原文:【最佳实践】阿里云 Elasticsearch 向量检索4步搭建“以图搜图”搜索引擎 - 2020.03.19
作者: 小森同学
阿里云Elasticsearch客户真实实践分享
文中涉及到的图片特征提取,使用了yongyuan.name的VGGNet库,表示感谢
“图片搜索”是作为导购类网站比较常见的一种功能,其实现的方式有很多,比如“哈西指纹+汉明距离计算”、“特征向量+milvus”,但在实际的应用场景中,要做到快速、精准、简单等特性是比较困难的事情.
1. “图片搜索”方式优缺点对比

1.1. 方案三查询效果
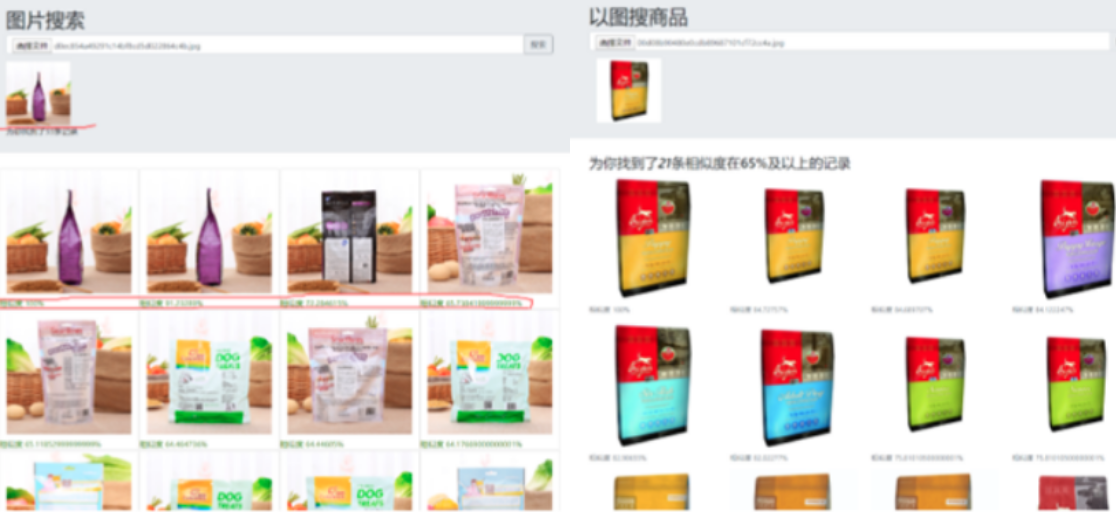
2. 搭建“以图搜图”搜索引擎
以下是基于 阿里云 Elasticsearch 6.7 版本,通过安装阿里云 Elasticsearch 向量检索插件【aliyun-knn】 实现,且设计图片向量特征为512维度。
如果自建 Elasticsearch ,是无法使用aliyun-knn插件的,自建建议使用开源 Elasticsearch 7.x版本,并安装 fast-elasticsearch-vector-scoring 插件.
依赖项:
mysql_connector_repackaged
elasticsearch
Pillow
tensorflow
requests
pandas
Keras
numpy2.1. Elasticsearch 索引设计
2.1.1. 索引结构
#创建一个图片索引
PUT images_v2
{
"aliases": {
"images": {}
},
"settings": {
"index.codec": "proxima",
"index.vector.algorithm": "hnsw",
"index.number_of_replicas":1,
"index.number_of_shards":3
},
"mappings": {
"_doc": {
"properties": {
"feature": {
"type": "proxima_vector",
"dim": 512
},
"relation_id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"image_path": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
} 2.1.2. DSL 语句
GET images/_search
"query": {
"hnsw": {
"feature": {
"vector": [255,....255],
"size": 3,
"ef": 1
}
}
},
"from": 0,
"size": 20,
"sort": [
{
"_score": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
],
"collapse": {
"field": "relation_id"
},
"_source": {
"includes": [
"relation_id",
"image_path"
]
} 2.2. 图片特征
extract_cnn_vgg16_keras.py:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Author: yongyuan.name
import numpy as np
from numpy import linalg as LA
from keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16
from keras.preprocessing import image
from keras.applications.vgg16 import preprocess_input
from PIL import Image, ImageFile
ImageFile.LOAD_TRUNCATED_IMAGES = True
class VGGNet:
def __init__(self):
# weights: 'imagenet'
# pooling: 'max' or 'avg'
# input_shape: (width, height, 3), width and height should >= 48
self.input_shape = (224, 224, 3)
self.weight = 'imagenet'
self.pooling = 'max'
self.model = VGG16(
weights = self.weight,
input_shape = (self.input_shape[0], self.input_shape[1], self.input_shape[2]),
pooling = self.pooling, include_top = False)
self.model.predict(np.zeros((1, 224, 224 , 3)))
def extract_feat(self, img_path):
'''
Use vgg16 model to extract features
Output normalized feature vector
'''
img = image.load_img(img_path, target_size=(self.input_shape[0], self.input_shape[1]))
img = image.img_to_array(img)
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
img = preprocess_input(img)
feat = self.model.predict(img)
norm_feat = feat[0]/LA.norm(feat[0])
return norm_feat
#
# 获取图片特征
from extract_cnn_vgg16_keras import VGGNet
model = VGGNet()
file_path = "./demo.jpg"
queryVec = model.extract_feat(file_path)
feature = queryVec.tolist() 2.3. 图片特征写入阿里云 Elasticsearch
helper.py:
import re
import urllib.request
def strip(path):
"""
需要清洗的文件夹名字
清洗掉Windows系统非法文件夹名字的字符串
:param path:
:return:
"""
path = re.sub(r'[?\\*|“<>:/]', '', str(path))
return path
def getfilename(url):
"""
通过url获取最后的文件名
:param url:
:return:
"""
filename = url.split('/')[-1]
filename = strip(filename)
return filename
def urllib_download(url, filename):
"""
下载
:param url:
