids = mrcnn_class_ids[:, :, 0]
b = 0
# Restore original image (reverse normalization)
sample_image = modellib.unmold_image(normalized_images[b], config)
# Compute anchor shifts.
indices = np.where(rpn_match[b] == 1)[0]
refined_anchors = utils.apply_box_deltas(anchors[indices], rpn_bbox[b, :len(indices)] * config.RPN_BBOX_STD_DEV)
log("anchors", anchors)
log("refined_anchors", refined_anchors)
# Get list of positive anchors
positive_anchor_ids = np.where(rpn_match[b] == 1)[0]
print("Positive anchors: {}".format(len(positive_anchor_ids)))
negative_anchor_ids = np.where(rpn_match[b] == -1)[0]
print("Negative anchors: {}".format(len(negative_anchor_ids)))
neutral_anchor_ids = np.where(rpn_match[b] == 0)[0]
print("Neutral anchors: {}".format(len(neutral_anchor_ids)))
# ROI breakdown by class
for c, n in zip(dataset.class_names, np.bincount(mrcnn_class_ids[b].flatten())):
if n:
print("{:23}: {}".format(c[:20], n))
rois shape: (4, 200, 4) min: 0.00000 max: 1023.00000 int32
mrcnn_class_ids shape: (4, 200, 1) min: 0.00000 max: 0.00000 int32
mrcnn_bbox shape: (4, 200, 81, 4) min: 0.00000 max: 0.00000 float32
mrcnn_mask shape: (4, 200, 28, 28, 81) min: 0.00000 max: 0.00000 float32
gt_class_ids shape: (4, 100) min: 0.00000 max: 76.00000 int32
gt_boxes shape: (4, 100, 4) min: 0.00000 max: 832.00000 int32
gt_masks shape: (4, 56, 56, 100) min: 0.00000 max: 1.00000 bool
rpn_match shape: (4, 261888, 1) min: -1.00000 max: 1.00000 int32
rpn_bbox shape: (4, 256, 4) min: -3.83894 max: 1.98054 float64
('image_id: ', 14422, 'http://cocodataset.org/#explore?id=549836')
anchors shape: (261888, 4) min: -362.03867 max: 1322.03867 float64
refined_anchors shape: (10, 4) min: 307.00000 max: 700.00000 float32
Positive anchors: 10
Negative anchors: 246
Neutral anchors: 261632
BG : 200
# Show positive anchors
visualize.draw_boxes(sample_image, boxes=anchors[positive_anchor_ids],
refined_boxes=refined_anchors)

# Show negative anchors
visualize.draw_boxes(sample_image, boxes=anchors[negative_anchor_ids])

# Show neutral anchors. 不用于训练
visualize.draw_boxes(sample_image, boxes=anchors[np.random.choice(neutral_anchor_ids, 100)])

- ROIs
###############################################
# ROIs
###############################################
if random_rois:
# Class aware bboxes
bbox_specific = mrcnn_bbox[b, np.arange(mrcnn_bbox.shape[1]),
mrcnn_class_ids[b], :]
# Refined ROIs
refined_rois = utils.apply_box_deltas(rois[b].astype(np.float32),
bbox_specific[:,
:4] * config.BBOX_STD_DEV)
# Class aware masks
mask_specific = mrcnn_mask[b, np.arange(mrcnn_mask.shape[1]), :, :,
mrcnn_class_ids[b]]
visualize.draw_rois(sample_image, rois[b], refined_rois, mask_specific,
mrcnn_class_ids[b], dataset.class_names)
# Any repeated ROIs?
rows = np.ascontiguousarray(rois[b]).view(
np.dtype((np.void, rois.dtype.itemsize * rois.shape[-1])))
_, idx = np.unique(rows, return_index=True)
print("Unique ROIs: {} out of {}".format(len(idx), rois.shape[1]))
if random_rois:
# Dispalay ROIs and corresponding masks and bounding boxes
ids = random.sample(range(rois.shape[1]), 8)
images = []
titles = []
for i in ids:
image = visualize.draw_box(sample_image.copy(), rois[b,i,:4].astype(np.int32), [255, 0, 0])
image = visualize.draw_box(image, refined_rois[i].astype(np.int64), [0, 255, 0])
images.append(image)
titles.append("ROI {}".format(i))
images.append(mask_specific[i] * 255)
titles.append(dataset.class_names[mrcnn_class_ids[b,i]][:20])
display_images(images, titles, cols=4, cmap="Blues", interpolation="none")
# Check ratio of positive ROIs in a set of images.
if random_rois:
limit = 10
temp_g = modellib.data_generator(
dataset, config, shuffle=True, random_rois=10000,
batch_size=1, detection_targets=True)
total = 0
for i in range(limit):
_, [ids, _, _] = next(temp_g)
positive_rois = np.sum(ids[0] > 0)
total += positive_rois
print("{:5} {:5.2f}".format(positive_rois, positive_rois/ids.shape[1]))
print("Average percent: {:.2f}".format(total/(limit*ids.shape[1])))
('Positive ROIs: ', 0)
('Negative ROIs: ', 200)
Positive Ratio: 0.00
Unique ROIs: 200 out of 200
0 0.00
0 0.00
0 0.00
0 0.00
0 0.00
0 0.00
0 0.00
0 0.00
0 0.00
0 0.00
Average percent: 0.00