:param filename:
:return:
"""
return urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filename) train.py:
# coding=utf-8
import mysql.connector
import os
from helper import urllib_download, getfilename
from elasticsearch5 import Elasticsearch, helpers
from extract_cnn_vgg16_keras import VGGNet
model = VGGNet()
http_auth = ("elastic", "123455")
es = Elasticsearch("http://127.0.0.1:9200", http_auth=http_auth)
mydb = mysql.connector.connect(
host="127.0.0.1", # 数据库主机地址
user="root", # 数据库用户名
passwd="123456", # 数据库密码
database="images" )
mycursor = mydb.cursor()
imgae_path = "./images/"
def get_data(page=1):
page_size = 20
offset = (page - 1) * page_size
sql = "SELECT id, relation_id, photo FROM images LIMIT {0},{1}"
mycursor.execute(sql.format(offset, page_size))
myresult = mycursor.fetchall()
return myresult
def train_image_feature(myresult):
indexName = "images"
photo_path = "http://域名/{0}"
actions = []
for x in myresult:
id = str(x[0])
relation_id = x[1]
# photo = x[2].decode(encoding="utf-8")
photo = x[2]
full_photo = photo_path.format(photo)
filename = imgae_path + getfilename(full_photo)
if not os.path.exists(filename):
try:
urllib_download(full_photo, filename)
except BaseException as e:
print("gid:{0}的图片{1}未能下载成功".format(gid, full_photo))
continue
if not os.path.exists(filename):
continue
try:
feature = model.extract_feat(filename).tolist()
action = {"_op_type": "index",
"_index": indexName,
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": id,
"_source": {
"relation_id": relation_id,
"feature": feature,
"image_path": photo
}
}
actions.append(action)
except BaseException as e:
print("id:{0}的图片{1}未能获取到特征".format(id, full_photo))
continue
# print(actions)
succeed_num = 0
for ok, response in helpers.streaming_bulk(es, actions):
if not ok:
print(ok)
print(response)
else:
succeed_num += 1
print("本次更新了{0}条数据".format(succeed_num))
es.indices.refresh(indexName)
page = 1
while True:
print("当前第{0}页".format(page))
myresult = get_data(page=page)
if not myresult:
print("没有获取到数据了,退出")
break
train_image_feature(myresult)
page += 1 2.4. 搜索图片
import requests
import json
import os
import time
from elasticsearch5 import Elasticsearch
from extract_cnn_vgg16_keras import VGGNet
model = VGGNet()
http_auth = ("elastic", "123455")
es = Elasticsearch("http://127.0.0.1:9200", http_auth=http_auth)
#上传图片保存
upload_image_path = "./runtime/"
upload_image = request.files.get("image")
upload_image_type = upload_image.content_type.split('/')[-1]
file_name = str(time.time())[:10] + '.' + upload_image_type
file_path = upload_image_path + file_name
upload_image.save(file_path)
# 计算图片特征向量
queryVec = model.extract_feat(file_path)
feature = queryVec.tolist()
# 删除图片
os.remove(file_path)
# 根据特征向量去ES中搜索
body = {
"query": {
"hnsw": {
"feature": {
"vector": feature,
"size": 5,
"ef": 10
}
}
},
# "collapse": {
# "field": "relation_id"
# },
"_source": {"includes": ["relation_id", "image_path"]},
"from": 0,
"size": 40
}
indexName = "images"
res = es.search(indexName, body=body)
# 返回的结果,最好根据自身情况,将得分低的过滤掉...经过测试, 得分在0.65及其以上的,比较符合要求 3. 总结
从“用户体验”角度考虑,在可感知层面,速度和精准度决定了产品在用户使用过程中,是否满足“好用”的感觉,通过阿里云 Elasticsearch 向量检索(aliyun-knn)简单四步搭建的“以图搜图”搜索引擎,不仅满足“好用”,同时操作简单一步到位的特征,也加分不少.